|
Marl Prairie
Marl prairies are wet prairies that allow for a slow seepage of overland water and exist in the Everglades, usually bordering deeper sloughs, and contain low-growth vegetation. Description Marl is loose earthy deposits mixed with clay and calcium carbonate and sits on limestone bedrock. Marl prairies are home to microbes, bacteria, and algae, and serve as an important food source to some fish, tadpoles, and invertebrates. Marl prairies are also thought to be the preferred breeding ground of the endangered Cape Sable Seaside Sparrow The Cape Sable seaside sparrow (''Ammospiza maritima mirabilis'') is a subspecies of the seaside sparrow, a species of bird in the family Passerellidae native to the United States. This subspecies is endemic to southern Florida. It is designat .... See also * Taylor Slough * Shark River Slough References {{Reflist Prairies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prairie
Prairies are ecosystems considered part of the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome by ecologists, based on similar temperate climates, moderate rainfall, and a composition of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, rather than trees, as the dominant vegetation type. Temperate grassland regions include the Pampas of Argentina, Brazil and Uruguay, and the steppe of Ukraine, Russia and Kazakhstan. Lands typically referred to as "prairie" tend to be in North America. The term encompasses the area referred to as the Interior Lowlands of Canada, the United States, and Mexico, which includes all of the Great Plains as well as the wetter, hillier land to the east. In the U.S., the area is constituted by most or all of the states of North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska, Kansas, and Oklahoma, and sizable parts of the states of Montana, Wyoming, Colorado, New Mexico, Texas, Missouri, Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, Wisconsin, and western and southern Minnesota. The Palouse of Washington and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Everglades
The Everglades is a natural region A natural region (landscape unit) is a basic geographic unit. Usually, it is a region which is distinguished by its common natural features of geography, geology, and climate. From the ecological point of view, the naturally occurring flora and ... of tropical climate, tropical wetlands in the southern portion of the U.S. state of Florida, comprising the southern half of a large drainage basin within the Neotropical realm. The system begins near Orlando, Florida, Orlando with the Kissimmee River, which discharges into the vast but shallow Lake Okeechobee. Water leaving the lake in the wet season forms a slow-moving river wide and over long, flowing southward across a limestone shelf to Florida Bay at the southern end of the state. The Everglades experiences a wide range of weather patterns, from frequent flooding in the wet season to drought in the dry season. Throughout the 20th century, the Everglades suffered significant loss of habi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slough (hydrology)
A slough ( or ) is a wetland, usually a swamp or shallow lake, often a backwater to a larger body of water. Water tends to be stagnant or may flow slowly on a seasonal basis. In North America, "slough" may refer to a side-channel from or feeding a river, or an inlet or natural channel only sporadically filled with water. An example of this is Finn Slough on the Fraser River, whose lower reaches have dozens of notable sloughs. Some sloughs, like Elkhorn Slough, used to be mouths of rivers, but have become stagnant because tectonic activity cut off the river's source. In the Sacramento River, Steamboat Slough was an alternate branch of the river, a preferred shortcut route for steamboats passing between Sacramento and San Francisco. Georgiana Slough was a steamboat route through the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta, from the Sacramento River to the San Joaquin River and Stockton. Plants and animals A slough, also called a tidal channel, is a channel in a wetland. Typic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae. Marl makes up the lower part of the cliffs of Dover, and the Channel Tunnel follows these marl layers between France and the United Kingdom. Marl is also a common sediment in post-glacial lakes, such as the marl ponds of the northeastern United States. Marl has been used as a soil conditioner and neutralizing agent for acid soil and in the manufacture of cement. Description Marl or marlstone is a carbonate-rich mud or mudstone which contains variable amounts of clays and silt. The term was originally loosely applied to a variety of materials, most of which occur as loose, earthy deposits consisting chiefly of an intimate mixture of clay and calcium carbonate, formed under freshwater conditions. These typically contain 35–65% clay and 65–35% carbonate. The te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4). Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay particles, but become hard, brittle and non–plastic upon drying or firing. Most pure clay minerals are white or light-coloured, but natural clays show a variety of colours from impurities, such as a reddish or brownish colour from small amounts of iron oxide. Clay is the oldest known ceramic material. Prehistoric humans discovered the useful properties of clay and used it for making pottery. Some of the earliest pottery shards have been dated to around 14,000 BC, and clay tablets were the first known writing medium. Clay is used in many modern industrial processes, such as paper making, cement production, and chemical filtering. Between one-half and two-thirds of the world's population live or work in buildings made with clay, ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for lime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Sable Seaside Sparrow
The Cape Sable seaside sparrow (''Ammospiza maritima mirabilis'') is a subspecies of the seaside sparrow, a species of bird in the family Passerellidae native to the United States. This subspecies is endemic to southern Florida. It is designated endangered under the Endangered Species Act. Description The Cape Sable seaside sparrow is 13 to 14 centimeters in length. The back is dark olive-gray and the tail and wings are olive-brown. Adults are light gray on the belly to almost white with dark olive-gray streaks on the breast and sides.Cape Sable Seaside Sparrow. In United States Fish and Wildlife Service. Original 1999, continually updated. Biology This subspecies occu ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
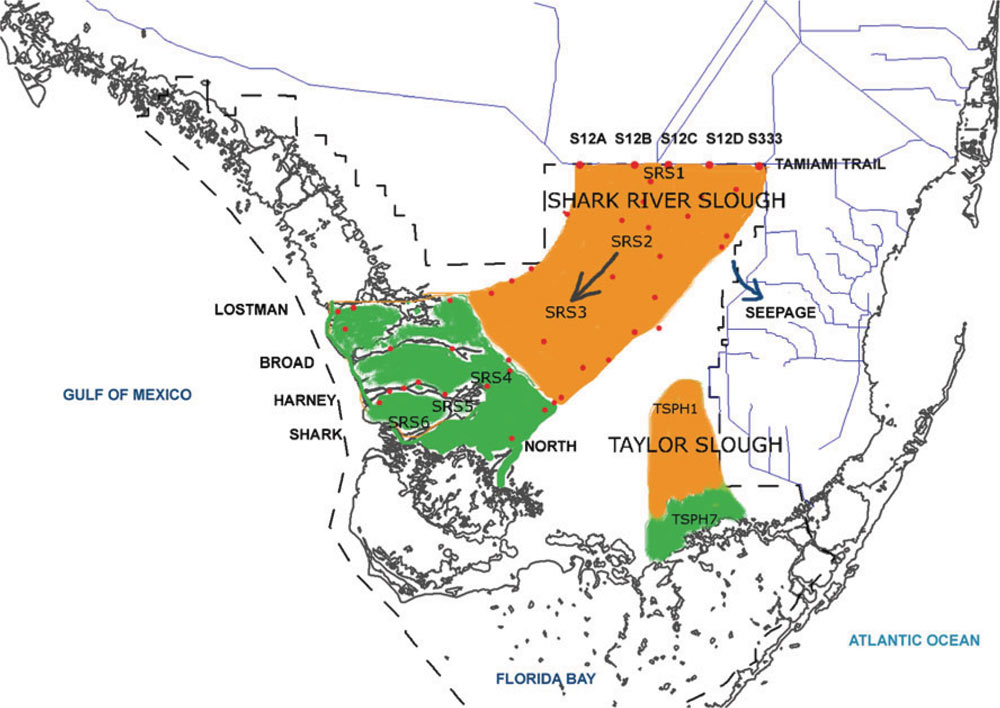
Taylor Slough
Taylor Slough, located in the southeastern corner of the Florida Everglades, along with the much larger Shark River Slough farther to the west, are the principal natural drainages for the freshwater Everglades and the essential conduit for providing overland freshwater to Florida Bay. Description Taylor Slough is a 247 square kilometer wetland system. The slough stretches from the east everglades, to the northern portion of Florida Bay. In its natural form, Taylor Slough is the primary source of overland, freshwater flow into the north eastern part of Florida Bay. A major portion of the Taylor Slough resides in Everglades National Park. Taylor Slough crosses over part of the C-111 basin. History The term slough (pronounced ''slew'') is used to describe areas of the Everglades where there is slightly deeper water than in the surrounding marshes and where a slow, but measurable, current is present. In essence, sloughs are the broad, shallow rivers of the Everglades. Sloughs oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shark River Slough
Shark River Slough (SRS) is a low-lying area of land that channels water through the Florida Everglades, beginning in Water Conservation Area 3, flowing through Everglades National Park, and ultimately into Florida Bay. Together with Taylor Slough to the east, Shark River Slough is an essential conduit of overland freshwater to Florida Bay. Shark River Slough is also known as the "River of Grass." Description Shark River Slough is the dominant path for flow of water into Everglades National Park. SRS is a mixture of sawgrass marshes, tree islands, sloughs, and wet prairies. The SRS is bordered by marl prairies. Everglades restoration Historically, Shark River Slough was the primary path for water flow in the Everglades system. Restoration of the historic function of the slough is essential to restoration of Everglades National Park. Tidal influence Shark River Slough has tides from the Gulf of Mexico that reach 30 km inland. See also * Taylor Slough * Cape Sable S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |