|
Livers
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a wide variety of high-volume biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of small and complex molecules, many of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
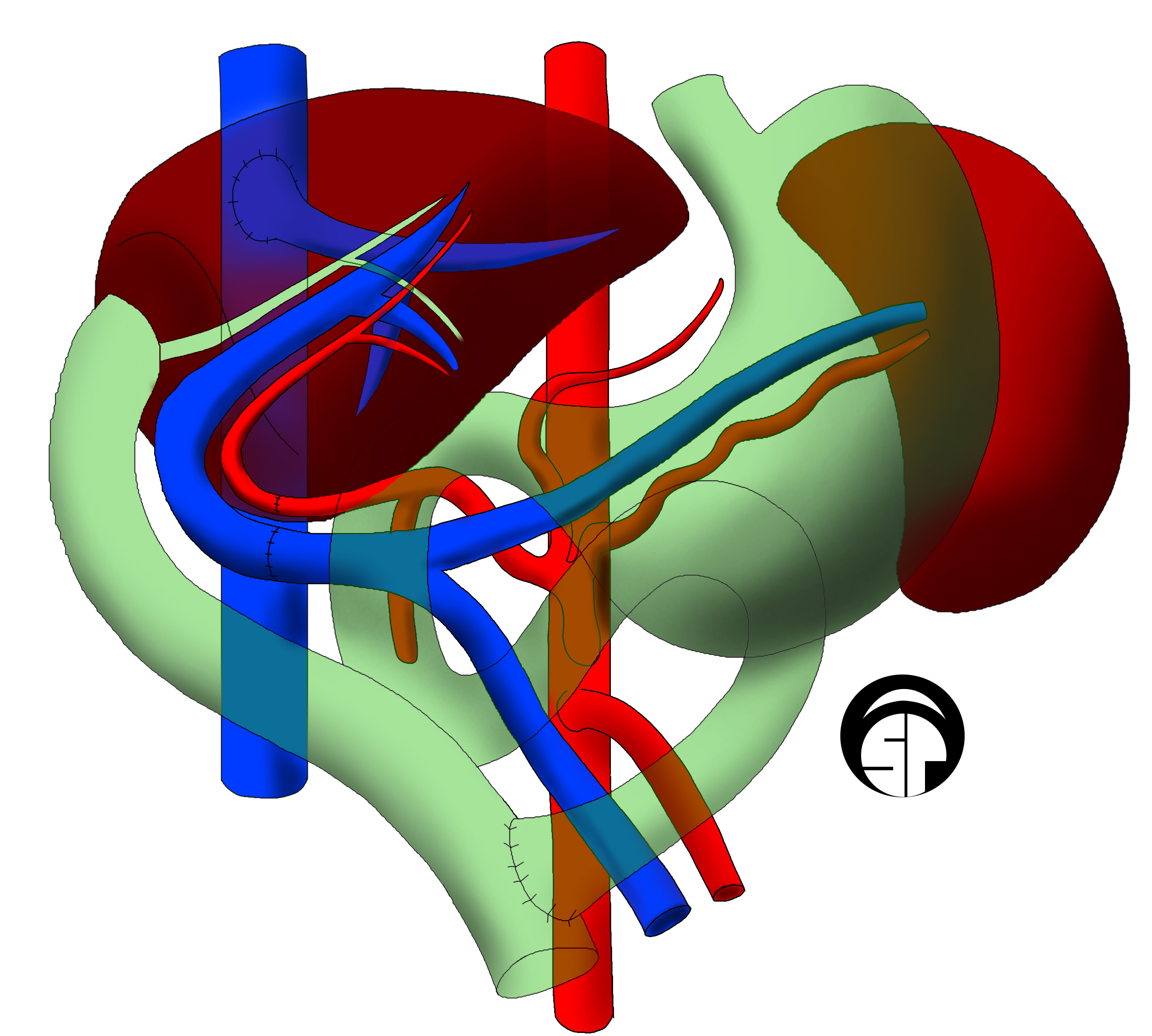
Liver Transplantation
Liver transplantation or hepatic transplantation is the replacement of a diseased liver with the healthy liver from another person (allograft). Liver transplantation is a treatment option for end-stage liver disease and acute liver failure, although availability of donor organs is a major limitation. The most common technique is orthotopic transplantation, in which the native liver is removed and replaced by the donor organ in the same anatomic position as the original liver. The surgical procedure is complex, requiring careful harvest of the donor organ and meticulous implantation into the recipient. Liver transplantation is highly regulated, and only performed at designated transplant medical centers by highly trained transplant physicians and supporting medical team. The duration of the surgery ranges from 4 to 18 hours depending on outcome. Favorable outcomes require careful screening for eligible recipient, as well as a well-calibrated live or cadaveric donor match. Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical functions as enzymes, structural proteins or hormones. Protein synthesis is a very similar process for both prokaryotes and eukaryotes but there are some distinct differences. Protein synthesis can be divided broadly into two phases - transcription and translation. During transcription, a section of DNA encoding a protein, known as a gene, is converted into a template molecule called messenger RNA (mRNA). This conversion is carried out by enzymes, known as RNA polymerases, in the nucleus of the cell. In eukaryotes, this mRNA is initially produced in a premature form (pre-mRNA) which undergoes post-transcriptional modifications to produce mature mRNA. The mature mRNA is exported from the cell nucleus via nuclear pores to the cytoplasm of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
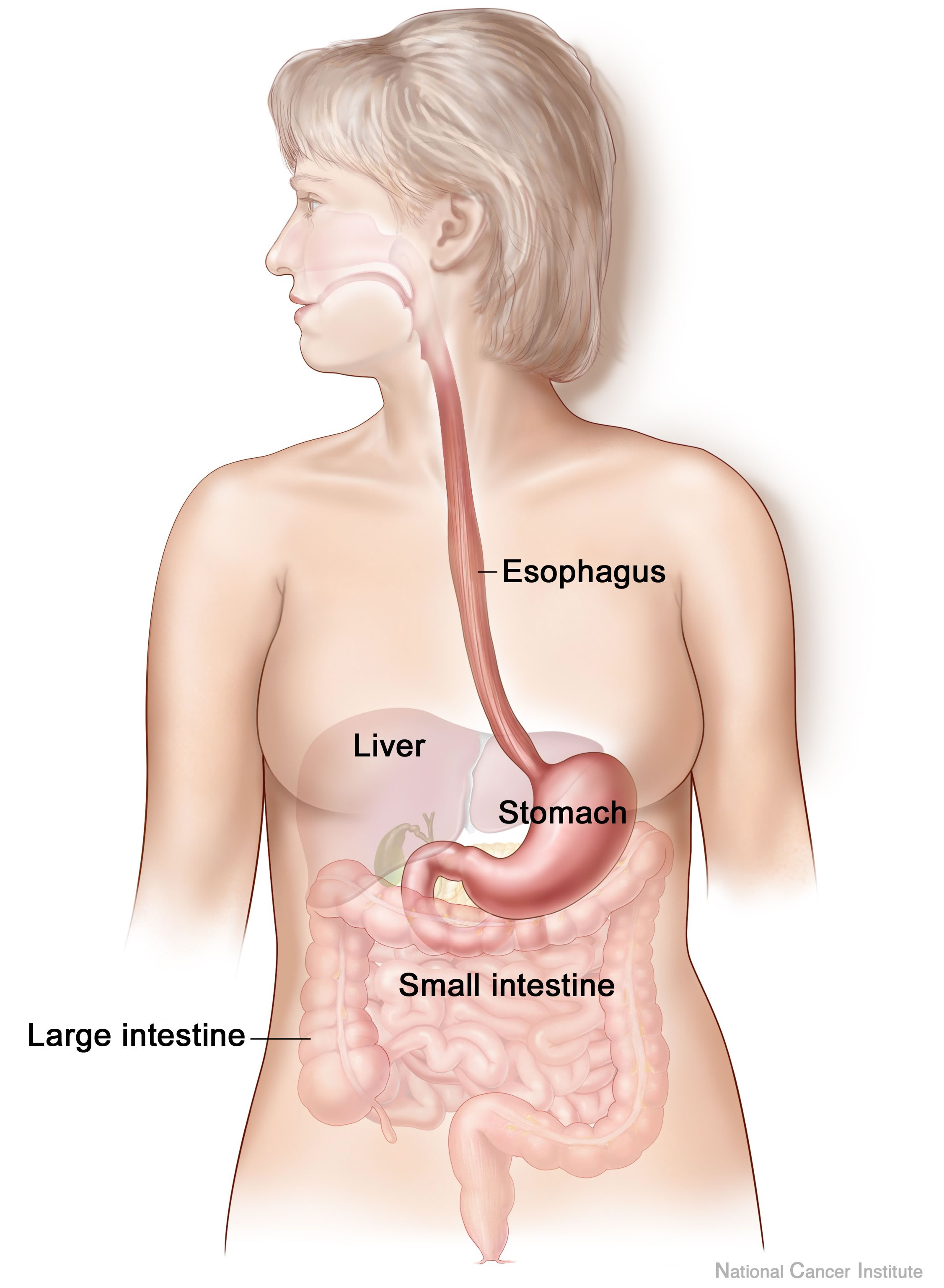
Human Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter the st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Portal Vein
The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approximately 75% of total liver blood flow is through the portal vein, with the remainder coming from the hepatic artery proper. The blood leaves the liver to the heart in the hepatic veins. The portal vein is not a true vein, because it conducts blood to capillary beds in the liver and not directly to the heart. It is a major component of the hepatic portal system, one of only two portal venous systems in the body – with the hypophyseal portal system being the other. The portal vein is usually formed by the confluence of the superior mesenteric, splenic veins, inferior mesenteric, left, right gastric veins and the pancreatic vein. Conditions involving the portal vein cause considerable illness and death. An important example of such a condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accessory Digestive Organ
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to enter the sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. The area occupied by the abdomen is called the abdominal cavity. In arthropods it is the posterior (anatomy), posterior tagma (biology), tagma of the body; it follows the thorax or cephalothorax. In humans, the abdomen stretches from the thorax at the thoracic diaphragm to the pelvis at the pelvic brim. The pelvic brim stretches from the lumbosacral joint (the intervertebral disc between Lumbar vertebrae, L5 and Vertebra#Sacrum, S1) to the pubic symphysis and is the edge of the pelvic inlet. The space above this inlet and under the thoracic diaphragm is termed the abdominal cavity. The boundary of the abdominal cavity is the abdominal wall in the front and the peritoneal surface at the rear. In vertebrates, the abdomen is a large body c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a base (chemistry), basic, ionic compound, ionic salt (chemistry), salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English language, English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the acid-base reaction theories#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word "alkali" is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning ''the calcined ashes'' (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membranes. When chemically isolated, it is a yellowish crystalline solid. Cholesterol also serves as a precursor for the biosynthesis of steroid hormones, bile acid and vitamin D. Cholesterol is the principal sterol synthesized by all animals. In vertebrates, hepatic cells typically produce the greatest amounts. It is absent among prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), although there are some exceptions, such as '' Mycoplasma'', which require cholesterol for growth. François Poulletier de la Salle first identified cholesterol in solid form in gallstones in 1769. However, it was not until 1815 that chemist Michel Eugène Chevreul named the compound "cholesterine". Etymology The word "cholesterol" comes from the Ancient Greek ''chole-'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bile Acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine residues to give anions called bile salts. Primary bile acids are those synthesized by the liver. Secondary bile acids result from bacterial actions in the colon (anatomy), colon. In humans, taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid (derivatives of cholic acid) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (derivatives of chenodeoxycholic acid) are the major bile salts. They are roughly equal in concentration. The salts of their 7-alpha-dehydroxylated derivatives, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, are also found, with derivatives of cholic, chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids accounting for over 90% of human biliary bile acids. Bile acids comprise about 80% of the organic compounds in bile (others are phospholipids and cholesterol). An increased secretion of bile acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
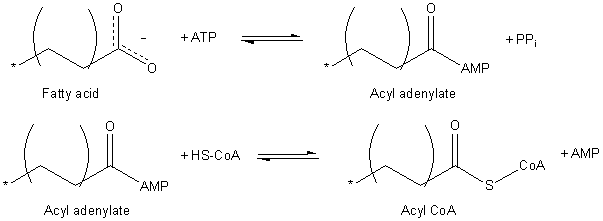
Fatty Acid Degradation
Fatty acid degradation is the process in which fatty acids are broken down into their metabolites, in the end generating acetyl-CoA, the entry molecule for the citric acid cycle, the main energy supply of living organisms, including bacteria and animals. It includes three major steps: * Lipolysis of and release from adipose tissue * Activation and transport into mitochondria * β-oxidation Lipolysis and release Initially in the process of degradation, fatty acids are stored in adipocytes. The breakdown of this fat is known as lipolysis. The products of lipolysis, free fatty acids, are released into the bloodstream and circulate throughout the body. During the breakdown of triacylglycerols into fatty acids, more than 75% of the fatty acids are converted back into triacylglycerol, a natural mechanism to conserve energy, even in cases of starvation and exercise. Activation and transport into mitochondria Fatty acids must be activated before they can be carried into the mitochondria, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatocyte
A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass. These cells are involved in: * Protein synthesis * Protein storage * Transformation of carbohydrates * Synthesis of cholesterol, bile salts and phospholipids * Detoxification, modification, and excretion of exogenous and endogenous substances * Initiation of formation and secretion of bile Structure The typical hepatocyte is cubical with sides of 20-30 μm, (in comparison, a human hair has a diameter of 17 to 180 μm).The diameter of human hair ranges from 17 to 181 μm. The typical volume of a hepatocyte is 3.4 x 10−9 cm3. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum is abundant in hepatocytes, in contrast to most other cell types. Microanatomy Hepatocytes display an eosinophilic cytoplasm, reflecting numerous mitochondria, and basophilic stippling due to large amounts of smooth endoplasmic reticulum and free ribosomes. Brown lipofuscin granules are also observed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |