|
Lutes
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted. More specifically, the term "lute" can refer to an instrument from the family of European lutes. The term also refers generally to any string instrument having the strings running in a plane parallel to the sound table (in the Hornbostel–Sachs system). The strings are attached to pegs or posts at the end of the neck, which have some type of turning mechanism to enable the player to tighten the tension on the string or loosen the tension before playing (which respectively raise or lower the pitch of a string), so that each string is tuned to a specific pitch (or note). The lute is plucked or strummed with one hand while the other hand "frets" (presses down) the strings on the neck's fingerboard. By pressing the strings on different places of the fingerboard, the player can short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Instrument
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the Baro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordophone
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the Baroque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
String Instrument
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the Baro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angélique (instrument)
The ''angélique'' (French, from Italian ''angelica'') is a plucked string instrument of the lute family of the baroque era. It combines features of the lute, the harp, and the theorbo. It shares the form of its pear-shaped body as well as its vibrating string length of 54 to 70 cm with the lute. Differing from the lute, the 16 string angelica was single-strung like a theorbo, with which it shares its extended neck with a second peg box, bearing six bass strings. Overview The angelica was tuned diatonically, like a harp: C – E – F – G – A – B – c – d – e – f – g – a – b – c’ – d’ – e’. That range is the same as that of the French or lesser theorbo, but the latter differs in that its tuning is reentrant: C – D – E – F – G – A – B – c – d – g – c' – e'– a – d'. The diatonic tuning limited its compass, but produced a full and clear tone by the increased use of open strings. Little surviving music for the ange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archlute
The archlute ( es, archilaúd, it, arciliuto, german: Erzlaute) is a European plucked string instrument developed around 1600 as a compromise between the very large theorbo, the size and re-entrant tuning of which made for difficulties in the performance of solo music, and the Renaissance tenor lute, which lacked the bass range of the theorbo. Essentially a tenor lute with the theorbo's neck-extension, the archlute lacks the power in the tenor and the bass that the theorbo's large body and typically greater string length provide. Overview The main differences between the archlute and the "baroque" lute of northern Europe are that the baroque lute has 11 to 13 courses, while the archlute typically has 14, and the tuning of the first six courses of the baroque lute outlines a d-minor chord, while the archlute preserves the tuning of the Renaissance lute, with perfect fourths surrounding a third in the middle for the first six. The archlute was often used as a solo instrument ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandolute
The Weymann Mandolute was one of the products sold under Weymann, the Philadelphia-based brand of Weymann and Sons, established 1864. The 'mandolutes' were actually mandolins with eight strings and tuned exactly the same. The scale length is also within the standard mandolin scale; between 13 inches (330 mm) and 13-7/8 inches (352 mm). They advertised using scientific principles to create vibrations, power and volume as well as sustained sweet and mellow tones, all in the same instrument. History Weymann and Son was a Philadelphia company, manufacturers of Weymann and Keystone State musical instruments. They manufactured the mandolute during the early 20th century. They also had a retail store on 1010 Chestnut Street. They advertised in the Philadelphia papers, with advertisements pushing culture. Young men and women, sitting around in a formal parlor setting, playing music together on Weymann Mandolins, dancing together around a Victrola record player. The Mandolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hopkinson Smith
Hopkinson Smith (born December 7, 1946) is an American lutenist and pedagogue, longtime resident in Basel, Switzerland. Smith was born in New York City, the son of architectural writer and photographer G. E. Kidder Smith. He graduated from Harvard University with Honors in Music (Thesis on ''"The Pavans of Daniel Bacheler"''). He moved to Europe in 1973 to study lute and vihuela with the renowned Catalan classical guitarist Emilio Pujol, as well as Eugen Mueller-Dombois. In the mid-1970s, Hopkinson Smith was involved in the founding of the ensemble Hespèrion XX, which led to his ten-year collaboration with Jordi Savall. Since the mid-1980s, Hopkinson Smith has focused principally on solo music for early plucked instruments. These include the vihuela, Renaissance lute, theorbo, Renaissance and Baroque guitars and the baroque lute. His 2000 recording of the J.S. Bach sonatas and partitas for solo violin adapted for baroque lute has been called 'arguably the best you can buy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Georg Hamann
Johann Georg Hamann (; ; 27 August 1730 – 21 June 1788) was a German Lutheran philosopher from Königsberg known as "the Wizard of the North" who was one of the leader figures of post-Kantian philosophy. His work was used by his student J. G. Herder as the main support of the ''Sturm und Drang'' movement, and is associated with the Counter-Enlightenment and Romanticism. He introduced Kant, also from Königsberg, to the works of both Hume – waking him from his "dogmatic slumber" – and Rousseau. Hamann was influenced by Hume, but he used his views to argue for rather than against Christianity. Goethe and Kierkegaard were among those who considered him to be the finest mind of his time. He was also a key influence on Hegel and Jacobi. Long before the linguistic turn, Hamann believed epistemology should be replaced by the philosophy of language. Early life Hamann was born on 27 August 1730 in Königsberg (now Kaliningrad, Russia). Initially he studied theology at the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutz Kirchhof
Lutz Kirchhof (born 1953, Frankfurt am Main) is a German lutenist. He often performs with his wife Marina as the Kirchhof duo. In 1996 he founded the Deutsche Lautengesellschaft (German Association for Lute). He performs in festivals all over the world, giving about a hundred concerts a year since 2002. He performs regularly with vocalists such as Max van Egmond and Derek Lee Ragin Derek Lee Ragin (born June 17, 1958) is an American countertenor. _Biography.html" ;"title="Derek Lee Ragin > Biography">Derek Lee Ragin > Biographyallmusic Early life Derek Ragin was born in West Point, New York and grew up in Newark, New Jerse ..., and numerous instrumentalists. Numerous recordings have appeared and he has recorded for Sony Classical, but now publishes his recordings independently. References External links Homepage (Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christopher Wilke
Christopher Wilke (born 1973) is an American composer, lutenist, guitarist, recording artist, and teacher. Biography Born in Cincinnati, Wilke studied guitar and composition at the College of Mount St. Joseph, and took his master's degree in guitar from the University of Cincinnati's College Conservatory. He completed his doctorate in Early Music Performance with an Emphasis on Historical Plucked Strings (lute, theorbo and guitar) at the Eastman School of Music, under the tutelage of Paul O'Dette. Composer Several of his compositions, including "Emperor Romulus Augustus, His Serious Funk" and "Diatribe," have been published by Les Productions d'Oz in Montreal, Canada. Performer Wilke has given solo recitals in Italy and Germany as well as the United States. He has taught at the Guitar Foundation of America's Convention and the American Musicological Society's Annual Meeting. His recordings have been featured on Concertzender radio in the Netherlands, on Canadian Television, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levin (guitar Company)
Levin was a Swedish manufacturer of musical instruments founded by Herman Carlson Levin. Active from 1900 to 1978, the company produced over half a million instruments, mostly guitars, but also mandolins, banjos and lutes, making Levin the largest instrument manufacturer in Scandinavia for many years. Levin is best known for originating Goya acoustic guitars. History Founding Herman Carlson Levin was born and raised in Åsaka, Sweden. At age 18, he attended carpentry school and later served an apprenticeship at a furniture maker in Gothenburg. In August 1887, Levin moved to America, working briefly as a carpenter before getting a job in 1888 at a guitar factory. Three years later, Levin and two partners started small-scale production of instruments in New York City. While on a visit to Sweden 1895, Levin recognized that demand for instruments was high and that manufacturing of instruments in Sweden could be profitable. So with 4,000 kronas to invest, Levin opened Herman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jozef Van Wissem
Jozef van Wissem (born 22 November 1962) is a Dutch minimalist composer and lute player based in Brooklyn. In 2013 Van Wissem won the Cannes Soundtrack Award for the score of ''Only Lovers Left Alive'' at the Cannes Film Festival. Career Jozef van Wissem was born in Maastricht. An incessantly touring musician, Van Wissem studied lute in New York with Patrick O'Brien in 1990s. Jozef van Wissem's solo albums, ''It Is All That Is Made'' (2009) and ''Ex Patris'' (2010), were released on Important Records. He released ''The Joy That Never Ends'', an album with Jim Jarmusch on the label in 2011. He wrote a score for the video game ''The Sims Medieval''. Van Wissem has earned much critical acclaim for his work, the ‘liberation of the lute’ as he calls it. According to Steve Dollar for the Washington Post,For him the lute is utterly contemporary. “I want to update it and also make it sexy again. It’s not interesting to a lot of people because it comes with all this baggage, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


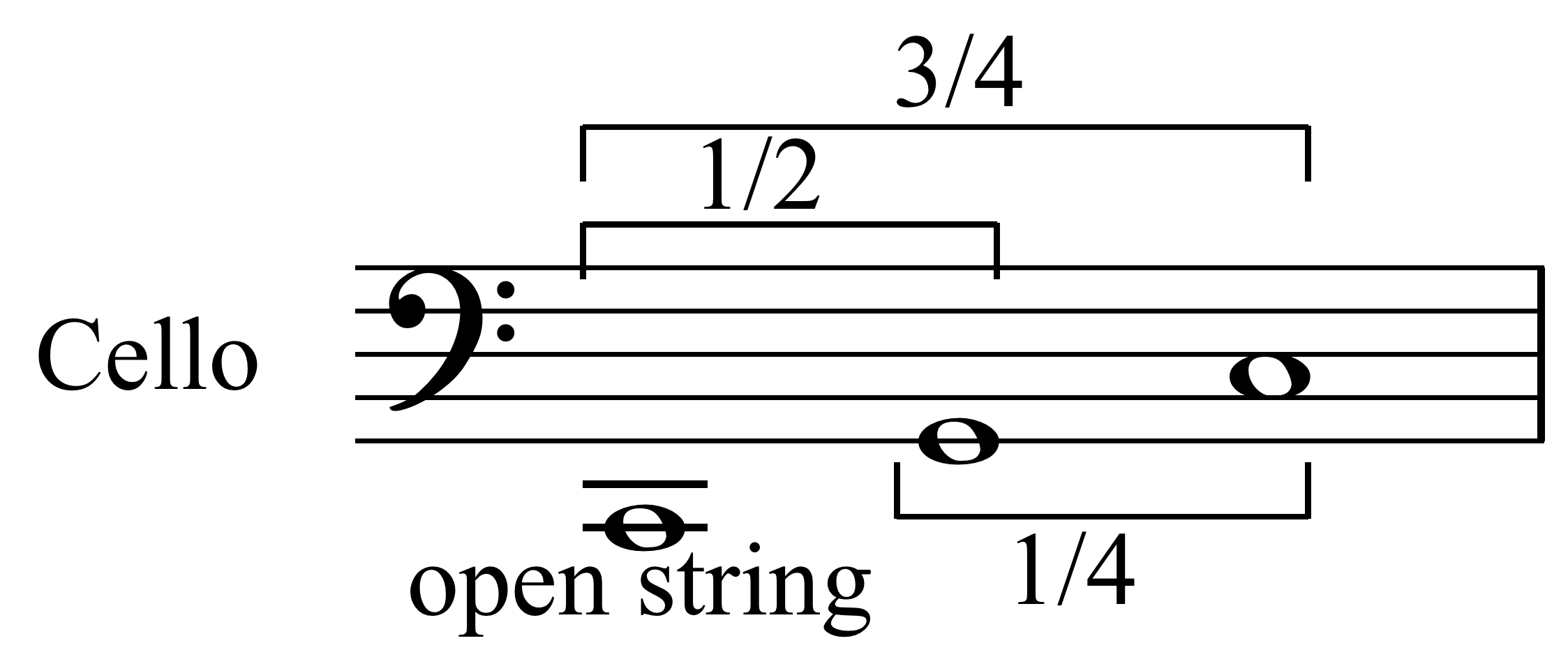


.jpg)