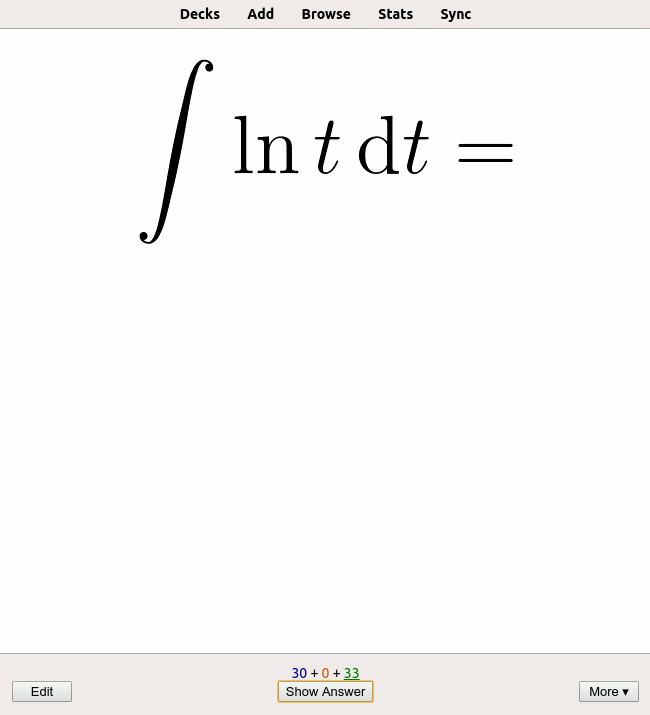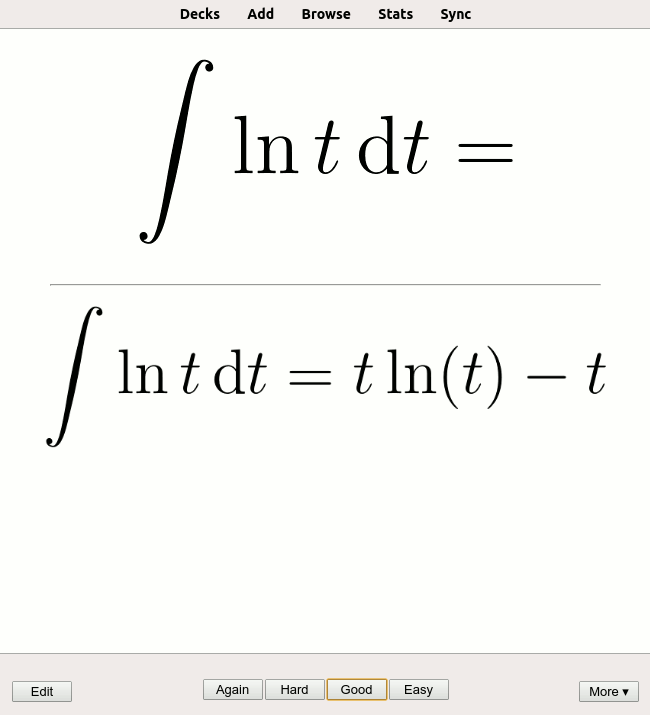|
Memorize
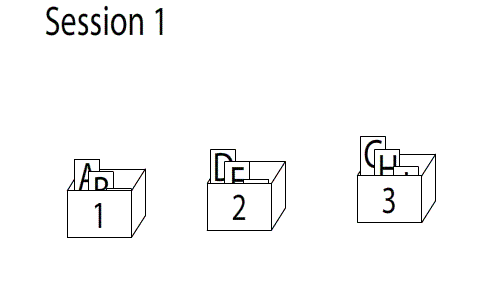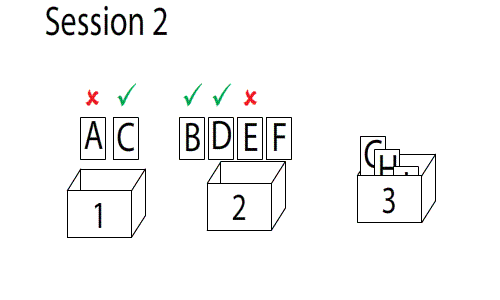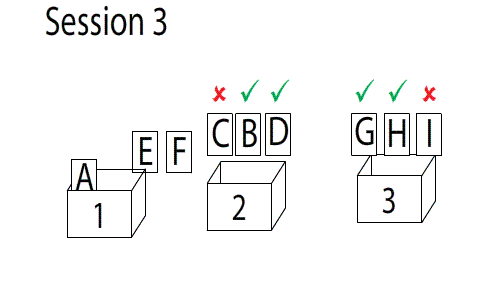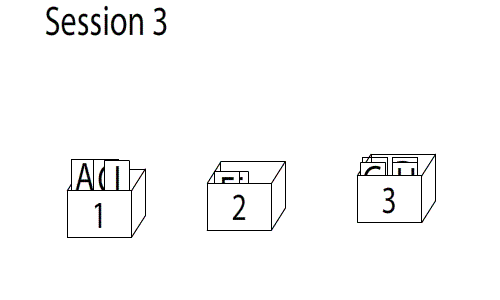
Memorization is the process of committing something to memory. It is a mental process undertaken in order to store in memory for later recall visual, auditory, or tactical information. The scientific study of memory is part of cognitive neuroscience, an interdisciplinary link between cognitive psychology and neuroscience. Development of memorization Within the first three years of a child's life, they begin to show signs of memory that is later improved into their adolescent years. This includes short-term memory, long-term memory, working memory, and autobiographical memory. Memory is a fundamental capacity that plays a special role in social, emotional, and cognitive functioning. Problems with studying the development of memorization include having to use verbal response and confirmation. Techniques Some principles and techniques that have been used to assist in memorization include: *Rote learning, a learning technique which focuses not on understanding but on memorization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Of Memory
The art of memory (Latin: ''ars memoriae'') is any of a number of loosely associated mnemonic principles and techniques used to organize memory impressions, improve recall, and assist in the combination and 'invention' of ideas. An alternative term is "Ars Memorativa" which is also translated as "art of memory" although its more literal meaning is "Memorative Art". It is also referred to as ''mnemotechnics''. It is an 'art' in the Aristotelian sense, which is to say a method or set of prescriptions that adds order and discipline to the pragmatic, natural activities of human beings.Carruthers 1990, p. 123 It has existed as a recognized group of principles and techniques since at least as early as the middle of the 1st millennium BC, first millennium BCE, and was usually associated with training in rhetoric or logic, but variants of the art were employed in other contexts, particularly the religious and the magical. Techniques commonly employed in the art include the association ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnemonic
A mnemonic ( ) device, or memory device, is any learning technique that aids information retention or retrieval (remembering) in the human memory for better understanding. Mnemonics make use of elaborative encoding, retrieval cues, and imagery as specific tools to encode information in a way that allows for efficient storage and retrieval. Mnemonics aid original information in becoming associated with something more accessible or meaningful—which, in turn, provides better retention of the information. Commonly encountered mnemonics are often used for lists and in auditory form, such as short poems, acronyms, initialisms, or memorable phrases, but mnemonics can also be used for other types of information and in visual or kinesthetic forms. Their use is based on the observation that the human mind more easily remembers spatial, personal, surprising, physical, sexual, humorous, or otherwise "relatable" information, rather than more abstract or impersonal forms of informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Method Of Loci
The method of loci is a strategy for memory enhancement, which uses visualizations of familiar spatial environments in order to enhance the recall of information. The method of loci is also known as the memory journey, memory palace, journey method, memory spaces, or mind palace technique. This method is a mnemonic device adopted in ancient Roman and Greek rhetorical treatises (in the anonymous ''Rhetorica ad Herennium'', Cicero's ''De Oratore'', and Quintilian's '' Institutio Oratoria''). Many memory contest champions report using this technique to recall faces, digits, and lists of words. The term is most often found in specialised works on psychology, neurobiology, and memory, though it was used in the same general way at least as early as the first half of the nineteenth century in works on rhetoric, logic, and philosophy. John O'Keefe and Lynn Nadel refer to:... "the method of loci", an imaginal technique known to the ancient Greeks and Romans and described by Yates (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnemonic Peg System
The mnemonic peg system, invented by Henry Herdson is a memory aid that works by creating mental associations between two concrete objects in a one-to-one fashion that will later be applied to to-be-remembered information. Typically this involves linking nouns to numbers and it is common practice to choose a noun that rhymes with the number it is associated with. These will be the pegs of the system. These associations have to be memorized one time and can be applied repeatedly to new information that needs to be memorized. Types of peg-word systems Rhyming peg-word system The Rhyming peg-word system is very simple, as stated above and could look something like this: # Bun: Visualize an association between the first item and a bun # Shoe: Visualize an association between the second item and a shoe # Tree: Visualize an association between the third item and a tree # Door: Visualize an association between the fourth item and a door # Hive: Visualize an association between the fifth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
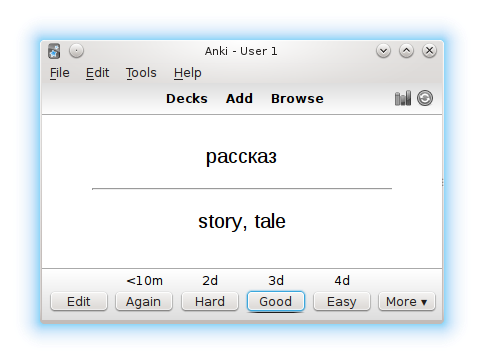
Flashcard
A flashcard or flash card (also known as an index card) is a card bearing information on both sides, which is intended to be used as an aid in memorization. Each flashcard bears a question on one side and an answer on the other. Flashcards are often used to memorize vocabulary, historical dates, formulas or any subject matter that can be learned via a question-and-answer format. Flashcards can be virtual (part of a flashcard software), or physical. Flashcards are an application of the testing effect − the finding that long-term memory is increased when some of the learning period is devoted to retrieving the information through testing with proper feedback. Study habits affect the rate at which a flashcard-user learns, and proper spacing of flashcards has been proven to accelerate learning. A number of spaced repetition software programs exist which take advantage of this principle. Use Flashcards exercise the mental process of active recall: given a prompt (the question ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory processor. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rote Learning
Rote learning is a memorization technique based on repetition. The method rests on the premise that the recall of repeated material becomes faster the more one repeats it. Some of the alternatives to rote learning include meaningful learning, associative learning, spaced repetition and active learning. Versus critical thinking Rote learning is widely used in the mastery of foundational knowledge. Examples of school topics where rote learning is frequently used include phonics in reading, the periodic table in chemistry, multiplication tables in mathematics, anatomy in medicine, cases or statutes in law, basic formulae in any science, etc. By definition, rote learning eschews comprehension, so by itself it is an ineffective tool in mastering any complex subject at an advanced level. For instance, one illustration of rote learning can be observed in preparing quickly for exams, a technique which may be colloquially referred to as " cramming". Rote learning is sometimes disparage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
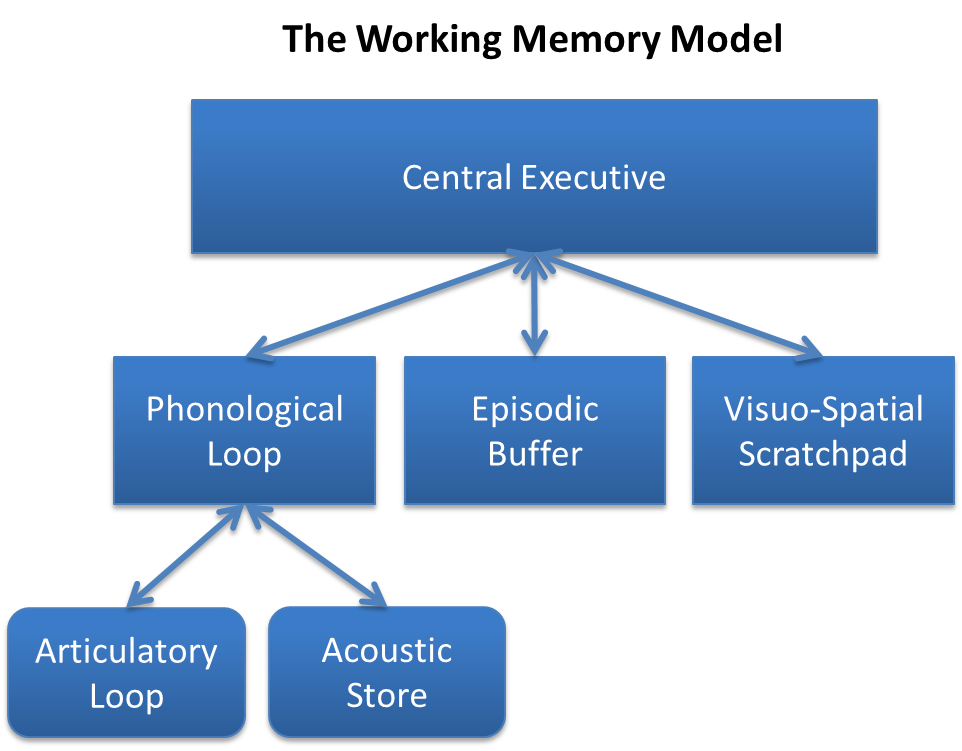
Working Memory
Working memory is a cognitive system with a limited capacity that can hold information temporarily. It is important for reasoning and the guidance of decision-making and behavior. Working memory is often used synonymously with short-term memory, but some theorists consider the two forms of memory distinct, assuming that working memory allows for the manipulation of stored information, whereas short-term memory only refers to the short-term storage of information. Working memory is a theoretical concept central to cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, and neuroscience. History The term "working memory" was coined by Miller, Galanter, and Pribram, and was used in the 1960s in the context of theories that likened the mind to a computer. In 1968, Atkinson and Shiffrin used the term to describe their "short-term store". What we now call working memory was formerly referred to variously as a "short-term store" or short-term memory, primary memory, immediate memory, operant memo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mnemonic Major System
The major system (also called the phonetic number system, phonetic mnemonic system, or Herigone's mnemonic system) is a mnemonic technique used to aid in memorizing numbers. The system works by converting numbers into consonants, then into words by adding vowels. The system works on the principle that images can be remembered more easily than numbers. One notable explanation of this system was given in Martin Gardner's book ''The First Scientific American Book of Mathematical Puzzles and Diversions'' (just ''Mathematical Puzzles and Diversions'' in the UK edition), which has since been republished in ''The New Martin Gardner Mathematical Library'' as ''Hexaflexagons, Probability Paradoxes, and the Tower of Hanoi''. In this, Gardner traces the history of the system back to Pierre Hérigone and Richard Grey with uses by Lewis Carroll and Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz. The system Each numeral is associated with one or more consonants. (In other words, the link is to the sound, not the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vedic Chant
The oral tradition of the Vedas (Śruti) consists of several pathas, "recitations" or ways of chanting the Vedic mantras. Such traditions of Vedic chant are often considered the oldest unbroken oral tradition in existence, the fixation of the Vedic texts ( samhitas) as preserved dating to roughly the time of Homer (early Iron Age).Scharfe, Ch. 13: "Memorising the Veda", p. 240 ff. UNESCO proclaimed the tradition of Vedic chant a Masterpiece of the Oral and Intangible Heritage of Humanity on November 7, 2008. Tones Vedic chantings use 4 tones – ''Udatta'' उदात्त (middle tone), ''Anudaatta'' अनुदात्त (lower tone), ''Svarita'' स्वरित (higher tone) and ''Deergha Svarita'' दीर्घस्वरित (High tone extended). These are usually marked with intuitive ''svara marks'' – an underline for lower tone, a small vertical line above the letter for a higher tone and two vertical lines for Deergha Svarita. Pathas The various pathas or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaced Repetition
Spaced repetition is an evidence-based learning technique that is usually performed with flashcards. Newly introduced and more difficult flashcards are shown more frequently, while older and less difficult flashcards are shown less frequently in order to exploit the psychological spacing effect. The use of spaced repetition has been proven to increase the rate of learning. Although the principle is useful in many contexts, spaced repetition is commonly applied in contexts in which a learner must acquire many items and retain them indefinitely in memory. It is, therefore, well suited for the problem of vocabulary acquisition in the course of second-language learning. A number of spaced repetition software programs have been developed to aid the learning process. It is also possible to perform spaced repetition with flashcards using the Leitner system. Alternative names for spaced repetition include spaced rehearsal, expanding rehearsal, graduated intervals, repetition spacing, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaced Repetition Software
Spaced repetition is an evidence-based learning technique that is usually performed with flashcards. Newly introduced and more difficult flashcards are shown more frequently, while older and less difficult flashcards are shown less frequently in order to exploit the psychological spacing effect. The use of spaced repetition has been proven to increase the rate of learning. Although the principle is useful in many contexts, spaced repetition is commonly applied in contexts in which a learner must acquire many items and retain them indefinitely in memory. It is, therefore, well suited for the problem of vocabulary acquisition in the course of second-language learning. A number of spaced repetition software programs have been developed to aid the learning process. It is also possible to perform spaced repetition with flashcards using the Leitner system. Alternative names for spaced repetition include spaced rehearsal, expanding rehearsal, graduated intervals, repetition spacing, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |