|
Mesogloea
Mesoglea refers to the extracellular matrix found in cnidarians like coral or jellyfish that functions as a hydrostatic skeleton. It is related to but distinct from mesohyl, which generally refers to extracellular material found in sponges. Description The mesoglea is mostly water. Other than water, the mesoglea is composed of several substances including fibrous proteins, like collagen and heparan sulphate proteoglycans. The mesoglea is mostly acellular, but in both cnidaria and ctenophora the mesoglea contains muscle bundles and nerve fibres. Other nerve and muscle cells lie just under the epithelial layers. The mesoglea also contains wandering amoebocytes that play a role in phagocytosing debris and bacteria. These cells also fight infections by producing antibacterial chemicals. The mesoglea may be thinner than either of the cell layers in smaller coelenterates like a hydra or may make up the bulk of the body in larger jellyfish. The mesoglea serves as an internal skeleto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jellyfish
Jellyfish and sea jellies are the informal common names given to the medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animals with umbrella-shaped bells and trailing tentacles, although a few are anchored to the seabed by stalks rather than being mobile. The bell can pulsate to provide propulsion for highly efficient animal locomotion, locomotion. The tentacles are armed with Cnidocyte, stinging cells and may be used to capture prey and defend against predators. Jellyfish have a complex Biological life cycle, life cycle; the medusa is normally the sexual phase, which produces planula larvae that disperse widely and enter a sedentary polyp (zoology), polyp phase before reaching sexual maturity. Jellyfish are found all over the world, from surface waters to the deep sea. Scyphozoans (the "true jellyfish") are exclusively marine habitats, marine, but some hydrozoans with a simila ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
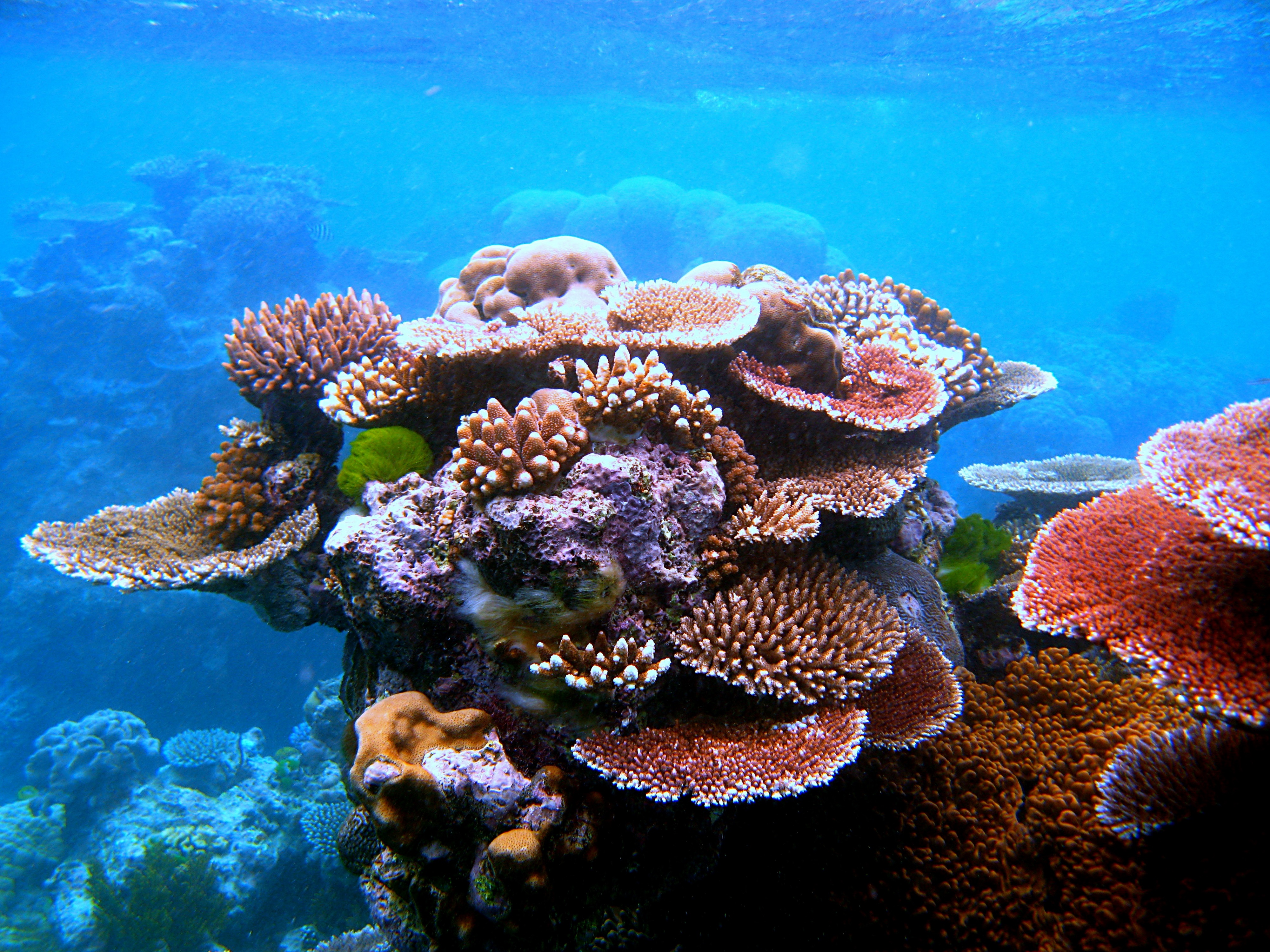
Coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton. A coral "group" is a colony of very many genetically identical polyps. Each polyp is a sac-like animal typically only a few millimeters in diameter and a few centimeters in height. A set of tentacles surround a central mouth opening. Each polyp excretes an exoskeleton near the base. Over many generations, the colony thus creates a skeleton characteristic of the species which can measure up to several meters in size. Individual colonies grow by asexual reproduction of polyps. Corals also breed sexually by spawning: polyps of the same species release gametes simultaneously overnight, often around a full moon. Fertilized eggs form planulae, a mobile early form of the coral polyp which, when matu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coral
Corals are marine invertebrates within the class Anthozoa of the phylum Cnidaria. They typically form compact colonies of many identical individual polyps. Coral species include the important reef builders that inhabit tropical oceans and secrete calcium carbonate to form a hard skeleton. A coral "group" is a colony of very many genetically identical polyps. Each polyp is a sac-like animal typically only a few millimeters in diameter and a few centimeters in height. A set of tentacles surround a central mouth opening. Each polyp excretes an exoskeleton near the base. Over many generations, the colony thus creates a skeleton characteristic of the species which can measure up to several meters in size. Individual colonies grow by asexual reproduction of polyps. Corals also breed sexually by spawning: polyps of the same species release gametes simultaneously overnight, often around a full moon. Fertilized eggs form planulae, a mobile early form of the coral polyp which, when matu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. History Phagocytosis was first noted by Canadian physician William Osler (1876), and later studied and named by Élie Metchnikoff (1880, 1883). In immune system Phagocytosis is one main mechanisms of the innate immune defense. It is one of the first processes responding to infection, and is also one of the initiating branches of an adaptive immune response. Altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium, non-epithelial blood cells and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme. The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center. The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3. Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesenchyme
Mesenchyme () is a type of loosely organized animal embryonic connective tissue of undifferentiated cells that give rise to most tissues, such as skin, blood or bone. The interactions between mesenchyme and epithelium help to form nearly every organ in the developing embryo. Vertebrates Structure Mesenchyme is characterized morphologically by a prominent ground substance matrix containing a loose aggregate of reticular fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal stem cells. Mesenchymal cells can migrate easily (in contrast to epithelial cells, which lack mobility), are organized into closely adherent sheets, and are polarized in an apical-basal orientation. Development The mesenchyme originates from the mesoderm. From the mesoderm, the mesenchyme appears as an embryologically primitive "soup". This "soup" exists as a combination of the mesenchymal cells plus serous fluid plus the many different tissue proteins. Serous fluid is typically stocked with the many serous elements, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basal Lamina
The basal lamina is a layer of extracellular matrix secreted by the epithelial cells, on which the epithelium sits. It is often incorrectly referred to as the basement membrane, though it does constitute a portion of the basement membrane. The basal lamina is visible only with the electron microscope, where it appears as an electron-dense layer that is 20–100 nm thick (with some exceptions that are thicker, such as basal lamina in lung alveoli and renal glomeruli). Structure The layers of the basal lamina ("BL") and those of the basement membrane ("BM") are described below: Anchoring fibrils composed of type VII collagen extend from the basal lamina into the underlying reticular lamina and loop around collagen bundles. Although found beneath all basal laminae, they are especially numerous in stratified squamous cells of the skin. These layers should not be confused with the lamina propria, which is found outside the basal lamina. Basement membrane The basement memb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Density
In quantum chemistry, electron density or electronic density is the measure of the probability of an electron being present at an infinitesimal element of space surrounding any given point. It is a scalar quantity depending upon three spatial variables and is typically denoted as either \rho(\textbf r) or n(\textbf r). The density is determined, through definition, by the normalised N-electron wavefunction which itself depends upon 4N variables (3N spatial and N spin coordinates). Conversely, the density determines the wave function modulo up to a phase factor, providing the formal foundation of density functional theory. According to quantum mechanics, due to the uncertainty principle on an atomic scale the exact location of an electron cannot be predicted, only the probability of its being at a given position; therefore electrons in atoms and molecules act as if they are "smeared out" in space. For one-electron systems, the electron density at any point is proportional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrodermis
The gastrodermis is the inner layer of cells that serves as a lining membrane of the gastrovascular cavity of Cnidarians. The term is also used for the analogous inner epithelial layer of Ctenophore Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and ...s. It has been shown that the gastrodermis is among the sites where early signals of heat stress are expressed in corals. References Digestive system {{Cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and Subcutaneous tissue, hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of stratified squamous epithelium, multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of Epithelium#Cell types, columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes (cell proliferation, proliferating basal and cell differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
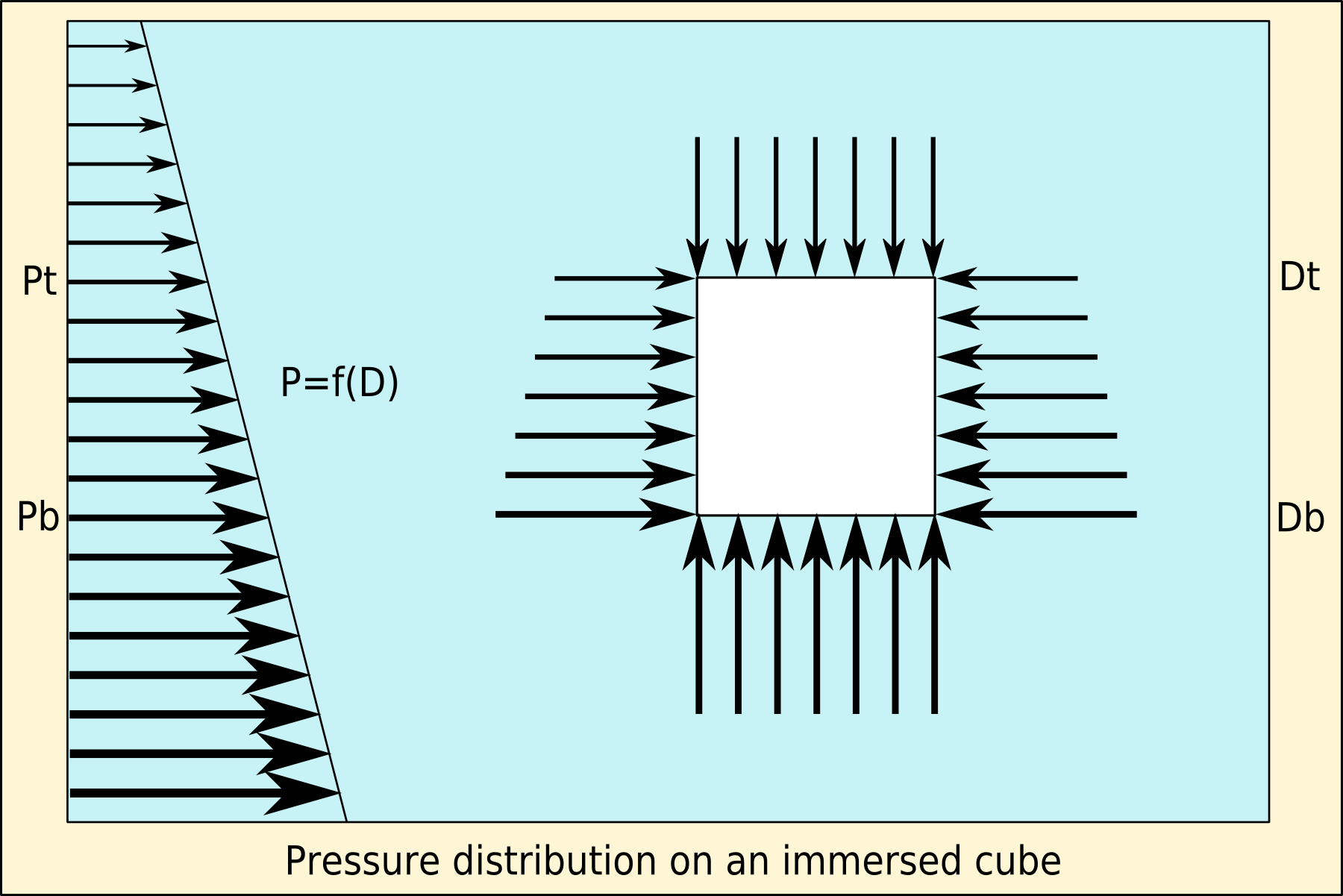
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidaria
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in Fresh water, freshwater and Marine habitats, marine environments, predominantly the latter. Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that they use mainly for capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell (biology), cell thick. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming Medusa (biology), medusae and Sessility (motility), sessile polyp (zoology), polyps, both of which are Symmetry (biology)#Radial symmetry, radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. Both forms have a single Body orifice, orifice and body cavity that are used for digestion and respiration (physiology), respiration. Many cnidarian species produce Colony (biology), colonies that are single organisms composed of medusa-like or polyp (z ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |