|
Marine Organisms
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life in part shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land (e.g. coral building reefs). Most life forms evolved initially in marine habitats. By volume, oceans provide about 90% of the living space on the planet. The earliest vertebrates appeared in the form of fish, which live exclusively in water. Some of these evolved into amphibians, which spend portions of their lives in water and portions on land. One group of amphibians evolved into reptiles and mammals and a few subsets of each returned to the ocean as sea snakes, sea turtles, seals, manatees, and whales. Plant forms such as kelp and other algae grow in the wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
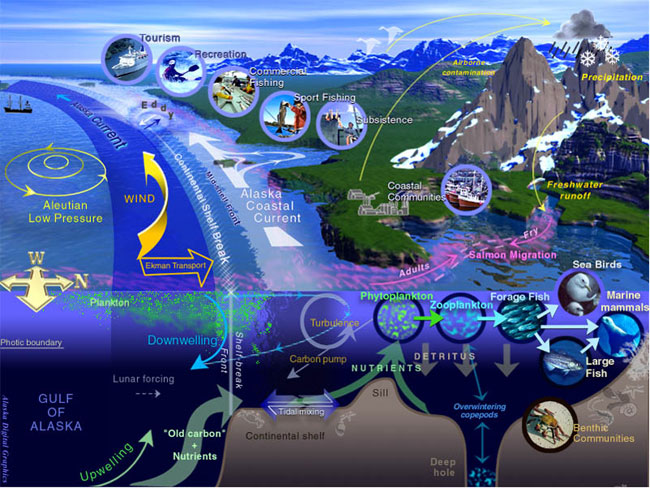
General Characteristics Of A Large Marine Ecosystem
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry. In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The term ''general'' is used in two ways: as the generic title for all grades of general officer and as a specific rank. It originates in the 16th century, as a shortening of ''captain general'', which rank was taken from Middle French ''capitaine général''. The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. Today, the title of ''general'' is known in some countries as a four-star rank. However, different countries use different systems of stars or other insignia for senior ranks. It has a NATO rank sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Live Science
Live Science is a science news website run by Future via Purch, which it purchased from Imaginova in 2009. Stories and editorial commentary are typically syndicated to major news outlets, such as Yahoo!, MSNBC, AOL, and Fox News.{{fact, date=March 2020 Live Science was originally launched in 2004, but was subsequently shut down and re-launched in 2007. Live Science covers scientific breakthroughs, research ventures and odd facts from around the world in an online newsmagazine format. Purch consumer brands (including Live Science) were acquired by Future in 2018.{{Cite web , url=https://www.futureplc.com/brand/live-science/ , title=Live Science , work=Future plc Future plc is an international multimedia company established in the United Kingdom in 1985. The company has over 220 brands that span magazines, newsletters, websites, and events in fields such as video games, technology, films, music, photogr ... , access-date=18 December 2018 References {{reflist External li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siphon (mollusc)
A siphon is an anatomical structure which is part of the body of aquatic molluscs in three classes: Gastropoda, Bivalvia and Cephalopoda (members of these classes include saltwater and freshwater snails, clams, octopus, squid and relatives). Siphons in molluscs are tube-like structures in which water (or, more rarely, air) flows. The water flow is used for one or more purposes such as locomotion, feeding, respiration, and reproduction. The siphon is part of the mantle of the mollusc, and the water flow is directed to (or from) the mantle cavity. A single siphon occurs in some gastropods. In those bivalves which have siphons, the siphons are paired. In cephalopods, there is a single siphon or funnel which is known as a hyponome. In gastropods In some (but not all) sea snails, marine gastropod molluscs, the animal has an anterior extension of the mantle called a siphon, or inhalant siphon, through which water is drawn into the mantle cavity and over the gill for r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Producer
Primary or primaries may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels * Primary (band), from Australia * Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea * Primary Music, Israeli record label Works * ''Primary'' (album) by Rubicon (2002) * "Primary" (song) by The Cure * "Primary", song by Spoon from the album '' Telephono'' Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * Primaries or primary beams, in E. E. Smith's science-fiction series '' Lensman'' * ''Primary'' (film), American political documentary (1960) Computing * PRIMARY, an X Window selection * Primary data storage, computer technology used to retain digital data * Primary server, main server on the server farm Education * Primary education, the first stage of compulsory education * Primary FRCA, academic examination for anaesthetists in the U.K. * Primary school, school providing primary education Mathematics * ''p''-group of prime power order * Primary deco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
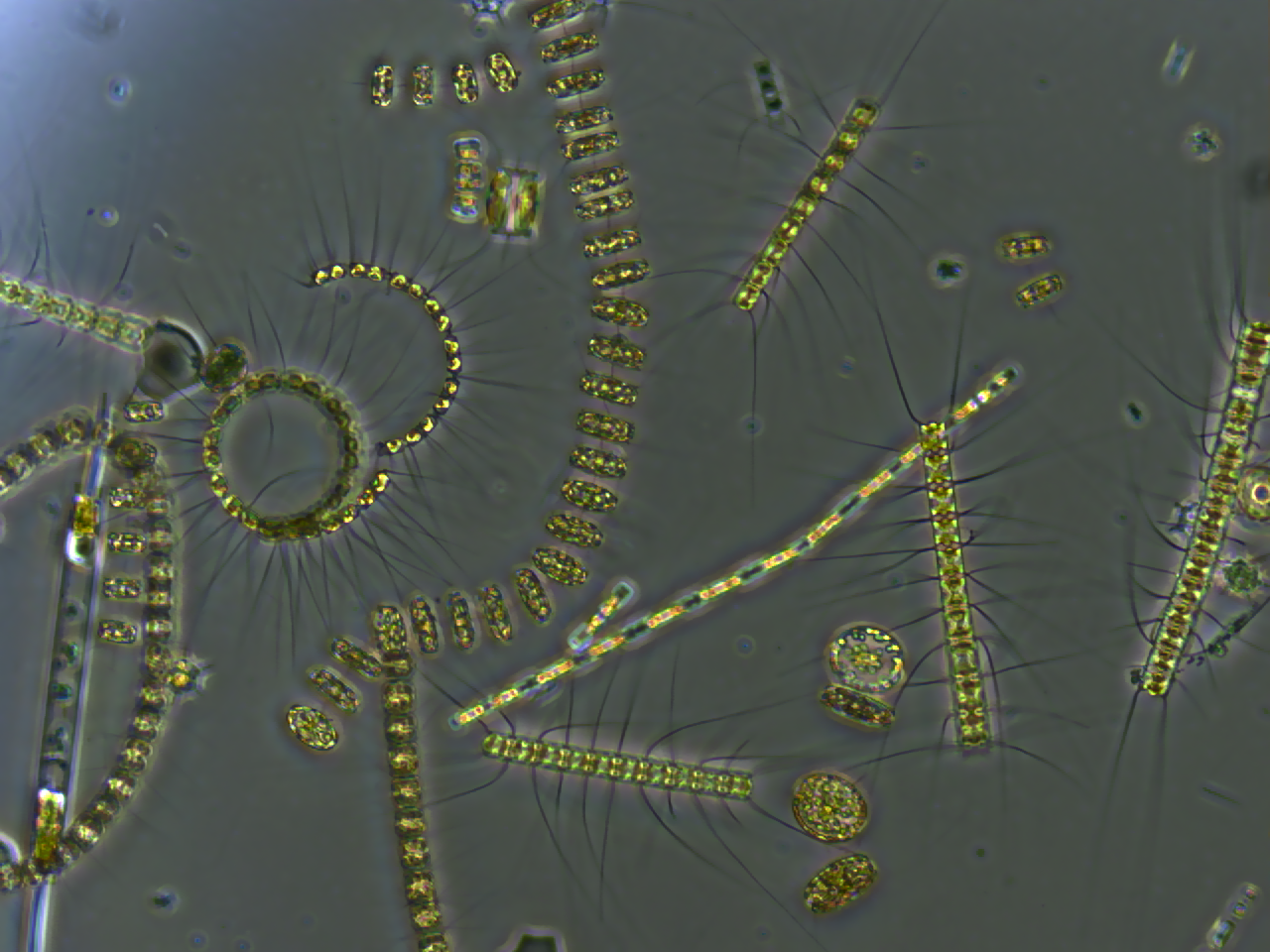
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers ( euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms (such as grass or algae which produce their own food via photosynthesis) and ending at an apex predator species (like grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivores (like earthworms or woodlice), or decomposer species (such as fungi or bacteria). A food chain also shows how organisms are related to each other by the food they eat. Each level of a food chain represents a different trophic level. A food chain differs from a food web because the complex network of different animals' feeding relations are aggregated and the chain only follows a direct, linear pathway of one animal at a time. Natural interconnections between food chains make it a food web. Food chains were first introduced by the Arab scientist and philosopher Al-Jahiz in the 10th century and later popularized in a book published in 1927 by Charles Elton, which also introduced the food web concept. A common metric used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a crucial source of food to many small and large aquatic organisms, such as bivalves, fish and whales. Marine plankton include bacteria, archaea, algae, protozoa and drifting or floating animals that inhabit the saltwater of oceans and the brackish waters of estuaries. Freshwater plankton are similar to marine plankton, but are found in the freshwaters of lakes and rivers. Plankton are usually thought of as inhabiting water, but there are also airborne versions, the aeroplankton, that live part of their lives drifting in the atmosphere. These include plant spores, pollen and wind-scattered seeds, as well as microorganisms swept into the air from terrestrial dust storms and oceanic plankton swept into the air by sea spray. Though m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as '' Chlorella'', '' Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the '' Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, '' Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. Algae that are carried by water are plankton, specifically phytoplankton. Algae constitute a polyphyletic group since they do not include a common ancestor, and although their plastids seem to have a single ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
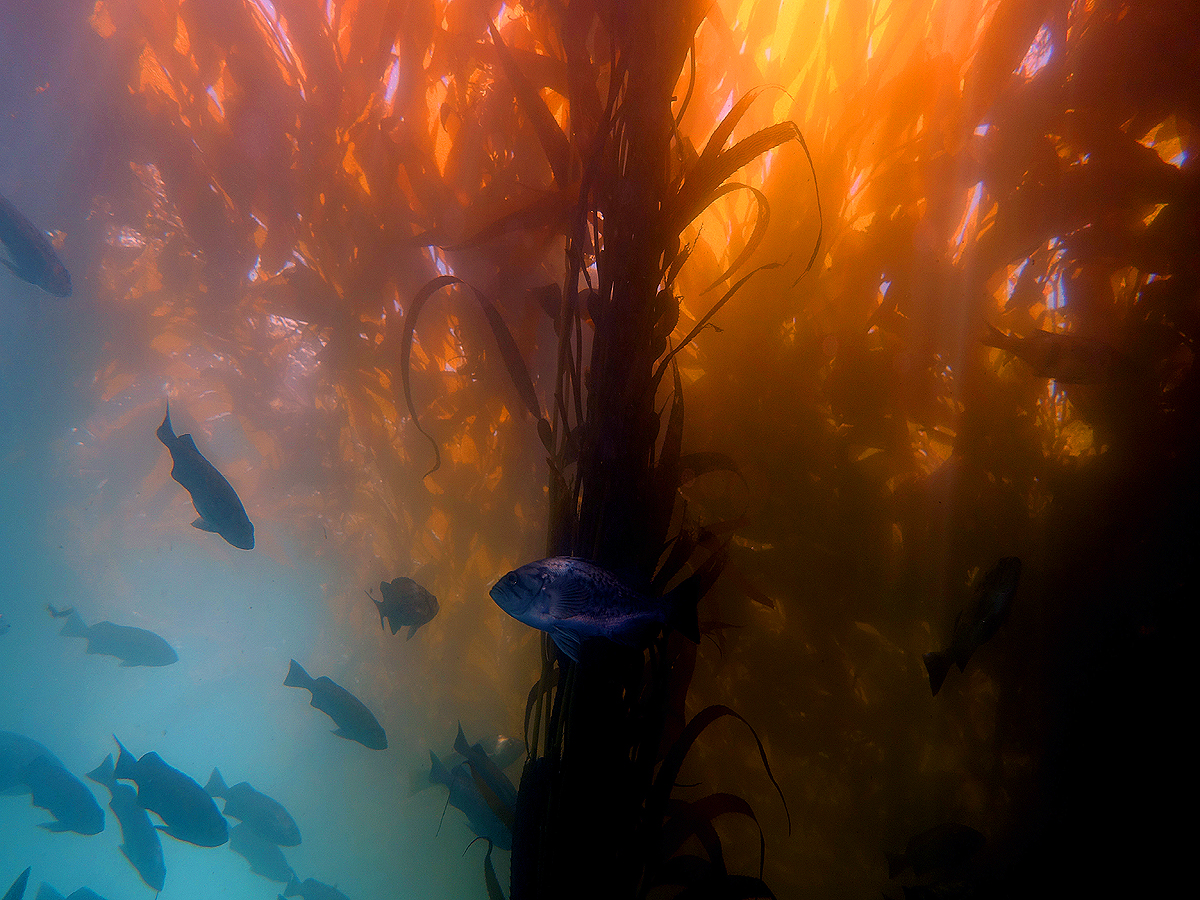
Kelp
Kelps are large brown algae seaweeds that make up the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera. Despite its appearance, kelp is not a plant - it is a heterokont, a completely unrelated group of organisms. Kelp grows in "underwater forests" ( kelp forests) in shallow oceans, and is thought to have appeared in the Miocene, 5 to 23 million years ago. The organisms require nutrient-rich water with temperatures between . They are known for their high growth rate—the genera '' Macrocystis'' and '' Nereocystis'' can grow as fast as half a metre a day, ultimately reaching .Thomas, D. 2002. ''Seaweeds.'' The Natural History Museum, London, p. 15. Through the 19th century, the word "kelp" was closely associated with seaweeds that could be burned to obtain soda ash (primarily sodium carbonate). The seaweeds used included species from both the orders Laminariales and Fucales. The word "kelp" was also used directly to refer to these processed ashes. Description In mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cetacean
Cetacea (; , ) is an infraorder of aquatic mammals that includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises. Key characteristics are their fully aquatic lifestyle, streamlined body shape, often large size and exclusively carnivorous diet. They propel themselves through the water with powerful up-and-down movement of their tail which ends in a paddle-like fluke, using their flipper-shaped forelimbs to maneuver. While the majority of cetaceans live in marine environments, a small number exclusively reside in brackish water or fresh water. Having a cosmopolitan distribution, they can be found in some rivers and all of Earth's oceans, and many species inhabit vast ranges where they migrate with the changing of the seasons. Cetaceans are famous for their high intelligence and complex social behaviour as well as for the enormous size of some of the group's members, such as the blue whale which reaches a maximum confirmed length of 29.9 meters (98 feet) and a weight of 173 tonnes (190 short tons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirenia
The Sirenia (), commonly referred to as sea-cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The Sirenia currently comprise two distinct families: Dugongidae (the dugong and the now extinct Steller's sea cow) and Trichechidae (manatees, namely the Amazonian manatee, West Indian manatee, and West African manatee) with a total of four species. The Protosirenidae (Eocene sirenians) and Prorastomidae (terrestrial sirenians) families are extinct. Sirenians are classified in the clade Paenungulata, alongside the elephants and the hyraxes, and evolved in the Eocene 50 million years ago (mya). The Dugongidae diverged from the Trichechidae in the late Eocene or early Oligocene (30–35 mya). Sirenians grow to between in length and in weight. The historic Steller's sea cow was the largest known sirenian to have lived, and could reach lengths of and weights of . Sirenia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinniped
Pinnipeds (pronounced ), commonly known as seals, are a widely range (biology), distributed and diverse clade of carnivorous, fin-footed, semiaquatic, mostly marine mammal, marine mammals. They comprise the extant taxon, extant family (biology), families Odobenidae (whose only living member is the walrus), Otariidae (the eared seals: sea lions and fur seals), and Phocidae (the earless seals, or true seals). There are 34 extant species of pinnipeds, and more than 50 extinct species have been described from fossils. While seals were historically thought to have descended from two ancestral lines, molecular phylogenetics, molecular evidence supports them as a monophyletic lineage (descended from one ancestral line). Pinnipeds belong to the order Carnivora; their closest living relatives are Musteloidea, musteloids (Mustelidae, weasels, Procyonidae, raccoons, skunks, and red pandas), having diverged about 50 million years ago. Seals range in size from the and Baikal sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |