|
Melodic Fission
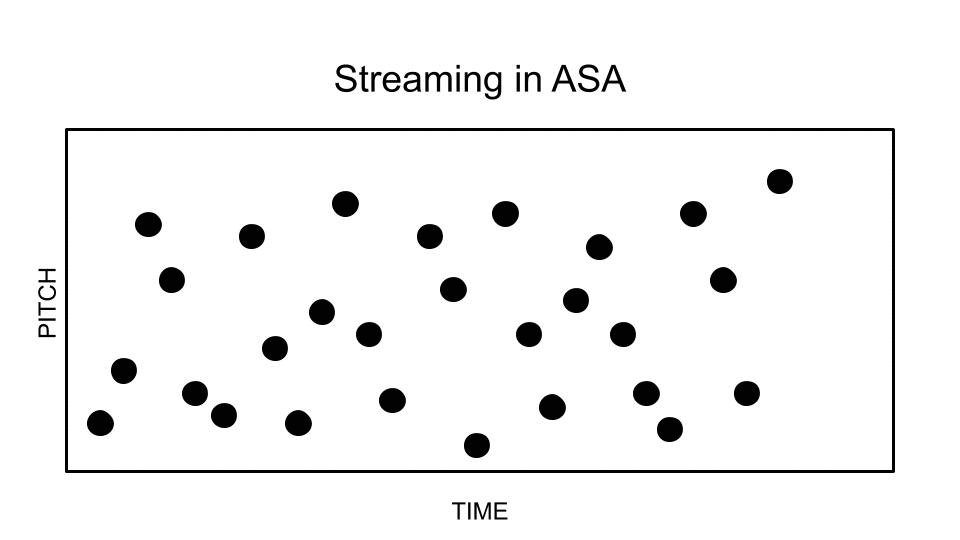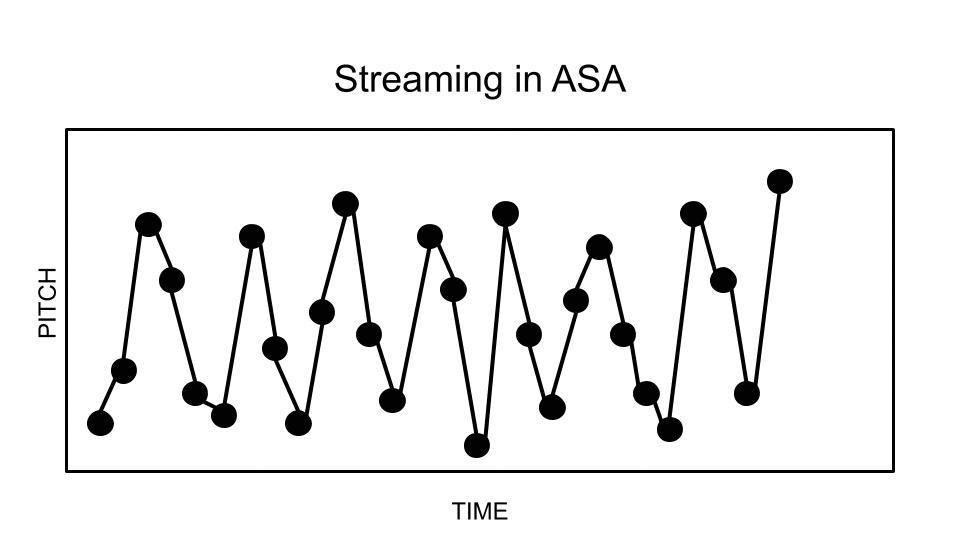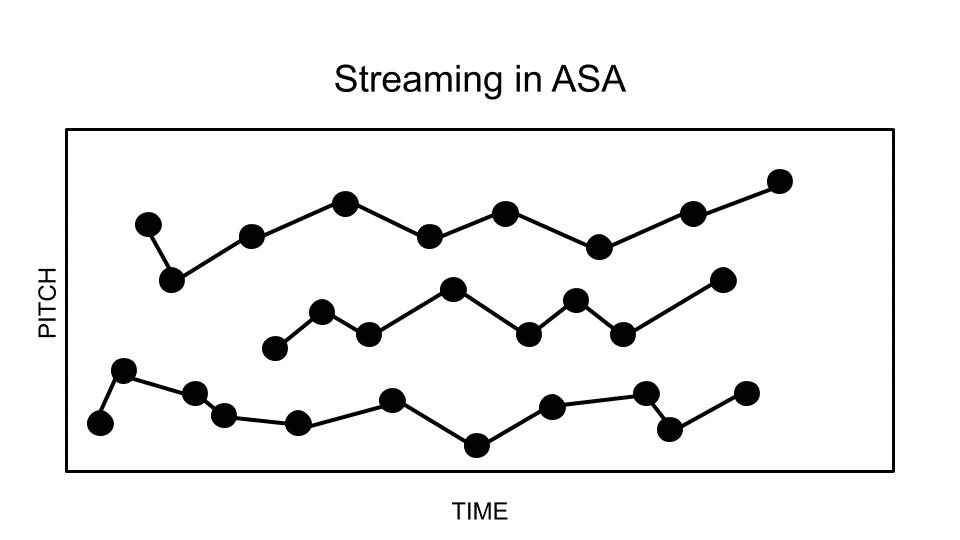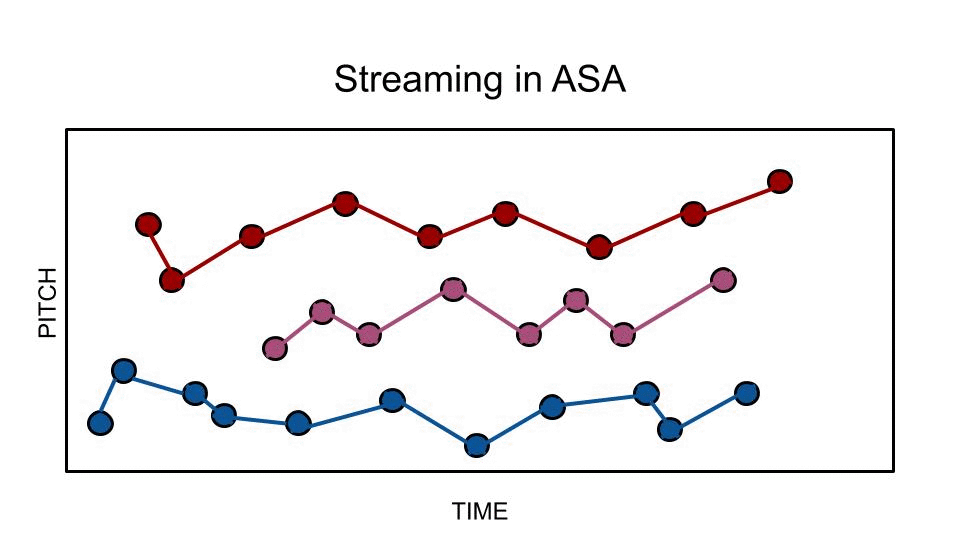
In music cognition, melodic fission (also known as melodic or auditory streaming, or stream segregation), is a phenomenon in which one line of pitches (an auditory stream) is heard as two or more separate melodic lines. This occurs when a phrase contains groups of pitches at two or more distinct registers or with two or more distinct timbres. The term appears to stem from a 1973 paper by W. J. Dowling. In music analysis and, more specifically, in Schenkerian analysis, the phenomenon is often termed compound melody. In psychophysics, auditory scene analysis is the process by which the brain separates and organizes sounds into perceptually distinct groups, known as auditory streams. The counterpart to melodic fission is melodic fusion. Contributing factors Register Listeners tend to perceive fast melodic sequences which contain tones from two different registers as two melodic lines. The greater the distance between groups of tones in a melody, the more likely they will b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BWV 1002 Allemande Melodic Fission Example
The (BWV; ; ) is a catalogue of compositions by Johann Sebastian Bach. It was first published in 1950, edited by Wolfgang Schmieder. The catalogue's second edition appeared in 1990. An abbreviated version of that second edition, known as BWV2a, was published in 1998. The catalogue groups compositions by genre. Even within a genre, compositions are not necessarily collated chronologically. For example, BWV 992 was composed many years before BWV 1. BWV numbers were assigned to 1,126 compositions in the 20th century, and more have been added to the catalogue in the 21st century. The Anhang (Anh.; Annex) of the BWV lists over 200 lost, doubtful and spurious compositions. History The first edition of the ''Bach-Werke-Verzeichnis'' was published in 1950. It allocated a unique number to every known composition by Bach. Wolfgang Schmieder, the editor of that catalogue, grouped the compositions by genre, largely following the 19th-century Bach Gesellschaft (BG) edition f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auditory Scene Analysis
In perception and psychophysics, auditory scene analysis (ASA) is a proposed model for the basis of auditory perception. This is understood as the process by which the human auditory system organizes sound into perceptually meaningful elements. The term was coined by psychologist Albert Bregman. The related concept in machine perception is computational auditory scene analysis (CASA), which is closely related to source separation and blind signal separation. The three key aspects of Bregman's ASA model are: segmentation, integration, and segregation. Background Sound reaches the ear and the eardrum vibrates as a whole. This signal has to be analyzed (in some way). Bregman's ASA model proposes that sounds will either be heard as "integrated" (heard as a whole – much like harmony in music), or "segregated" into individual components (which leads to counterpoint). For example, a bell can be heard as a 'single' sound (integrated), or some people are able to hear the individual ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melody
A melody (from Greek language, Greek μελῳδία, ''melōidía'', "singing, chanting"), also tune, voice or line, is a Linearity#Music, linear succession of musical tones that the listener perceives as a single entity. In its most literal sense, a melody is a combination of pitch (music), pitch and rhythm, while more figuratively, the term can include other musical elements such as Timbre, tonal color. It is the foreground to the background accompaniment. A line or part (music), part need not be a foreground melody. Melodies often consist of one or more musical Phrase (music), phrases or Motif (music), motifs, and are usually repeated throughout a musical composition, composition in various forms. Melodies may also be described by their melodic motion or the pitches or the interval (music), intervals between pitches (predominantly steps and skips, conjunct or disjunct or with further restrictions), pitch range, tension (music), tension and release, continuity and coheren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klangfarbenmelodie
''Klangfarbenmelodie'' (German for "sound-color melody") is a musical technique that involves splitting a musical line or melody between several instruments, rather than assigning it to just one instrument (or set of instruments), thereby adding color (timbre) and texture to the melodic line. The technique is sometimes compared to " pointillism", a neo-impressionist painting technique. History The term derives from Arnold Schoenberg's ''Harmonielehre'', where he discusses the creation of "timbre structures". Schoenberg and Anton Webern are particularly noted for their use of the technique, Schoenberg most notably in the third of his ''Five Pieces for Orchestra'' (Op. 16), and Webern in his Op. 10 (likely a response to Schoenberg's Op. 16), his Concerto for Nine Instruments (Op. 24), the Op. 11 pieces for cello and piano, and his orchestration of the six-part ''ricercar'' from Bach's ''Musical Offering'': This may be compared with Bach's open score of the subject and the tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Countermelody
In music, a counter-melody (often countermelody) is a sequence of notes, perceived as a melody, written to be played simultaneously with a more prominent lead melody. In other words, it is a secondary melody played in counterpoint with the primary melody. A counter-melody performs a subordinate role, and it is typically heard in a texture consisting of a melody plus accompaniment. In marches, the counter-melody is often given to the trombones or horns. American composer David Wallis Reeves is credited with this innovation in 1876. The more formal term countersubject applies to a secondary or subordinate melodic idea in a fugue. A countermelody differs from a harmony part sung by a backup singer in that whereas the harmony part typically lacks its own independent musical line, a countermelody is a distinct melodic line. See also *Nebenstimme *Parallel harmony *Traditional sub-Saharan African harmony Traditional sub-Saharan African harmony is a music theory of harmony in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterpoint
In music, counterpoint is the relationship between two or more musical lines (or voices) which are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. It has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradition, strongly developing during the Renaissance and in much of the common practice period, especially in the Baroque period. The term originates from the Latin ''punctus contra punctum'' meaning "point against point", i.e. "note against note". In Western pedagogy, counterpoint is taught through a system of species (see below). There are several different forms of counterpoint, including imitative counterpoint and free counterpoint. Imitative counterpoint involves the repetition of a main melodic idea across different vocal parts, with or without variation. Compositions written in free counterpoint often incorporate non-traditional harmonies and chords, chromaticism and dissonance. General principles The term "counterpoint" has been us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perceptual Attack Time
Perceptual Attack Time (often abbreviated "PAT") is a subjective measure of the time instant at which a musical sound's rhythmic emphasis is heard. It is analogous to the perceptual centre (aka "p-centre") in speech. It is different from both the physical onset (i.e., the time at which the sound's acoustic energy first begins) and the perceptual onset (i.e., the subjective time at which a listener first notices that the sound has begun). For a very percussive sound such as a note played on a closed hi hat cymbal the perceptual attack time may be just a few millisecond A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called ...s, while for a note bowed slowly on a violin the perceptual attack time may be as much as 50–100 milliseconds after the physical onset. Applications Understand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technische Hogeschool Eindhoven
The Eindhoven University of Technology ( nl, Technische Universiteit Eindhoven), abbr. TU/e, is a public technical university in the Netherlands, located in the city of Eindhoven. In 2020–21, around 14,000 students were enrolled in its BSc and MSc programs and around 1350 students were enrolled in its PhD and PDEng programs. In 2021, the TU/e employed around 3900 people. Eindhoven University of Technology has been ranked in the top 200 universities in three major ranking systems. The 2019 QS World University Rankings place Eindhoven 99th in the world, 34th in Europe, and 3rd in the Netherlands. TU/e is the Dutch member of thEuroTech Universities Alliance a strategic partnership of universities of science & technology in Europe: Technical University of Denmark (DTU), École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), École Polytechnique (L’X), The Technion, Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e), and Technical University of Munich (TUM). History The Eindhoven Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Press
Academic Press (AP) is an academic book publisher founded in 1941. It was acquired by Harcourt, Brace & World in 1969. Reed Elsevier bought Harcourt in 2000, and Academic Press is now an imprint of Elsevier. Academic Press publishes reference books, serials and online products in the subject areas of: * Communications engineering * Economics * Environmental science * Finance * Food science and nutrition * Geophysics * Life sciences * Mathematics and statistics * Neuroscience * Physical sciences * Psychology Well-known products include the ''Methods in Enzymology'' series and encyclopedias such as ''The International Encyclopedia of Public Health'' and the ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience''. See also * Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft (AVG) — the German predecessor, founded in 1906 by Leo Jolowicz (1868–1940), the father of Walter Jolowicz Walter may refer to: People * Walter (name), both a surname and a given name * Little Walter, American blues harmonica player Marion Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychophysics
Psychophysics quantitatively investigates the relationship between physical stimuli and the sensations and perceptions they produce. Psychophysics has been described as "the scientific study of the relation between stimulus and sensation" or, more completely, as "the analysis of perceptual processes by studying the effect on a subject's experience or behaviour of systematically varying the properties of a stimulus along one or more physical dimensions". ''Psychophysics'' also refers to a general class of methods that can be applied to study a perceptual system. Modern applications rely heavily on threshold measurement, ideal observer analysis, and signal detection theory. Psychophysics has widespread and important practical applications. For example, in the study of digital signal processing, psychophysics has informed the development of models and methods of lossy compression. These models explain why humans perceive very little loss of signal quality when audio and video sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Cognition
Music psychology, or the psychology of music, may be regarded as a branch of both psychology and musicology. It aims to explain and understand musical behaviour and experience, including the processes through which music is perceived, created, responded to, and incorporated into everyday life. Modern music psychology is primarily empirical; its knowledge tends to advance on the basis of interpretations of data collected by systematic observation of and interaction with human participants. Music psychology is a field of research with practical relevance for many areas, including music performance, composition, education, criticism, and therapy, as well as investigations of human attitude, skill, performance, intelligence, creativity, and social behavior. Music psychology can shed light on non-psychological aspects of musicology and musical practice. For example, it contributes to music theory through investigations of the perception and computational modelling of musical structures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unfolding (music)
In Schenkerian analysis, unfolding (German: '' Ausfaltung'') or compound melody is the implication of more than one melody or line by a single voice through skipping back and forth between the notes of the two melodies. In music cognition, the phenomenon is also known as melodic fission. The term "compound melody" may have its origin in Walter Piston's ''Counterpoint'' (New York, Norton, 1947), under the form "compound melodic line" (London edition, 1947, p. 23). In the context of Schenkerian analysis, it appears among others in Forte & Gilbert, ''Introduction to Schenkerian Analysis'' (1982), Chapter 3, pp. 67-80. Manfred Bukofzer, ''Music in the Baroque Era'', New York, Norton, 1947, had spoken of "implied polyphony". Unfolding is "a prolongation by means of the unfolding of intervals horizontally." Though the notes skipped between, those heard, may be considered near the foreground, the dyads, those implied, are in the middle or background. Middleground dyads are "unfold ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |