|
Mesocorticolimbic Pathway
Dopaminergic pathways (dopamine pathways, dopaminergic projections) in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. Each pathway is a set of projection neuron, projection neurons, consisting of individual dopaminergic neurons. The four major dopaminergic pathways are the mesolimbic pathway, the mesocortical pathway, the nigrostriatal pathway, and the tuberoinfundibular pathway.The mesolimbic pathway and the mesocortical pathway form the mesocorticolimbic system. Two other dopaminergic pathways to be considered are the hypothalamospinal tract and the incertohypothalamic pathway. Parkinson's disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), substance use disorders (addiction), and restless legs syndrome (RLS) can be attributed to dysfunction in specific dopaminergic pathways. The dopamine neurons of the dopaminergic pathways synthesize and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopaminergic Pathways
Dopaminergic pathways (dopamine pathways, dopaminergic projections) in the human brain are involved in both physiological and behavioral processes including movement, cognition, executive functions, reward, motivation, and neuroendocrine control. Each pathway is a set of projection neuron, projection neurons, consisting of individual dopaminergic neurons. The four major dopaminergic pathways are the mesolimbic pathway, the mesocortical pathway, the nigrostriatal pathway, and the tuberoinfundibular pathway.The mesolimbic pathway and the mesocortical pathway form the mesocorticolimbic system. Two other dopaminergic pathways to be considered are the hypothalamospinal tract and the incertohypothalamic pathway. Parkinson's disease, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), substance use disorders (addiction), and restless legs syndrome (RLS) can be attributed to dysfunction in specific dopaminergic pathways. The dopamine neurons of the dopaminergic pathways synthesize and r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopa Decarboxylase
Aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC or AAAD), also known as DOPA decarboxylase (DDC), tryptophan decarboxylase, and 5-hydroxytryptophan decarboxylase, is a lyase enzyme (), located in region 7p12.2-p12.1. Mechanism The enzyme uses pyridoxal phosphate (PLP), the active form of vitamin B6, as a cofactor. PLP is essential to the mechanism of decarboxylation in AADC. In the active enzyme, PLP is bound to lysine-303 of AADC as a Schiff base. Upon substrate binding, Lys-303 is displaced by the substrate's amine. This positions the carboxylate of the substrate within the active site such that decarboxylation is favored. Decarboxylation of the substrate produces a quinonoid intermediate, which is subsequently protonated to produce a Schiff base adduct of PLP and the decarboxylated product. Lys-303 can then regenerate the original Schiff base, releasing the product while retaining PLP. Probing this PLP-catalyzed decarboxylation, it has been discovered that there is a difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
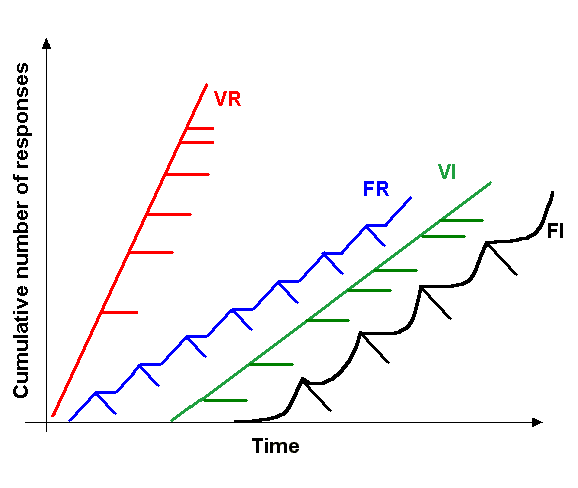
Positive Reinforcement
In behavioral psychology, reinforcement is a consequence applied that will strengthen an organism's future behavior whenever that behavior is preceded by a specific antecedent stimulus. This strengthening effect may be measured as a higher frequency of behavior (e.g., pulling a lever more frequently), longer duration (e.g., pulling a lever for longer periods of time), greater magnitude (e.g., pulling a lever with greater force), or shorter latency (e.g., pulling a lever more quickly following the antecedent stimulus). The model of self-regulation has three main aspects of human behavior, which are self-awareness, self-reflection, and self-regulation. Reinforcements traditionally align with self-regulation. The behavior can be influenced by the consequence but behavior also needs antecedents. There are four types of reinforcement: positive reinforcement, negative reinforcement, extinction, and punishment. Positive reinforcement is the application of a positive reinforcer. Negati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleasure
Pleasure refers to experience that feels good, that involves the enjoyment of something. It contrasts with pain or suffering, which are forms of feeling bad. It is closely related to value, desire and action: humans and other conscious animals find pleasure enjoyable, positive or worthy of seeking. A great variety of activities may be experienced as pleasurable, like eating, having sex, listening to music or playing games. Pleasure is part of various other mental states such as ecstasy, euphoria and flow. Happiness and well-being are closely related to pleasure but not identical with it. There is no general agreement as to whether pleasure should be understood as a sensation, a quality of experiences, an attitude to experiences or otherwise. Pleasure plays a central role in the family of philosophical theories known as hedonism. Overview "Pleasure" refers to experience that feels good, that involves the enjoyment of something. The term is primarily used in association wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incentive Salience
Motivational salience is a cognitive process and a form of attention that ''motivates'' or propels an individual's behavior towards or away from a particular stimulus (psychology), object, perceived event or outcome. Motivational salience regulates the intensity of behaviors that facilitate the attainment of a particular goal, the amount of time and energy that an individual is willing to expend to attain a particular goal, and the Risk aversion (psychology), amount of risk that an individual is willing to accept while working to attain a particular goal. Motivational salience is composed of two component processes that are defined by their attractive or aversive effects on an individual's behavior relative to a particular stimulus: ''incentive salience'' and ''aversive salience''. Incentive salience is the attractive form of motivational salience that causes approach behavior, and is associated with operant reinforcement, reward system, desirable outcomes, and pleasurable stimuli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reward System
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and classical conditioning), and positively-valenced emotions, particularly ones involving pleasure as a core component (e.g., joy, euphoria and ecstasy). Reward is the attractive and motivational property of a stimulus that induces appetitive behavior, also known as approach behavior, and consummatory behavior. A rewarding stimulus has been described as "any stimulus, object, event, activity, or situation that has the potential to make us approach and consume it is by definition a reward". In operant conditioning, rewarding stimuli function as positive reinforcers; however, the converse statement also holds true: positive reinforcers are rewarding. The reward system motivates animals to approach stimuli or engage in behaviour that increases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prefix (linguistics)
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the stem of a word. Adding it to the beginning of one word changes it into another word. For example, when the prefix ''un-'' is added to the word ''happy'', it creates the word ''unhappy''. Particularly in the study of languages, a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed. Prefixes, like other affixes, can be either inflectional, creating a new form of the word with the same basic meaning and same lexical category (but playing a different role in the sentence), or derivational, creating a new word with a new semantic meaning and sometimes also a different lexical category. Prefixes, like all other affixes, are usually bound morphemes. In English, there are no inflectional prefixes; English uses suffixes instead for that purpose. The word ''prefix'' is itself made up of the stem ''fix'' (meaning "attach", in this case), and the prefix ''pre-'' (meaning "before"), both of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory Tubercle
The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to play a role in locomotor and attentional behaviors, particularly in relation to social and sensory responsiveness, and it may be necessary for behavioral flexibility. The OT is interconnected with numerous brain regions, especially the sensory, arousal, and reward centers, thus making it a potentially critical interface between processing of sensory information and the subsequent behavioral responses. The OT is a composite structure that receives direct input from the olfactory bulb and contains the morphological and histochemical characteristics of the ventral pallidum and the striatum of the forebrain. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus Accumbens
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle collectively form the ventral striatum. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum, which is the main component of the basal ganglia. The dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic pathway project onto the GABAergic medium spiny neurons of the nucleus accumbens and olfactory tubercle. Each cerebral hemisphere has its own nucleus accumbens, which can be divided into two structures: the nucleus accumbens core and the nucleus accumbens shell. These substructures have different morphology and functions. Different NAcc subregions (core vs shell) and neuron subpopulations within each region (D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons) are responsible for different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ventral Striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia. Functionally, the striatum coordinates multiple aspects of cognition, including both motor and action planning, decision-making, motivation, reinforcement, and reward perception. The striatum is made up of the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus. The lentiform nucleus is made up of the larger putamen, and the smaller globus pallidus. Strictly speaking the globus pallidus is part of the striatum. It is common practice, however, to implicitly exclude the globus pallidus when referring to striatal structures. In primates, the striatum is divided into a ventral striatum, and a dorsal striatum, subdivisions that are base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal (alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', "middle", and ''enkephalos'', "brain". Structure The principal regions of the midbrain are the tectum, the cerebral aqueduct, tegmentum, and the cerebral peduncles. Rostrally the midbrain adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus, hypothalamus, etc.), while caudally it adjoins the hindbrain (pons, medulla and cerebellum). In the rostral direction, the midbrain noticeably splays laterally. Sectioning of the midbrain is usually performed axially, at one of two levels – that of the superior colliculi, or that of the inferior colliculi. One common technique for remembering the structures of the midbrain involves visualizing these cross-sections (especially at the level of the superior colliculi) as the upside-down face of a be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |