|
Marine Protection, Research, And Sanctuaries Act Of 1972
Marine Protection, Research and Sanctuaries Act of 1972 (MPRSA) or Ocean Dumping Act is one of several key environmental laws passed by the US Congress in 1972. The Act has two essential aims: to regulate intentional ocean disposal of materials, and to authorize any related research.Claudia Copeland. Cong. Bill. Washington, D.C.: Congressional Research Service, Library of Congress, 1999. While the MPRSA regulates the ocean dumping of waste and provides for a research program on ocean dumping, it also provides for the designation and regulation of marine sanctuaries.The Office of Health, Safety and Security - Home. Web. 09 Nov. 2011. The act regulates the ocean dumping of all material beyond the territorial limit ( from shore) and prevents or strictly limits dumping material that "would adversely affect human health, welfare, or amenities, or the marine environment, ecological systems, or economic potentialities". The MPRSA authorized the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) to reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservation
Conservation is the preservation or efficient use of resources, or the conservation of various quantities under physical laws. Conservation may also refer to: Environment and natural resources * Nature conservation, the protection and management of the environment and natural resources * ''Conservation'' (magazine), published by the Society for Conservation Biology from 2000 to 2014 ** ''Conservation Biology'' (journal), scientific journal of the Society for Conservation Biology * Conservation biology, the science of protection and management of biodiversity * Conservation movement, political, environmental, or social movement that seeks to protect natural resources, including biodiversity and habitat * Conservation organization, an organization dedicated to protection and management of the environment or natural resources * Wildlife conservation, the practice of protecting wild species and their habitats in order to prevent species from going extinct Physical laws * Conse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, multi-mission service unique among the United States military branches for having a maritime law enforcement mission with jurisdiction in both domestic and international waters and a federal regulatory agency mission as part of its duties. It is the largest and most powerful coast guard in the world, rivaling the capabilities and size of most navies. The U.S. Coast Guard is a humanitarian and security service. It protects the United States' borders and economic and security interests abroad; and defends its sovereignty by safeguarding sea lines of communication and commerce across vast territorial waters spanning 95,000 miles of coastline and its Exclusive Economic Zone. With national and economic security depending upon open global trade a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Debris
Marine debris, also known as marine litter, is human-created waste that has deliberately or accidentally been released in a sea or ocean. Floating oceanic debris tends to accumulate at the center of gyres and on coastlines, frequently washing aground, when it is known as ''beach litter'' or tidewrack. Deliberate disposal of wastes at sea is called ''ocean dumping''. Naturally occurring debris, such as driftwood and drift seeds, are also present. With the increasing use of plastic, human influence has become an issue as many types of (petrochemical) plastics do not biodegrade quickly, as would natural or organic materials. The largest single type of plastic pollution (~10 %) and majority of large plastic in the oceans is discarded and lost nets from the fishing industry. Waterborne plastic poses a serious threat to fish, seabirds, marine reptiles, and marine mammals, as well as to boats and coasts. Dumping, container spillages, litter washed into storm drains and waterways and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation CHASE
Operation CHASE (an acronym for "Cut Holes And Sink 'Em") was a United States Department of Defense program for the disposal of unwanted munitions at sea from May 1964 until the early 1970s.Kurak, Steve "Operation Chase" ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'' September 1967 pp. 40-46 Munitions were loaded onto ships to be scuttled once they were at least 250 miles (400 km) offshore.Mauroni, Al.The US Army Chemical Corps: Past, Present, and Future", ''Army Historical Foundation''. Retrieved 26 November 2007. While most of the sinkings involved conventional weapons, four of them involved chemical weapons. The disposal site for the chemical weapons was a three-mile (5 km) area of the Atlantic Ocean between the coast of the U.S. state of Florida and the Bahamas.Wagner, Travis. "Hazardous Waste: Evolution of a National Environmental Problem",Project Muse, ''Journal of Policy History'', 16.4 (2004) pp. 306-331. Retrieved 26 November 2007. The CHASE program was preceded by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Maine Regional Marine Research Program
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay (geography), bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden. See also * References External links * {{Authority control Gulfs, Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretary Of Commerce
The United States secretary of commerce (SecCom) is the head of the United States Department of Commerce. The secretary serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters relating to commerce. The secretary reports directly to the president and is a statutory member of Cabinet of the United States. The secretary is appointed by the president, with the advice and consent of the United States Senate. The secretary of commerce is concerned with promoting American businesses and industries; the department states its mission to be "to foster, promote, and develop the foreign and domestic commerce". Until 1913, there was one secretary of commerce and labor, uniting this department with the United States Department of Labor, which is now headed by a separate United States secretary of labor. Secretary of Commerce is a Level I position in the Executive Schedule, thus earning a salary of US$221,400, as of January 2021. The current secretary of commer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Bight
The New York Bight is the geological identification applied to a roughly triangular indentation, regarded as a bight, along the Atlantic coast of the United States that extends northeasterly from Cape May Inlet in New Jersey to Montauk Point on the eastern tip of Long Island. As the result of direct contact with the Gulf Stream along the coast of North America, the coastal climate of the bight area is temperate. Geography The bight is formed by the roughly right-angled intersection of the generally north-south Atlantic coast of New Jersey and the approximately east–west southern coast of Long Island at the mouth of the Hudson River. The New York Bight Apex is the area including and between the Hudson River estuary and the Raritan River estuary extending 6–7 km of the coast, and it includes Raritan Bay and the Lower New York Bay. Weather The geography of the bight has long been of major concern to meteorologists in the study of tropical storm patterns along the easte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
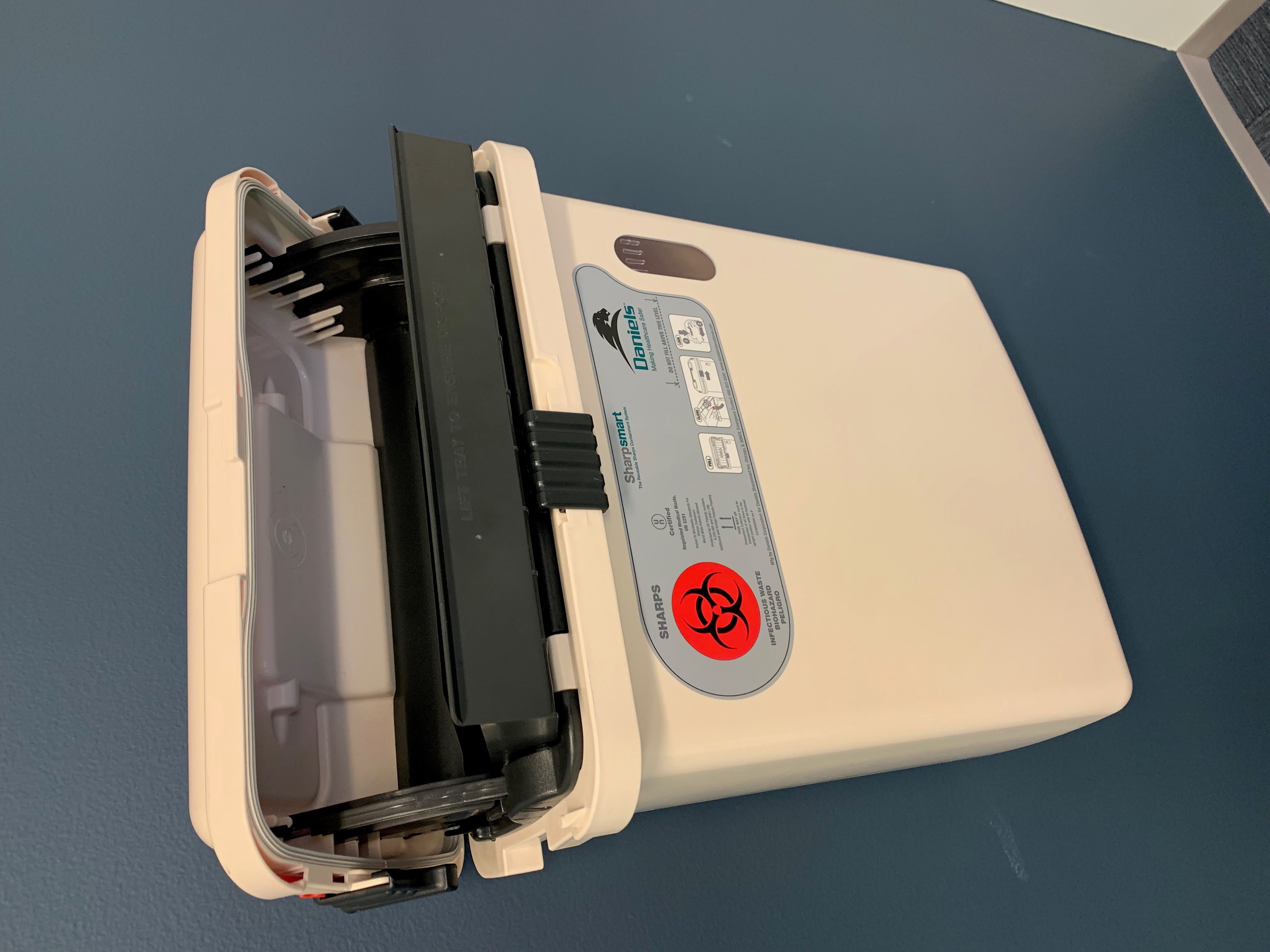
Medical Waste
Biomedical waste or hospital waste is any kind of waste containing infectious (or potentially infectious) materials. It may also include waste associated with the generation of biomedical waste that visually appears to be of medical or laboratory origin (e.g. packaging, unused bandages, infusion kits etc.), as well research laboratory waste containing biomolecules or organisms that are mainly restricted from environmental release. As detailed below, discarded sharps are considered biomedical waste whether they are contaminated or not, due to the possibility of being contaminated with blood and their propensity to cause injury when not properly contained and disposed. Biomedical waste is a type of biowaste. Biomedical waste may be solid or liquid. Examples of infectious waste include discarded blood, sharps, unwanted microbiological cultures and stocks, identifiable body parts (including those as a result of amputation), other human or animal tissue, used bandages and dressings, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Waste
Radioactive waste is a type of hazardous waste that contains radioactive material. Radioactive waste is a result of many activities, including nuclear medicine, nuclear research, nuclear power generation, rare-earth mining, and nuclear weapons reprocessing. The storage and disposal of radioactive waste is regulated by government agencies in order to protect human health and the environment. Radioactive waste is broadly classified into low-level waste (LLW), such as paper, rags, tools, clothing, which contain small amounts of mostly short-lived radioactivity, intermediate-level waste (ILW), which contains higher amounts of radioactivity and requires some shielding, and high-level waste (HLW), which is highly radioactive and hot due to decay heat, so requires cooling and shielding. In nuclear reprocessing plants about 96% of spent nuclear fuel is recycled back into uranium-based and mixed-oxide (MOX) fuels. The residual 4% is minor actinides and fission products the latter of w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Secretary Of The Army
The secretary of the Army (SA or SECARMY) is a senior civilian official within the United States Department of Defense, with statutory responsibility for all matters relating to the United States Army: manpower, personnel, reserve affairs, installations, environmental issues, weapons systems and equipment acquisition, communications and financial management. The secretary of the Army is nominated by the president of the United States and confirmed by the United States Senate. The secretary is a non-Cabinet-level official, subordinate to the secretary of Defense. This position was created on September 18, 1947, replacing the secretary of war, when the Department of War was split into the Department of the Army and Department of the Air Force. On May 28, 2021, Christine Wormuth was sworn in as the 25th (and current) secretary of the Army, the first woman to serve in the role. Roles and responsibilities The Army senior leadership consists of two civilians; the secretary of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the system through photosynthesis and is incorporated into plant tissue. By feeding on plants and on one another, animals play an important role in the movement of matter and energy through the system. They also influence the quantity of plant and microbial biomass present. By breaking down dead organic matter, decomposers release carbon back to the atmosphere and facilitate nutrient cycling by converting nutrients stored in dead biomass back to a form that can be readily used by plants and microbes. Ecosystems are controlled by external and internal factors. External factors such as climate, parent material which forms the soil and topography, control the overall structure of an ecosystem but are not themselves influenced by the ecosystem. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Environment
Marine habitats are habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term ''marine'' comes from the Latin ''mare'', meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species.Abercrombie, M., Hickman, C.J. and Johnson, M.L. 1966.''A Dictionary of Biology.'' Penguin Reference Books, London The marine environment supports many kinds of these habitats. Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf. Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal zones. Pelagic habitats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)