|
Macrohistorical
Macrohistory seeks out large, long-term trends in world history in search of ultimate patterns by a comparison of proximate details. It favors a comparative or world-historical perspective to determine the roots of changes as well as the developmental paths of society or a historical process. A macrohistorical study might examine Japanese feudalism and European feudalism to decide whether feudal structures are an inevitable outcome because of certain conditions. Macrohistorical studies often "assume that macro-historical processes repeat themselves in explainable and understandable ways." The approach can identify stages in the development of humanity as a whole such as the large-scale direction towards greater rationality, greater liberty or the development of productive forces and communist society, among others. Description Macrohistory is distinguished from microhistory, which involves the rigorous and in-depth study of a single event in history. However, these two can be co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World History (field)
World history or global history as a field of historical study examines history from a global perspective. It emerged centuries ago; leading practitioners have included Voltaire (1694–1778), Hegel (1770–1831), Karl Marx (1818–1883) and Arnold J. Toynbee (1889–1975). The field became much more active (in terms of university teaching, text books, scholarly journals, and academic associations) in the late 20th century. It is not to be confused with comparative history, which, like world history, deals with the history of multiple cultures and nations, but does not do so on a global scale. World history looks for common patterns that emerge across all cultures. World historians use a thematic approach, with two major focal points: integration (how processes of world history have drawn people of the world together) and difference (how patterns of world history reveal the diversity of the human experience). Establishment and perimeters of the field Jerry H. Bentley has observe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Rise Of The West
''The Rise of the West: A History of the Human Community'' is a book by University of Chicago The University of Chicago (UChicago, Chicago, U of C, or UChi) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Its main campus is located in Chicago's Hyde Park neighborhood. The University of Chicago is consistently ranked among the b ... historian William H. McNeill (historian), William H. McNeill, first published in 1963 and enlarged with a retrospective preface in 1991. It explores World history (field), world history in terms of the effect different old world civilizations had on one another, and especially the deep influence of Western culture, Western civilization on the rest of the world in the past 500 years. He argues that societal contact with foreign civilizations is the primary force in driving historical change. In 1964 it won the National Book Award List of winners of the National Book Award#History and Biography, in History and Biography. Description Part I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microhistory
Microhistory is a genre of history that focuses on small units of research, such as an event, community, individual or a settlement. In its ambition, however, microhistory can be distinguished from a simple case study insofar as microhistory aspires to " sklarge questions in small places", according to the definition given by Charles Joyner. It is closely associated with social and cultural history. Origins Microhistory became popular in Italy in the 1970s. According to Giovanni Levi, one of the pioneers of the approach, it began as a reaction to a perceived crisis in existing historiographical approaches. Carlo Ginzburg, another of microhistory's founders, has written that he first heard the term used around 1977, and soon afterwards began to work with Levi and Simona Cerutti on ''Microstorie'', a series of microhistorical works. The word "microhistory" dates back to 1959, when the American historian George R. Stewart published ''Pickett's Charge: A Microhistory of the Final Attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longue Durée
The ''longue durée'' (; en, the long term) is the French Annales School approach to the study of history. It gives priority to long-term historical structures over what François Simiand called ''histoire événementielle'' ("evental history", the short-term time-scale that is the domain of the chronicler and the journalist). It concentrates instead on all-but-permanent or slowly evolving structures, and replaces elite biographies with the broader syntheses of prosopography. The crux of the idea is to examine extended periods of time and draw conclusions from historical trends and patterns. Approach The ''longue durée'' is part of a tripartite system that includes short-term ''événements'' and medium-term conjunctures (periods of decades or centuries when more profound cultural changes such as the industrial revolution can take place). The approach, which incorporates social scientific methods such as the recently evolved field of economic history into general history, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliometrics
Cliometrics (, also ), sometimes called new economic history or econometric history, is the systematic application of economic theory, econometric techniques, and other formal or mathematical methods to the study of history (especially social and economic history). It is a quantitative approach to economic history (as opposed to qualitative or ethnographic). Edward L. Glaeser"Remembering the Father of Transportation Economics" ''The New York Times'' (Economix), October 27, 2009. There has been a revival in 'new economic history' since the late 1990s. History The new economic history originated in 1958 with ''The Economics of Slavery in the Antebellum South'' by American economists Alfred H. Conrad and John R. Meyer. The book would cause a firestorm of controversy with its claim, based on statistical data, that slavery would not have ended in the absence of the U.S. Civil War, as the practice was economically efficient and highly profitable for slaveowners. The term ''cliometrics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cliodynamics
Cliodynamics () is a transdisciplinary area of research that integrates cultural evolution, economic history/cliometrics, macrosociology, the mathematical modeling of historical processes during the ''longue durée'', and the construction and analysis of historical databases. Cliodynamics treats history as science. Its practitioners develop theories that explain such dynamical processes as the rise and fall of empires, population booms and busts, and the spread and disappearance of religions. These theories are translated into mathematical models. Finally, model predictions are tested against data. Thus, building and analyzing massive databases of historical and archaeological information is one of the most important goals of cliodynamics. Etymology The word ''cliodynamics'' is composed of ''clio-'' and ''-dynamics''. In Greek mythology, Clio is the muse of history. Dynamics, most broadly, is the study of how and why phenomena change with time. The term was originally coined by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big History
Big History is an academic discipline which examines history from the Big Bang to the present. Big History resists specialization, and searches for universal patterns or trends. It examines long time frames using a multidisciplinary approach based on combining numerous disciplines from science and the humanities, and explores human existence in the context of this bigger picture. It integrates studies of the cosmos, Earth, life, and humanity using empirical evidence to explore cause-and-effect relations, and is taught at universities and primary and secondary schools often using web-based interactive presentations. Historian David Christian has been credited with coining the term "Big History" while teaching one of the first such courses at Macquarie University. An all-encompassing study of humanity's relationship to cosmology and natural history has been pursued by scholars since the Renaissance, and the new field, Big History, continues such work. Comparison with conven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unified Growth Theory
Unified growth theory was developed in light of the failure of endogenous growth theory to capture key empirical regularities in the growth processes and their contribution to the momentous rise in Economic inequality, inequality across nations in the past two centuries. Unlike earlier growth theories that have focused entirely on the modern growth regime, unified growth theory captures the growth process over the entire course of human existence, highlighting the critical role of the differential timing of the transition from Malthusian trap, Malthusian stagnation to sustained economic growth in the emergence of inequality across countries and regions. Unified growth theory was first advanced by Oded Galor and his co-authors who were able to characterize in a single dynamical system a phase transition from an epoch of Malthusian stagnation to an era of sustained economic growth. Due to the evolution of latent state variables during the Malthusian epoch, the stable Malthusian equili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oded Galor
Oded Galor (born 1953) is an Israeli-American economist who is currently Herbert H. Goldberger Professor of Economics at Brown University. He is the founder of unified growth theory. Galor has contributed to the understanding of process of development over the entire course of human history and prehistory, and the role of deep-rooted factors in the transition from stagnation to growth and in the emergence of the vast inequality across the globe. Moreover, he has pioneered the exploration of the impact of human evolution, population diversity, and inequality on the process of development over most of human existence. Career Galor completed his BA and MA at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and his PhD at Columbia University. He served as a Chilewich Professor of Economics at the Hebrew University, and he is currently the Herbert H. Goldberger Professor of Economics at Brown University. He was awarded Doctor Honoris Causa from Poznań University of Economics & Business and from U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Solow
Robert Merton Solow, GCIH (; born August 23, 1924) is an American economist whose work on the theory of economic growth culminated in the exogenous growth model named after him. He is currently Emeritus Institute Professor of Economics at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, where he has been a professor since 1949. He was awarded the John Bates Clark Medal in 1961, the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1987, and the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2014. Four of his PhD students, George Akerlof, Joseph Stiglitz, Peter Diamond and William Nordhaus later received Nobel Memorial Prizes in Economic Sciences in their own right. Biography Robert Solow was born in Brooklyn, New York, into a Jewish family on August 23, 1924, the oldest of three children. He regarded his parents as being very intelligent despite their not being able to attend college due to the necessity to work. He was well educated in the neighborhood public schools and excelled academically early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
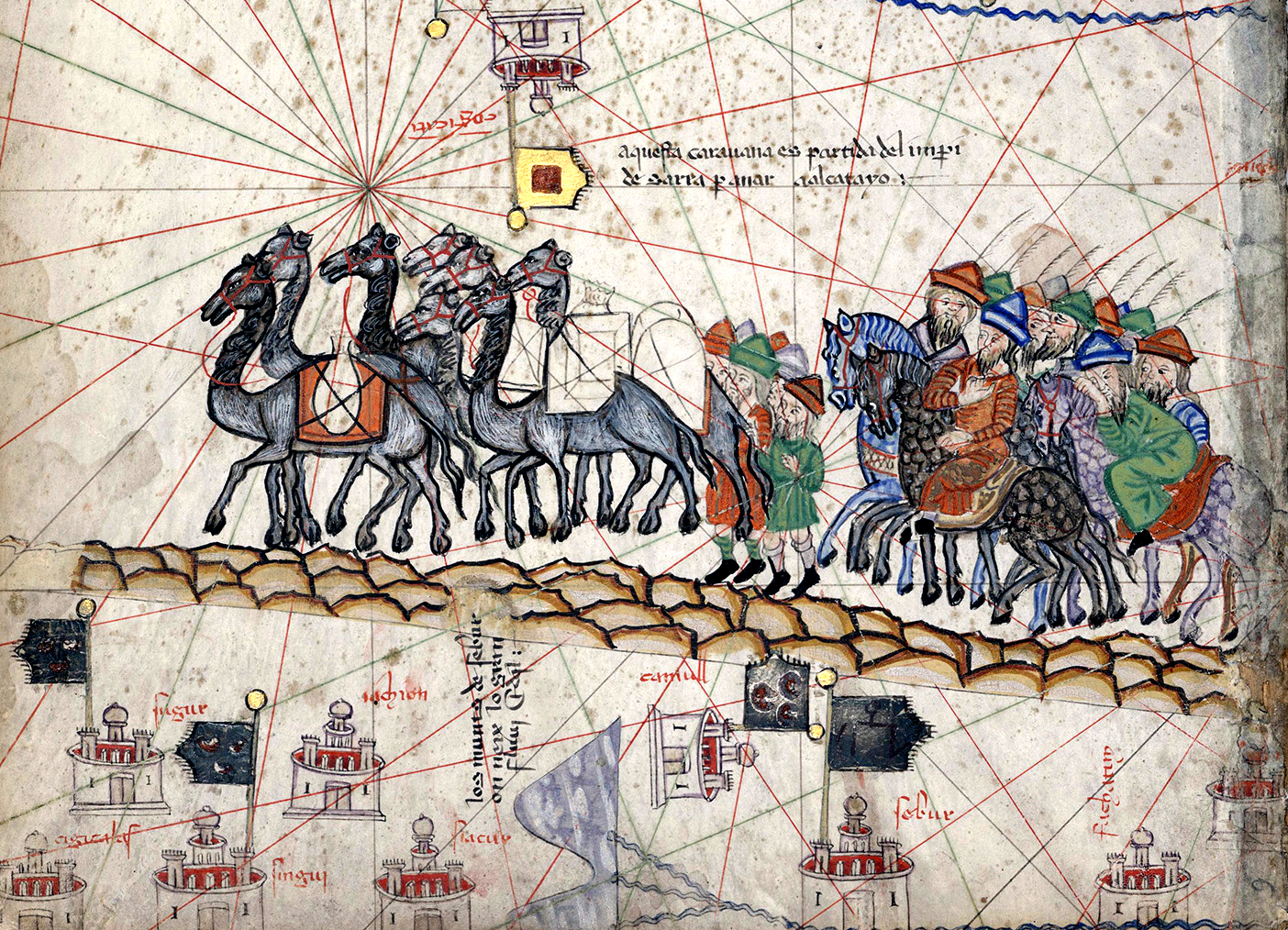
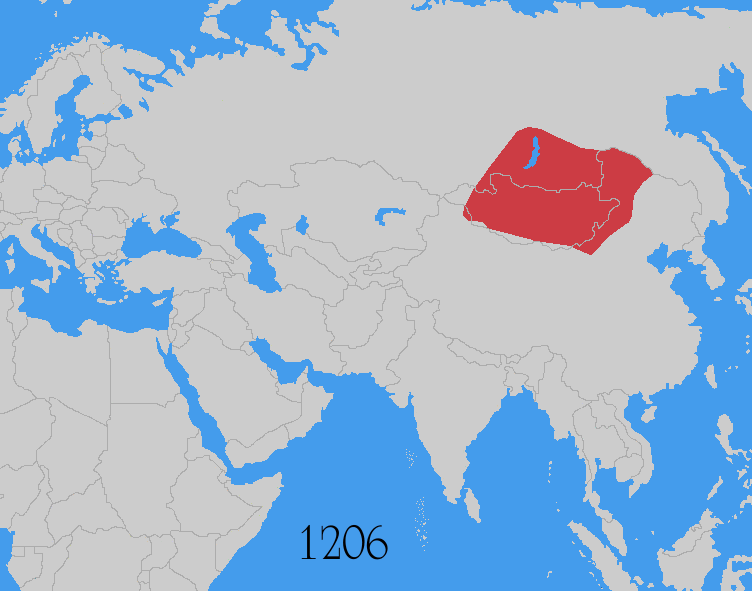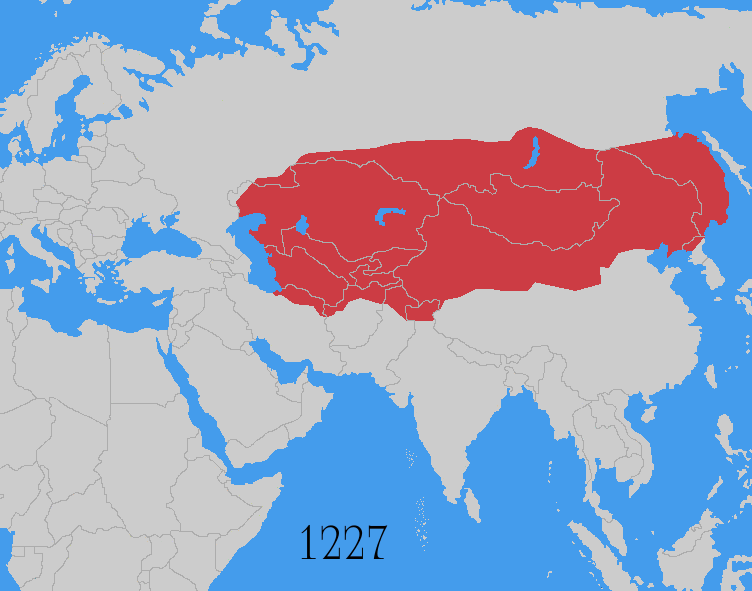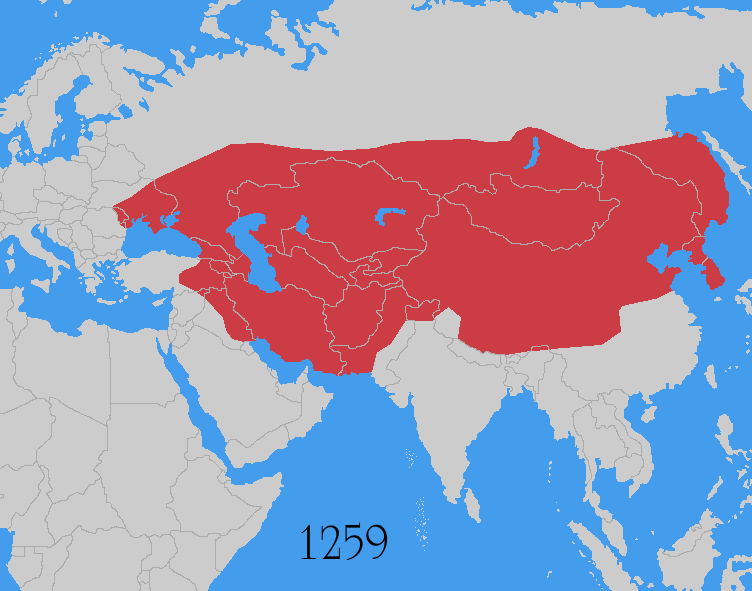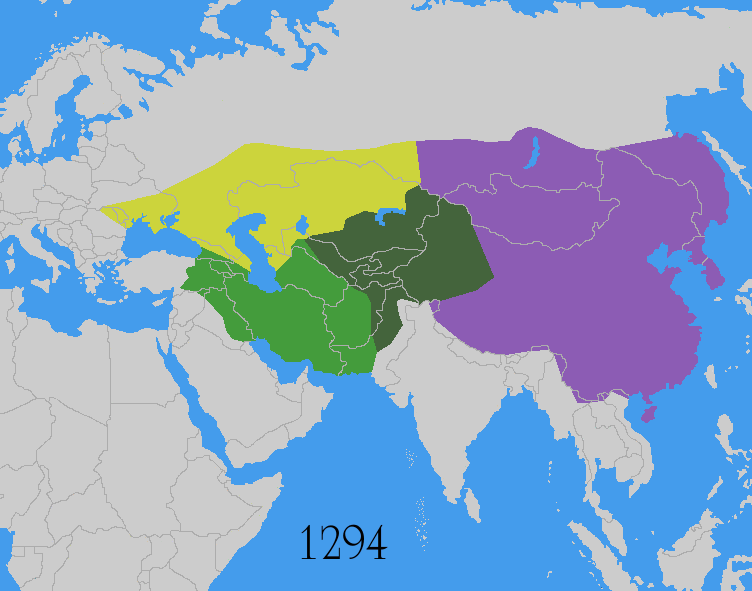
Pax Mongolica
The ''Pax Mongolica'' (Latin for "Mongol Peace"), less often known as ''Pax Tatarica'' ("Tatar Peace"), is a historiographical term modelled after the original phrase ''Pax Romana'' which describes the stabilizing effects of the conquests of the Mongol Empire on the social, cultural and economic life of the inhabitants of the vast Eurasian territory that the Mongols conquered in the 13th and 14th centuries. The term is used to describe the eased communication and commerce the unified administration helped to create and the period of relative peace that followed the Mongols' vast conquests. The conquests of Genghis Khan (r. 1206–1227) and his successors, spanning from Southeast Asia to Eastern Europe, effectively connected the Eastern world with the Western world. The Silk Road, connecting trade centres across Asia and Europe, came under the sole rule of the Mongol Empire. It was commonly said that "a maiden bearing a nugget of gold on her head could wander safely throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Conquests
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history. In addition, Mongol expeditions may have spread the bubonic plague across much of Eurasia, helping to spark the Black Death of the 14th century. The Mongol Empire developed in the course of the 13th century through a series of victorious campaigns throughout Asia, reaching Eastern Europe by the 1240s. In contrast with later "empires of the sea" such as European colonial powers, the Mongol Empire was a land power, fueled by the grass-foraging Mongol cavalry and cattle. Thus most Mongol conquest and plundering took place during the warmer seasons, when there was sufficient grazing for their herds. The rise of the Mongols was preceded by 15 years of wet and warm weather conditions from 1211 t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |