|
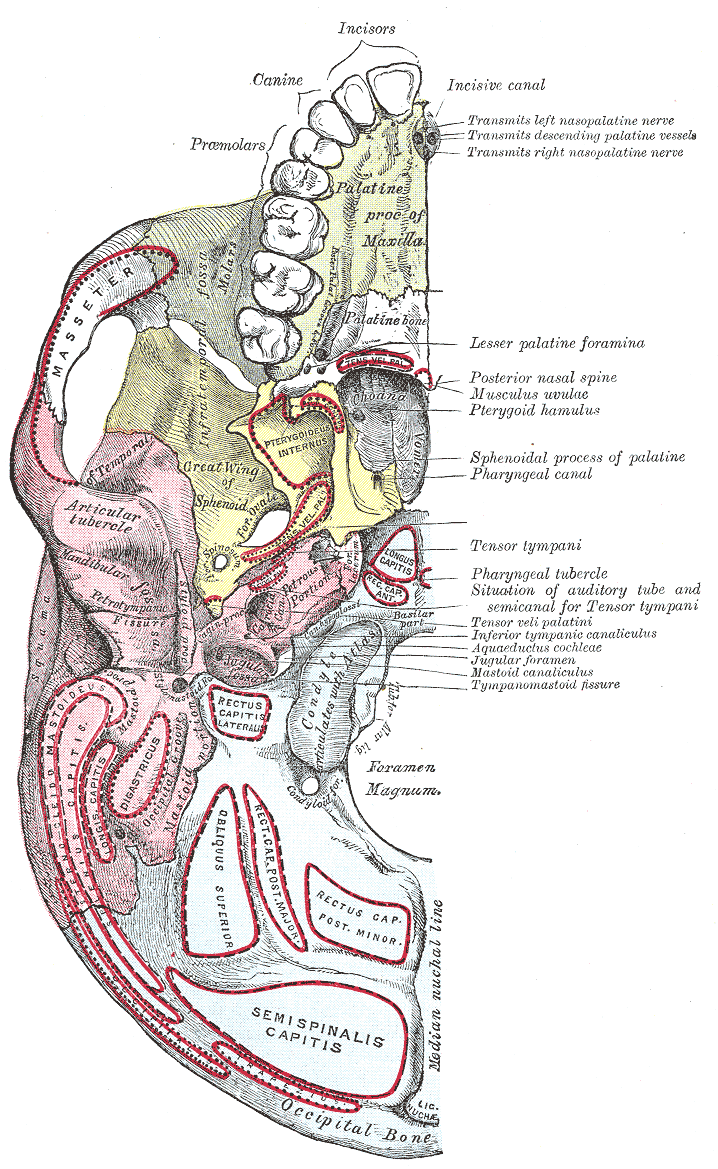
Mastoid Foramen
The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone. It transmits an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus, and a small branch of the occipital artery, the posterior meningeal artery to the dura mater. Structure The mastoid foramen is a hole in the posterior border of the temporal bone of the skull. The opening of the mastoid foramen is an average of 18 mm from the asterion, and around 34 mm from the external auditory meatus. It is typically very narrow. This may be around 2 mm. Variation The position and size of this foramen are very variable. It is not always present. Sometimes, it is duplicated on one side or both sides. Sometimes, it is situated in the occipital bone, or in the suture between the temporal bone and the occipital bone. Function The mastoid foramen transmits: * an emissary vein between the sigmoid sinus and the suboccipital venous plexus or the posterior auricular vein. * a small branch of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Bone
The temporal bones are situated at the sides and base of the skull, and lateral to the temporal lobes of the cerebral cortex. The temporal bones are overlaid by the sides of the head known as the temples, and house the structures of the ears. The lower seven cranial nerves and the major vessels to and from the brain traverse the temporal bone. Structure The temporal bone consists of four parts— the squamous, mastoid, petrous and tympanic parts. The squamous part is the largest and most superiorly positioned relative to the rest of the bone. The zygomatic process is a long, arched process projecting from the lower region of the squamous part and it articulates with the zygomatic bone. Posteroinferior to the squamous is the mastoid part. Fused with the squamous and mastoid parts and between the sphenoid and occipital bones lies the petrous part, which is shaped like a pyramid. The tympanic part is relatively small and lies inferior to the squamous part, anterior to the mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Meningeal Artery
The posterior meningeal artery is the largest vessel supplying the dura region of the posterior fossa. It typically arises from the ascending pharyngeal artery although other origins have been seen, such as the occipital artery. The artery or its branches enter the cranium through jugular foramen, foramen magnum or hypoglossal canal The hypoglossal canal is a foramen in the occipital bone of the skull. It is hidden medially and superiorly to each occipital condyle. It transmits the hypoglossal nerve. Structure The hypoglossal canal lies in the epiphyseal junction between ....Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography, 2nd edition, Anne G. Osborn See also * Meninges References * Diagnostic Cerebral Angiography, 2nd edition, Anne G. Osborn Arteries of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emissary Veins
The emissary veins connect the extracranial venous system with the intracranial venous sinuses. They connect the veins outside the cranium to the venous sinuses inside the cranium. They drain from the scalp, through the skull, into the larger meningeal veins and dural venous sinuses. Emissary veins have an important role in selective cooling of the head. They also serve as routes where infections are carried into the cranial cavity from the extracranial veins to the intracranial veins. There are several types of emissary veins including posterior condyloid, mastoid, occipital and parietal emissary vein. Structure There are also emissary veins passing through the foramen ovale, jugular foramen, foramen lacerum, and hypoglossal canal. Function Because the emissary veins are valveless, they are an important part in selective brain cooling through bidirectional flow of cooler blood from the evaporating surface of the head. In general, blood flow is from external to internal but t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cranial Sutures
In anatomy, fibrous joints are joints connected by fibrous tissue, consisting mainly of collagen Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole .... These are fixed joints where bones are united by a layer of white fibrous tissue of varying thickness. In the skull the joints between the bones are called Suture (anatomy), sutures. Such immovable joints are also referred to as synarthrosis, synarthroses. Types Most fibrous joints are also called "fixed" or "immovable". These joints have no joint cavity and are connected via fibrous connective tissue. The skull bones are connected by fibrous joints called ''#Sutures, sutures''. In fetus, fetal skulls the sutures are wide to allow slight movement during birth. They later become rigid (synarthrosis, synarthrodial). Some of the long bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Bone
The occipital bone () is a neurocranium, cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. At the base of skull in the occipital bone, there is a large oval opening called the foramen magnum, which allows the passage of the spinal cord. Like the other cranial bones, it is classed as a flat bone. Due to its many attachments and features, the occipital bone is described in terms of separate parts. From its front to the back is the basilar part of occipital bone, basilar part, also called the basioccipital, at the sides of the foramen magnum are the lateral parts of occipital bone, lateral parts, also called the exoccipitals, and the back is named as the squamous part of occipital bone, squamous part. The basilar part is a thick, somewhat quadrilateral piece in front of the foramen magnum and directed towards the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Auditory Meatus
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal extends from the pinna to the eardrum and is about in length and in diameter. Structure The human ear canal is divided into two parts. The elastic cartilage part forms the outer third of the canal; its anterior and lower wall are cartilaginous, whereas its superior and back wall are fibrous. The cartilage is the continuation of the cartilage framework of pinna. The cartilaginous portion of the ear canal contains small hairs and specialized sweat glands, called apocrine glands, which produce cerumen ( ear wax). The bony part forms the inner two thirds. The bony part is much shorter in children and is only a ring (''annulus tympanicus'') in the newborn. The layer of epithelium encompassing the bony portion of the ear canal is much thinner and therefore, more sensitive in comparison to the cartilaginous portion. Size and sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asterion (anatomy)
The asterion is a meeting point between three sutures between bones of the skull. It is an important surgical landmark. Structure In human anatomy, the asterion is a visible ( craniometric) point on the exposed skull. It is just posterior to the ear. It is the point where three cranial sutures meet: * the lambdoid suture. * parietomastoid suture. * occipitomastoid suture. It is also the point where three cranial bones meet: * the parietal bone. * the occipital bone. * the mastoid portion of the temporal bone. In the adult, it lies 4 cm behind and 12 mm above the center of the entrance to the ear canal. Its relation to other anatomical structures is fairly variable. Clinical significance Neurosurgeons may use the asterion to orient themselves, in order to plan safe entry into the skull for some operations, such as when using a retro-sigmoid approach. Etymology The asterion receives its name from the Greek ἀστέριον (''astērion''), meaning "star" or "starry" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dura Mater
In neuroanatomy, dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. The other two meningeal layers are the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. It envelops the arachnoid mater, which is responsible for keeping in the cerebrospinal fluid. It is derived primarily from the neural crest cell population, with postnatal contributions of the paraxial mesoderm. Structure The dura mater has several functions and layers. The dura mater is a membrane that envelops the arachnoid mater. It surrounds and supports the dural sinuses (also called dural venous sinuses, cerebral sinuses, or cranial sinuses) and carries blood from the brain toward the heart. Cranial dura mater has two layers called ''lamellae'', a superficial layer (also called the periosteal layer), which serves as the skull's inner periosteum, called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occipital Artery
The occipital artery arises from the external carotid artery opposite the facial artery. Its path is below the posterior belly of digastric to the occipital region. This artery supplies blood to the back of the scalp and sternocleidomastoid muscles, and deep muscles in the back and neck. Structure At its origin, it is covered by the posterior belly of the digastricus and the stylohyoideus, and the hypoglossal nerve winds around it from behind forward; higher up, it crosses the internal carotid artery, the internal jugular vein, and the vagus and accessory nerves. It next ascends to the interval between the transverse process of the atlas and the mastoid process of the temporal bone, and passes horizontally backward, grooving the surface of the latter bone, being covered by the sternocleidomastoideus, splenius capitis, longissimus capitis, and digastricus, and resting upon the rectus capitis lateralis, the obliquus superior, and semispinalis capitis. It then changes its course and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Of The Skull
The base of skull, also known as the cranial base or the cranial floor, is the most inferior area of the skull. It is composed of the endocranium and the lower parts of the calvaria. Structure Structures found at the base of the skull are for example: Bones There are five bones that make up the base of the skull: *Ethmoid bone * Sphenoid bone * Occipital bone *Frontal bone *Temporal bone Sinuses *Occipital sinus * Superior sagittal sinus *Superior petrosal sinus Foramina of the skull * Foramen cecum *Optic foramen *Foramen lacerum *Foramen rotundum * Foramen magnum * Foramen ovale *Jugular foramen *Internal auditory meatus *Mastoid foramen *Sphenoidal emissary foramen *Foramen spinosum Sutures *Frontoethmoidal suture *Sphenofrontal suture *Sphenopetrosal suture *Sphenoethmoidal suture * Petrosquamous suture *Sphenosquamosal suture Other *Sphenoidal lingula *Subarcuate fossa *Dorsum sellae *Jugular process *Petro-occipital fissure *Condylar canal * Jugular tubercle * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suboccipital Venous Plexus
The suboccipital venous plexus drains deoxygenated blood from the back of the head. It communicates with the external vertebral venous plexuses. The external vertebral venous plexuses travel inferiorly from this suboccipital region to drain into the brachiocephalic vein. The occipital vein joins in the formation of the plexus deep to the musculature of the back and from here drains into the external jugular vein. The plexus surrounds segments of the vertebral artery The vertebral arteries are major arteries An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry o .... Veins of the head and neck {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmoid Sinus
The sigmoid sinuses (sigma- or s-shaped hollow curve), also known as the , are venous sinuses within the skull that receive blood from posterior dural venous sinus veins. Structure The sigmoid sinus is a dural venous sinus situated within the dura mater. The sigmoid sinus receives blood from the transverse sinuses, which track the posterior wall of the cranial cavity, travels inferiorly along the parietal bone, temporal bone and occipital bone, and converges with the inferior petrosal sinuses to form the internal jugular vein. Each sigmoid sinus begins beneath the temporal bone and follows a tortuous course to the jugular foramen, at which point the sinus becomes continuous with the internal jugular vein. Function The sigmoid sinus receives blood from the transverse sinuses, which receive blood from the posterior aspect of the skull. Along its course, the sigmoid sinus also receives blood from the cerebral veins, cerebellar veins, diploic veins, and emissary veins. See als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |