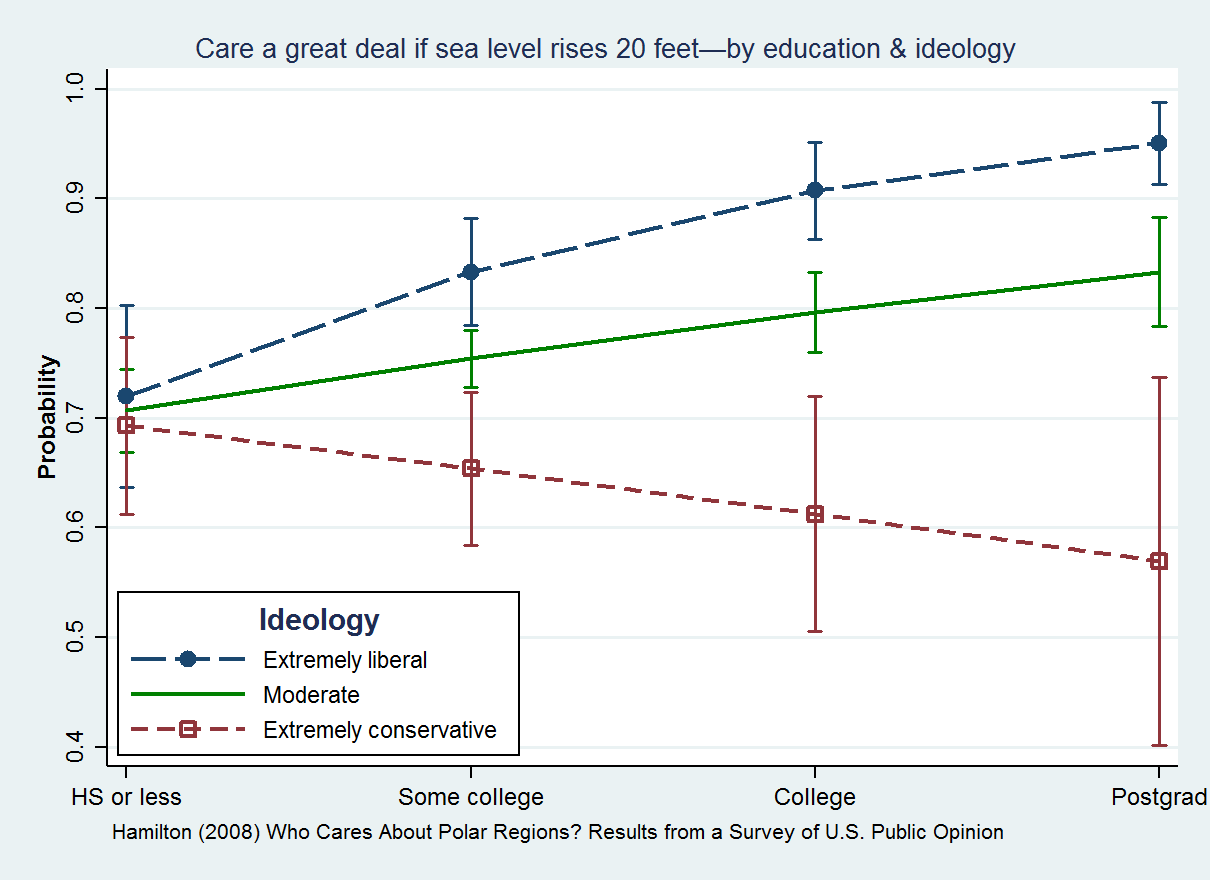
|
Mediator Variable
In statistics, a mediation model seeks to identify and explain the mechanism or process that underlies an observed relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable via the inclusion of a third hypothetical variable, known as a mediator variable (also a mediating variable, intermediary variable, or intervening variable). Rather than a direct causal relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable, a mediation model proposes that the independent variable influences the mediator variable, which in turn influences the dependent variable. Thus, the mediator variable serves to clarify the nature of the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Mediation analyses are employed to understand a known relationship by exploring the underlying mechanism or process by which one variable influences another variable through a mediator variable.Cohen, J.; Cohen, P.; West, S. G.; Aiken, L. S. (2003) ''Applied multiple regression/co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Mediation Model
Simple or SIMPLE may refer to: *Simplicity, the state or quality of being simple Arts and entertainment * ''Simple'' (album), by Andy Yorke, 2008, and its title track * "Simple" (Florida Georgia Line song), 2018 * "Simple", a song by Johnny Mathis from the 1984 album ''A Special Part of Me'' * "Simple", a song by Collective Soul from the 1995 album ''Collective Soul'' * "Simple", a song by Katy Perry from the 2005 soundtrack to ''The Sisterhood of the Traveling Pants'' * "Simple", a song by Khalil from the 2017 album ''Prove It All'' * "Simple", a song by Kreesha Turner from the 2008 album '' Passion'' * "Simple", a song by Ty Dolla Sign from the 2017 album ''Beach House 3'' deluxe version * ''Simple'' (video game series), budget-priced console games Businesses and organisations * Simple (bank), an American direct bank * SIMPLE Group, a consulting conglomeration based in Gibraltar * Simple Shoes, an American footwear brand * Simple Skincare, a British brand of soap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-parametric Statistics
Nonparametric statistics is the branch of statistics that is not based solely on parametrized families of probability distributions (common examples of parameters are the mean and variance). Nonparametric statistics is based on either being distribution-free or having a specified distribution but with the distribution's parameters unspecified. Nonparametric statistics includes both descriptive statistics and statistical inference. Nonparametric tests are often used when the assumptions of parametric tests are violated. Definitions The term "nonparametric statistics" has been imprecisely defined in the following two ways, among others: Applications and purpose Non-parametric methods are widely used for studying populations that take on a ranked order (such as movie reviews receiving one to four stars). The use of non-parametric methods may be necessary when data have a ranking but no clear numerical interpretation, such as when assessing preferences. In terms of levels of me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediated Moderation Model 1
''Mediated: How the Media Shapes Your World and the Way You Live in It'' is a non-fiction book by anthropologist Thomas de Zengotita published in 2005 by Bloomsbury about the effect of the media in the Western world. Summary ''Mediated'' aims at creating awareness rather than offering ready-made solutions to remedy the intrusion of too much media in our industrial societies. Rather than writing yet another pamphlet against the media, the author chooses to focus on the mechanisms and the processes of our ''mediated'' society. The basis of his analysis is that the opposite of reality is not phony or superficial, it is optional. We choose between options to determine who we are, to make statements to the world about who we are. People, he argues, have always done so, but the difference with today's situation is that we have a lot more options. In terms of options, comparing the modern world with the post-modern world is like comparing a breeze with a hurricane. The media forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moderated Mediation
In statistics, moderation and mediation can occur together in the same model.Muller, D., Judd, C. M., & Yzerbyt, V. Y. (2005). When moderation is mediated and mediation is moderated. ''Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 89'', 852–863. Moderated mediation, also known as conditional indirect effects,Preacher, K. J., Rucker, D. D., & Hayes, A. F. (2007) Addressing moderated mediation hypotheses: Theory, Methods, and Prescriptions. ''Multivariate Behavioral Research, 42,'' 185–227. occurs when the treatment effect of an independent variable A on an outcome variable C via a mediator variable B differs depending on levels of a moderator variable D. Specifically, either the effect of A on B, and/or the effect of B on C depends on the level of D. Langfred (2004) model Langfred (2004) was the first to provide a comprehensive treatment of the question of how to conceptualize moderated mediation, classify different types of moderated mediation models, and to develop the logic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interaction Effect
In statistics, an interaction may arise when considering the relationship among three or more variables, and describes a situation in which the effect of one causal variable on an outcome depends on the state of a second causal variable (that is, when effects of the two causes are not additive). Although commonly thought of in terms of causal relationships, the concept of an interaction can also describe non-causal associations (then also called moderation or effect modification). Interactions are often considered in the context of regression analyses or factorial experiments. The presence of interactions can have important implications for the interpretation of statistical models. If two variables of interest interact, the relationship between each of the interacting variables and a third "dependent variable" depends on the value of the other interacting variable. In practice, this makes it more difficult to predict the consequences of changing the value of a variable, parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moderating Variable
In statistics and regression analysis, moderation (also known as effect modification) occurs when the relationship between two variables depends on a third variable. The third variable is referred to as the moderator variable (or effect modifier) or simply the moderator (or modifier). The effect of a moderating variable is characterized statistically as an interaction (statistics), interaction; that is, a Categorical variable, categorical (e.g., sex, ethnicity, class) or Level of measurement, continuous (e.g., age, level of reward) variable (mathematics), variable that is associated with the direction and/or magnitude of the relation between dependent and independent variables. Specifically within a correlational analysis framework, a moderator is a third variable that affects the zero-order correlation between two other variables, or the value of the slope of the dependent variable on the independent variable. In analysis of variance (ANOVA) terms, a basic moderator effect can be r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suppressor Variable
A suppressor variable is a variable that increases the predictive validity of another variable when included in a regression equation. Krus, D. J., & Wilkinson, S. M. (1986). Demonstration of properties of a suppressor variable. ''Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, & Computers'', 18(1), 21-24. Suppression can occur when a single causal variable is related to an outcome variable through two separate mediator variables, and when one of those mediated effects is positive and one is negative. In such a case, each mediator variable suppresses or conceals the effect that is carried through the other mediator variable. For example, higher intelligence scores (a causal variable, A) may cause an increase in error detection (a mediator variable, B) which in turn may cause a decrease in errors made at work on an assembly line (an outcome variable, X); at the same time, intelligence could also cause an increase in boredom (C), which in turn may cause an increase in errors (X). Thus, in one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediation Model With Two Covariates
Mediation is a structured, interactive process where an impartial third party neutral assists disputing parties in resolving conflict through the use of specialized communication and negotiation techniques. All participants in mediation are encouraged to actively participate in the process. Mediation is a "party-centered" process in that it is focused primarily upon the needs, rights, and interests of the parties. The mediator uses a wide variety of techniques to guide the process in a constructive direction and to help the parties find their optimal solution. A mediator is facilitative in that she/he manages the interaction between parties and facilitates open communication. Mediation is also evaluative in that the mediator analyzes issues and relevant norms ("reality-testing"), while refraining from providing prescriptive advice to the parties (e.g., "You should do..."). Mediation, as used in law, is a form of alternative dispute resolution resolving disputes between two or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confounding Variable
In statistics, a confounder (also confounding variable, confounding factor, extraneous determinant or lurking variable) is a variable that influences both the dependent variable and independent variable, causing a spurious association. Confounding is a causal concept, and as such, cannot be described in terms of correlations or associations.Pearl, J., (2009). Simpson's Paradox, Confounding, and Collapsibility In ''Causality: Models, Reasoning and Inference'' (2nd ed.). New York : Cambridge University Press. The existence of confounders is an important quantitative explanation why correlation does not imply causation. Confounds are threats to internal validity. Definition Confounding is defined in terms of the data generating model. Let ''X'' be some independent variable, and ''Y'' some dependent variable. To estimate the effect of ''X'' on ''Y'', the statistician must suppress the effects of extraneous variables that influence both ''X'' and ''Y''. We say that ''X'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causal Model
In the philosophy of science, a causal model (or structural causal model) is a conceptual model that describes the causal mechanisms of a system. Causal models can improve study designs by providing clear rules for deciding which independent variables need to be included/controlled for. They can allow some questions to be answered from existing observational data without the need for an interventional study such as a randomized controlled trial. Some interventional studies are inappropriate for ethical or practical reasons, meaning that without a causal model, some hypotheses cannot be tested. Causal models can help with the question of ''external validity'' (whether results from one study apply to unstudied populations). Causal models can allow data from multiple studies to be merged (in certain circumstances) to answer questions that cannot be answered by any individual data set. Causal models have found applications in signal processing, epidemiology and machine learning. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moderation (statistics)
In statistics and regression analysis, moderation (also known as effect modification) occurs when the relationship between two variables depends on a third variable. The third variable is referred to as the moderator variable (or effect modifier) or simply the moderator (or modifier). The effect of a moderating variable is characterized statistically as an interaction; that is, a categorical (e.g., sex, ethnicity, class) or continuous (e.g., age, level of reward) variable that is associated with the direction and/or magnitude of the relation between dependent and independent variables. Specifically within a correlational analysis framework, a moderator is a third variable that affects the zero-order correlation between two other variables, or the value of the slope of the dependent variable on the independent variable. In analysis of variance (ANOVA) terms, a basic moderator effect can be represented as an interaction between a focal independent variable and a factor that speci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morgan Kaufmann
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers is a Burlington, Massachusetts (San Francisco, California until 2008) based publisher specializing in computer science and engineering content. Since 1984, Morgan Kaufmann has published content on information technology, computer architecture, data management, computer networking, computer systems, human computer interaction, computer graphics, multimedia information and systems, artificial intelligence, computer security, and software engineering. Morgan Kaufmann's audience includes the research and development communities, information technology (IS/IT) managers, and students in professional degree programs. The company was founded in 1984 by publishers Michael B. Morgan and William Kaufmann and computer scientist Nils Nilsson. It was held privately until 1998, when it was acquired by Harcourt General and became an imprint of the Academic Press, a subsidiary of Harcourt. Harcourt was acquired by Reed Elsevier in 2001; Morgan Kaufmann is now an impri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |