|
Lymphangitis Carcinomatosa
Lymphangitis carcinomatosa is inflammation of the lymph vessels (lymphangitis) caused by a malignancy. Breast, lung, stomach, pancreas, and prostate cancers are the most common tumors that result in lymphangitis. Lymphangitis carcinomatosa was first described by pathologist Gabriel Andral in 1829 in a patient with uterine cancer. Lymphangitis carcinomatosa may show the presence of Kerley B lines on chest X-ray. Lymphangitis carcinomatosa most often affects people 40–49 years of age. Lymphangitis carcinomatosa may be caused by the following malignancies as suggested by the mnemonic: "''C''ertain ''C''ancers ''S''pread ''B''y ''P''lugging ''T''he ''L''ymphatics" (cervical cancer, colon cancer, stomach cancer, breast cancer/bronchiogenic carcinoma, pancreatic cancer, thyroid cancer, laryngeal cancer) Pathology In most cases, lymphangitis carcinomatosis is caused by the dissemination of a tumor with its cells along the lymphatics. However, in about 20 percent of cases, the inflam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is concerned with: * The diagnosis of any cancer in a person (pathology) * Therapy (e.g. surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities) * Follow-up of cancer patients after successful treatment * Palliative care of patients with terminal malignancies * Ethical questions surrounding cancer care * Screening efforts: ** of populations, or ** of the relatives of patients (in types of cancer that are thought to have a hereditary basis, such as breast cancer) Diagnosis Medical histories remain an important screening tool: the character of the complaints and nonspecific symptoms (such as fatigue, weight loss, unexplained anemia, fever of unknown origin, paraneoplastic phenome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomach Cancer
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a cancer that develops from the lining of the stomach. Most cases of stomach cancers are gastric carcinomas, which can be divided into a number of subtypes, including gastric adenocarcinomas. Lymphomas and mesenchymal tumors may also develop in the stomach. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Later signs and symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and blood in the stool, among others. The cancer may spread from the stomach to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, lining of the abdomen, and lymph nodes. The most common cause is infection by the bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'', which accounts for more than 60% of cases. Certain types of ''H. pylori'' have greater risks than others. Smoking, dietary factors such as pickled vegetables and obesity are other risk factors. About 10% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphangitis
Lymphangitis is an inflammation or an infection of the lymphatic channels that occurs as a result of infection at a site distal to the channel. The most common cause of lymphangitis in humans is ''Streptococcus pyogenes'' (Group A strep), hemolytic streptococci, and in some cases, mononucleosis, cytomegalovirus, tuberculosis, syphilis, and the fungus ''Sporothrix schenckii''. Lymphangitis is sometimes mistakenly called "blood poisoning". In reality, "blood poisoning" is synonymous with ''sepsis''. Lymphatic vessels are smaller than capillaries and tiny venules and are ubiquitous in the body. These vessels are fitted with valves to direct flow in only one direction. Fluid diffusing through the thin-walled small capillaries should be collected and the lymphatic system does just that: a fluid rich in protein, minerals, nutrients, and other substances useful for tissue growth. As well as essential nutrients, the lymphatic system can also transport or carry cancer cells, defective or d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilum Of Lung
The root of the lung is a group of structures that emerge at the hilum of each lung, just above the middle of the mediastinal surface and behind the cardiac impression of the lung. It is nearer to the back (posterior border) than the front (anterior border). The root of the lung is connected by the structures that form it to the heart and the trachea. The rib cage is separated from the lung by a two-layered membranous coating, the pleura. The hilum is the large triangular depression where the connection between the parietal pleura (covering the rib cage) and the visceral pleura (covering the lung) is made, and this marks the meeting point between the mediastinum and the pleural cavities. Location The root of the right lung lies behind the superior vena cava and part of the right atrium, and below the azygos vein. That of the left lung passes beneath the aortic arch and in front of the descending aorta; the phrenic nerve, pericardiacophrenic artery and vein, and the anterior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laryngeal Cancer
Laryngeal cancers are mostly squamous-cell carcinomas, reflecting their origin from the epithelium of the larynx. Cancer can develop in any part of the larynx. The prognosis is affected by the location of the tumour. For the purposes of staging, the larynx is divided into three anatomical regions: the glottis (true vocal cords, anterior and posterior commissures); the supraglottis (epiglottis, arytenoids and aryepiglottic folds, and false cords); and the subglottis. Most laryngeal cancers originate in the glottis, with supraglottic and subglottic tumours being less frequent. Laryngeal cancer may spread by: direct extension to adjacent structures, metastasis to regional cervical lymph nodes, or via the blood stream. The most common site of distant metastases is the lung. Laryngeal cancer occurred in 177,000 people in 2018, and resulted in 94,800 deaths (an increase from 76,000 deaths in 1990). Five-year survival rates in the United States are 60.3%. Signs and symptoms The symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
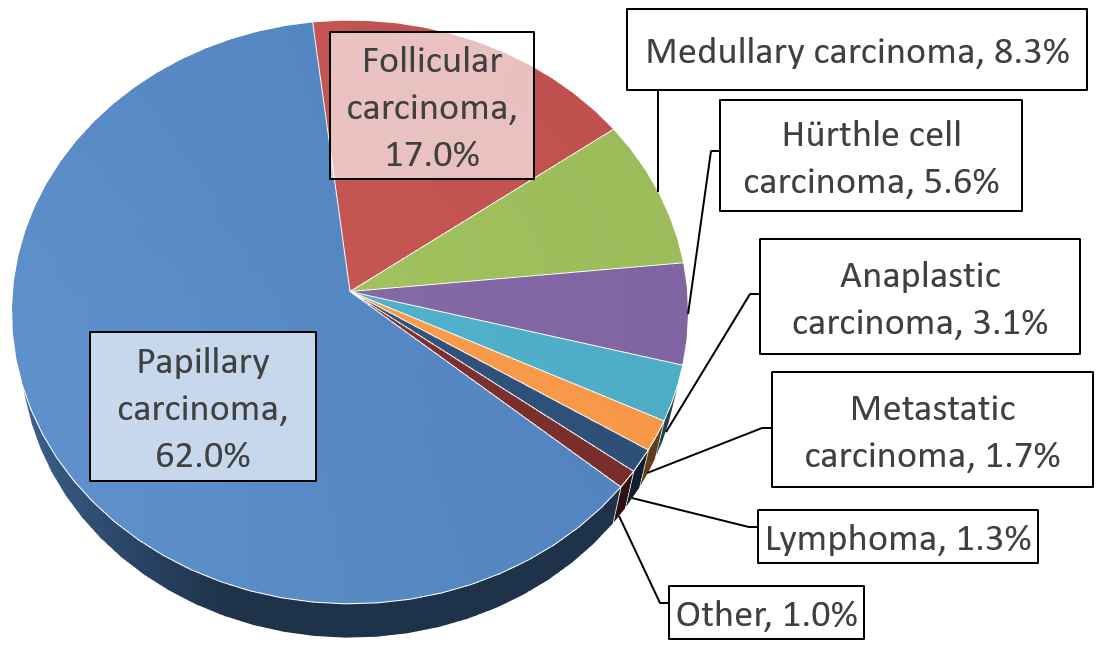
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer is cancer that develops from the tissues of the thyroid gland. It is a disease in which cells grow abnormally and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body. Symptoms can include swelling or a lump in the neck. Cancer can also occur in the thyroid after spread from other locations, in which case it is not classified as thyroid cancer. Risk factors include radiation exposure at a young age, having an enlarged thyroid, and family history. The four main types are papillary thyroid cancer, follicular thyroid cancer, medullary thyroid cancer, and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Diagnosis is often based on ultrasound and fine needle aspiration. Screening people without symptoms and at normal risk for the disease is not recommended as of 2017. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy including radioactive iodine, chemotherapy, thyroid hormone, targeted therapy, and watchful waiting. Surgery may involve removing part or all of the thyroid. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic cancer arises when cell (biology), cells in the pancreas, a glandular organ behind the stomach, begin to multiply out of control and form a Neoplasm, mass. These cancerous cells have the malignant, ability to invade other parts of the body. A number of types of pancreatic cancer are known. The most common, pancreatic adenocarcinoma, accounts for about 90% of cases, and the term "pancreatic cancer" is sometimes used to refer only to that type. These adenocarcinomas start within the part of the pancreas that makes digestive enzymes. Several other types of cancer, which collectively represent the majority of the non-adenocarcinomas, can also arise from these cells. About 1–2% of cases of pancreatic cancer are neuroendocrine tumors, which arise from the hormone-producing neuroendocrine cell, cells of the pancreas. These are generally less aggressive than pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Signs and symptoms of the most-common form of pancreatic cancer may include jaundice, ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a lack of physical exercise, alcoholism, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at first menstruation, having children late in life or not at all, older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About 5–10% of cases are the result of a genetic predisposition inherited from a person's parents, including BRCA1 and BRCA2 among others. Breast cancer most commonly develops in cells from the lining of milk ducts and the lobules that supply these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colon Cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC), also known as bowel cancer, colon cancer, or rectal cancer, is the development of cancer from the colon or rectum (parts of the large intestine). Signs and symptoms may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, and fatigue. Most colorectal cancers are due to old age and lifestyle factors, with only a small number of cases due to underlying genetic disorders. Risk factors include diet, obesity, smoking, and lack of physical activity. Dietary factors that increase the risk include red meat, processed meat, and alcohol. Another risk factor is inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis. Some of the inherited genetic disorders that can cause colorectal cancer include familial adenomatous polyposis and hereditary non-polyposis colon cancer; however, these represent less than 5% of cases. It typically starts as a benign tumor, often in the form of a polyp, which over time becomes cancerous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymph Vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavian ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse. While bleeding after sex may not be serious, it may also indicate the presence of cervical cancer. Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) causes more than 90% of cases; most women who have had HPV infections, however, do not develop cervical cancer. HPV 16 and 18 strains are responsible for nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers. Other risk factors include smoking, a weak immune system, birth control pills, starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners, but these are less important. Genetic factors also contribute to cervical cancer risk. Cervical cancer typically develops from precancerous changes over 10 to 20 years. About 90% of cervical cancer cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest Radiograph
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine. Like all methods of radiography, chest radiography employs ionizing radiation in the form of X-rays to generate images of the chest. The mean radiation dose to an adult from a chest radiograph is around 0.02 mSv (2 mrem) for a front view (PA, or posteroanterior) and 0.08 mSv (8 mrem) for a side view (LL, or latero-lateral). Together, this corresponds to a background radiation equivalent time of about 10 days. Medical uses Conditions commonly identified by chest radiography * Pneumonia * Pneumothorax * Interstitial lung disease * Heart failure * Bone fracture * Hiatal hernia Chest radiographs are used to diagnose many conditions involving the chest wall, including its bones, and also structures contained within the thoracic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |