|
List Of Extinct Animals Of The British Isles
This is a list of extinct animals of the British Isles, including extirpated species. Only a small number of the listed species are globally extinct (most famously the Irish elk, great auk and woolly mammoth). Most of the remainder survive to some extent outside the islands. The list includes introduced species only in cases where they were able to form self-sustaining colonies for a time. Only Pleistocene species, and specifically those extinct since the Ipswichian interglacial (c.130,000 - c.115,000 before present (BP)), Devensian glaciation (c.115,000 – c. 11,700 BP) or into the Holocene (c.11,700 BP - present), are included (that is, the assemblage that can be approximately considered the 'modern' fauna which displays insular differences from the mainland European fauna). The date beside each species is the last date when a specimen was observed in the wild or, where this is not known, the approximate date of extinction. Overview For most of its history, the British I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, and over six thousand smaller islands."British Isles", ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. They have a total area of and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland (which covers roughly five-sixths of Ireland), and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are normally taken to be part of the British Isles, even though they do not form part of the archipelago. The oldest rocks are 2.7 billion years old and are found in Ireland, Wales and the northwest of Scotland. During the Silurian period, the north-western regions collided with the south-east, which had been part of a separate continental landmass. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
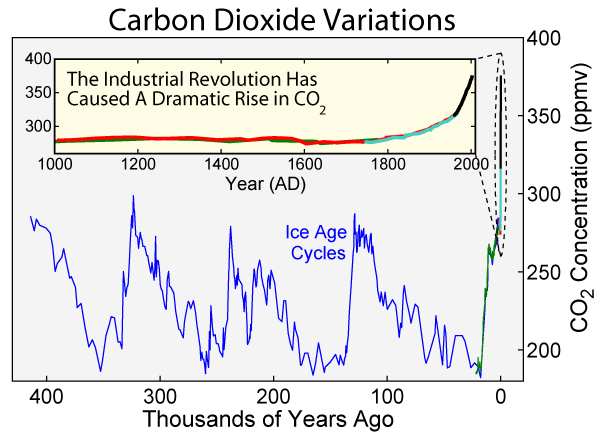
Ipswichian Interglacial
The Eemian (also called the last interglacial, Sangamonian Stage, Ipswichian, Mikulin, Kaydaky, penultimate,NOAA - Penultimate Interglacial Period http://www.ncdc.noaa.gov/global-warming/penultimate-interglacial-period Valdivia or Riss-Würm) was the interglacial period which began about 130,000 years ago at the end of the Penultimate Glacial Period and ended about 115,000 years ago at the beginning of the Last Glacial Period. It corresponds to Marine Isotope Stage 5e. Although sometimes referred to as the "last interglacial" (in the "most recent previous" sense of "last"), it was the second-to-latest interglacial period of the current Ice Age, the most recent being the Holocene which extends to the present day (having followed the last glacial period). The prevailing Eemian climate was, on average, around 1 to 2 degrees Celsius (1.8 to 3.6 Fahrenheit) warmer than that of the Holocene. During the Eemian, the proportion of in the atmosphere was about 280 parts per million. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primates
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including humans). Primates arose 85–55 million years ago first from small terrestrial mammals, which adapted to living in the trees of tropical forests: many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging environment, including large brains, visual acuity, color vision, a shoulder girdle allowing a large degree of movement in the shoulder joint, and dextrous hands. Primates range in size from Madame Berthe's mouse lemur, which weighs , to the eastern gorilla, weighing over . There are 376–524 species of living primates, depending on which classification is used. New primate species continue to be discovered: over 25 species were described in the 2000s, 36 in the 2010s, and three in the 2020s. Primates have large bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbary Macaque
The Barbary macaque (''Macaca sylvanus''), also known as Barbary ape, is a macaque species native to the Atlas Mountains of Algeria, Libya, Tunisia and Morocco, along with a small introduced population in Gibraltar. It is the type species of the genus ''Macaca''. The species is of particular interest because males play an atypical role in rearing young. Because of uncertain paternity, males are integral to raising all infants. Generally, Barbary macaques of all ages and sexes contribute in alloparental care of young. The diet of the Barbary macaque consists primarily of plants and insects and they are found in a variety of habitats. Males live to around 25 years old while females may live up to 30 years. Besides humans, they are the only free-living primates in Europe. Although the species is commonly referred to as the "Barbary ape", the Barbary macaque is actually a true monkey. Its name refers to the Barbary Coast of Northwest Africa. The population of the Barbary macaques i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woolly Mammoth
The woolly mammoth (''Mammuthus primigenius'') is an extinct species of mammoth that lived during the Pleistocene until its extinction in the Holocene epoch. It was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with '' Mammuthus subplanifrons'' in the early Pliocene. The woolly mammoth began to diverge from the steppe mammoth about 800,000 years ago in East Asia. Its closest extant relative is the Asian elephant. DNA studies show that the Columbian mammoth was a hybrid between woolly mammoths and another lineage descended from steppe mammoths. The appearance and behaviour of this species are among the best studied of any prehistoric animal because of the discovery of frozen carcasses in Siberia and North America, as well as skeletons, teeth, stomach contents, dung, and depiction from life in prehistoric cave paintings. Mammoth remains had long been known in Asia before they became known to Europeans in the 17th century. The origin of these remains was long a matter o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephantidae
Elephantidae is a family (biology), family of large, herbivorous proboscidean mammals collectively called elephants and mammoths. These are terrestrial animal, terrestrial large mammals with a snout modified into a Elephant#Trunk, trunk and teeth modified into tusks. Most Genus, genera and species in the family are extinction, extinct. Only two genera, ''Loxodonta'' (African elephants) and ''Elephas'' (Asiatic elephants), are Extant taxon, living. The family was first described by John Edward Gray in 1821, and later assigned to taxonomic ranks within the order Proboscidea. Elephantidae has been revised by various authors to include or exclude other extinct proboscidean genera. Classification Scientific classification of Elephantidae taxa embraces an extensive record of fossil specimens, over millions of years, some of which existed until the end of the last ice age. Some species were extirpated more recently. The discovery of new specimens and proposed cladistics have result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proboscidea
The Proboscidea (; , ) are a taxonomic order of afrotherian mammals containing one living family (Elephantidae) and several extinct families. First described by J. Illiger in 1811, it encompasses the elephants and their close relatives. From the mid-Miocene onwards, most proboscideans were very large. The largest land mammal of all time may have been a proboscidean; ''Palaeoloxodon namadicus'' was up to at the shoulder and may have weighed up to , almost double the weight of some sauropods like ''Diplodocus carnegii''. The largest extant proboscidean is the African bush elephant, with a record of size of at the shoulder and . In addition to their enormous size, later proboscideans are distinguished by tusks and long, muscular trunks, which were less developed or absent in early proboscideans. Three species of elephant are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. Elephantidae is the only surviving family of the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straight-tusked Elephant
The straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'') is an extinct species of elephant that inhabited Europe and Western Asia during the Middle and Late Pleistocene (781,000–30,000 years before present). Recovered individuals have reached up to in height, and an estimated in weight. The straight-tusked elephant probably lived in small herds, flourishing in interglacial periods, when its range would extend as far north as Great Britain. Isolated tusks are often found while partial or whole skeletons are rare, and there is evidence of predation by early humans. It is the ancestral species of most dwarf elephants that inhabited islands in the Mediterranean. Description ''Palaeoloxodon antiquus'' was quite large, with individuals reaching in height. Like other members of '' Palaeoloxodon'', ''P. antiquus'' possesses a well developed parieto-occipital crest at the top of the cranium that anchored the splenius as well as possibly the rhomboid muscles to support the lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evidence Of Absence
Evidence of absence is evidence of any kind that suggests something is missing or that it does not exist. What counts as evidence of absence has been a subject of debate between scientists and philosophers. It is often distinguished from absence of evidence. Overview Evidence of absence and absence of evidence are similar but distinct concepts. This distinction is captured in the aphorism "Absence of evidence is not evidence of absence." This antimetabole is often attributed to Martin Rees or Carl Sagan, but a version appeared as early as 1888 in a writing by William Wright. In Sagan's words, the expression is a critique of the "impatience with ambiguity" exhibited by appeals to ignorance. Despite what the expression may seem to imply, a lack of evidence can be informative. For example, when testing a new drug, if no harmful effects are observed then this suggests that the drug is safe. This is because, if the drug were harmful, evidence of that fact can be expected to turn up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Absence Of Evidence
Argument from ignorance (from la, argumentum ad ignorantiam), also known as appeal to ignorance (in which ''ignorance'' represents "a lack of contrary evidence"), is a fallacy in informal logic. It asserts that a proposition is true because it has not yet been proven false or a proposition is false because it has not yet been proven true. This represents a type of false dichotomy in that it excludes the possibility that there may have been an insufficient investigation to prove that the proposition is either true or false. It also does not allow for the possibility that the answer is unknowable, only knowable in the future, or neither completely true nor completely false. In debates, appealing to ignorance is sometimes an attempt to shift the burden of proof. The term was likely coined by philosopher John Locke in the late 17th century. Examples * "I take the view that this lack (of enemy subversive activity in the west coast) is the most ominous sign in our whole situation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Storegga Slide
The three Storegga Slides ( no, Storeggaraset) are amongst the largest known submarine landslides. They occurred at the edge of Norway's continental shelf in the Norwegian Sea, approximately 6225–6170 BCE. The collapse involved an estimated length of coastal shelf, with a total volume of of debris, which caused a tsunami in the North Atlantic Ocean. Description Storegga (Norwegian: ''Great Edge'') is located at the edge of Norway's continental shelf in the Norwegian Sea, north-west of the Møre coast. In around 6200 BCE, structural failures of the shelf caused three underwater landslides, which triggered very large tsunamis in the North Atlantic Ocean. The collapses involved an estimated length of coastal shelf, with a total volume of of debris. Based on carbon dating of plant material recovered from sediment deposited by the tsunamis, the latest incident occurred around approximately 6225–6170 BCE. In Scotland, traces of the subsequent tsunami have been recorded, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)






