|
Lips
The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy. Structure The upper and lower lips are referred to as the "Labium superius oris" and "Labium inferius oris", respectively. The juncture where the lips meet the surrounding skin of the mouth area is the vermilion border, and the typically reddish area within the borders is called the vermilion zone. The vermilion border of the upper lip is known as the cupid's bow. The fleshy protuberance located in the center of the upper lip is a tubercle known by various terms including the procheilon (also spelled ''prochilon''), the "tuberculum labii superioris", and the "labial tubercle". The vertical groove extending from the procheilon to the nasal septum is called the philtr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Lip
The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be an erogenous zone when used in kissing and other acts of intimacy. Structure The upper and lower lips are referred to as the "Labium superius oris" and "Labium inferius oris", respectively. The juncture where the lips meet the surrounding skin of the mouth area is the vermilion border, and the typically reddish area within the borders is called the vermilion zone. The vermilion border of the upper lip is known as the cupid's bow. The fleshy protuberance located in the center of the upper lip is a tubercle known by various terms including the procheilon (also spelled ''prochilon''), the "tuberculum labii superioris", and the "labial tubercle". The vertical groove extending from the procheilon to the nasal septum is called the phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
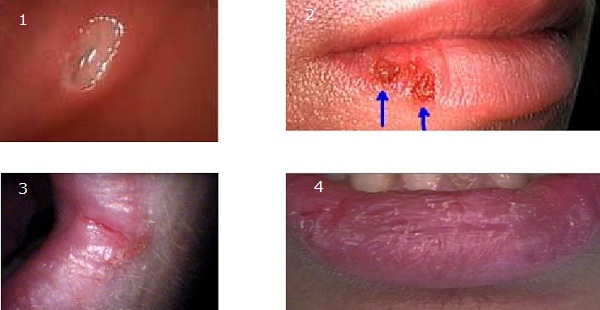
Chapped
Cheilitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the lips. The inflammation may include the perioral skin (the skin around the mouth), the vermilion border, or the labial mucosa. The skin and the vermilion border are more commonly involved, as the mucosa is less affected by inflammatory and allergic reactions. ''Cheilitis'' is a general term, and there are many recognized types and different causes. According to its onset and course, cheilitis can be either acute or chronic. Most cheilitis is caused by exogenous factors such as dryness (chapping) and acute sun exposure. Allergic tests may identify allergens that cause cheilitis. Chapped lips Chapped lips (also known as cheilitis simplex or common cheilitis) is characterized by the cracking, fissuring, and peeling of the skin of the lips, and is one of the most common types of cheilitis. While both lips may be affected, the lower lip is the most common site. There may also be burning or the formation of large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiss
A kiss is the touch or pressing of one's lips against another person or an object. Cultural connotations of kissing vary widely. Depending on the culture and context, a kiss can express sentiments of love, passion, romance, sexual attraction, sexual activity, sexual arousal, affection, respect, greeting, friendship, peace, and good luck, among many others. In some situations, a kiss is a ritual, formal or symbolic gesture indicating devotion, respect, or a sacramental. The word came from Old English '' cyssan'' (" to kiss"), in turn from '' coss '' ("a kiss"). History Anthropologists disagree on whether kissing is an instinctual or learned behaviour. Those that believe kissing to be an instinctual behaviour, cite similar behaviours in other animals such as bonobos, which are known to kiss after fighting - possibly to restore peace. Others believe that it is a learned behaviour, having evolved from activities such as suckling or premastication in early human cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermilion Border
The vermilion border (sometimes spelled vermillion border), also called margin or zone, is the normally sharp demarcation between the lip and the adjacent normal skin. It represents the change in the epidermis from highly keratinized external skin to less keratinized internal skin. It has no sebaceous glands, sweat glands, or facial hair. It has a prominence on the face, creating a focus for cosmetics (it is where lipstick is sometimes applied) and is also a location for several skin diseases. Its functional properties, however, remain unknown. Structure The lips are composed wholly of soft tissue. The skin of the face is thicker than the skin overlying the lips where blood vessels are closer to the surface. As a consequence, the margin of the lips shows a transition between the thicker and thinner skin, represented by the vermilion border. It therefore has the appearance of a sharp line between the coloured edge of the lip and adjoining skin. It has been described as a pale, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philtrum
The philtrum ( la, philtrum from Ancient Greek ''phíltron,'' lit. "love charm"), or medial cleft, is a vertical indentation in the middle area of the upper lip, common to therian mammals, extending in humans from the nasal septum to the tubercle of the upper lip. Together with a glandular rhinarium and slit-like nostrils, it is believed to constitute the primitive condition for at least therian mammals. Monotremes lack a philtrum, though this could be due to the specialised, beak-like jaws in living species. Function In most mammals, the philtrum is a narrow groove that may carry dissolved odorants from the rhinarium or nose pad to the vomeronasal organ via ducts inside the mouth. For humans and most primates, the philtrum survives only as a vestigial medial depression between the nose and upper lip. The human philtrum, bordered by ridges, is also known as the ''infranasal depression'', but has no apparent function. That may be because most higher primates rely more on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cupid's Bow
The Cupid's bow is a facial feature where the double curve of a human upper lip is said to resemble the bow of Cupid, the Roman god of erotic love. The peaks of the bow coincide with the philtral columns giving a prominent bow appearance to the lip. See also * Philtrum The philtrum ( la, philtrum from Ancient Greek ''phíltron,'' lit. "love charm"), or medial cleft, is a vertical indentation in the middle area of the upper lip, common to therian mammals, extending in humans from the nasal septum to the tuberc ... * White roll References External links Facial features Phrases and idioms derived from Greek mythology Cupid Lips {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inferior Labial Artery
The inferior labial artery (inferior labial branch of facial artery) arises near the angle of the mouth as a branch of the facial artery; it passes upward and forward beneath the triangularis and, penetrating the orbicularis oris, runs in a tortuous course along the edge of the lower lip between this muscle and the mucous membrane. It supplies the labial glands, the mucous membrane, and the muscles of the lower lip The lips are the visible body part at the mouth of many animals, including humans. Lips are soft, movable, and serve as the opening for food intake and in the articulation of sound and speech. Human lips are a tactile sensory organ, and can be ...; and anastomoses with the artery of the opposite side, and with the mental branch of the inferior alveolar artery. Additional images File:Lateral head anatomy detail.jpg, Lateral head anatomy detail File:Head ap anatomy.jpg, Head anatomy anterior view File:Slide2bbb.JPG, Inferior labial artery References Exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandibular Prominence
The mandibular prominence is an embryological structure which gives rise to the lower portion of the face. The mandible and lower lip derive from it. The mesenchymal cells within the mandibular prominence condense to form Meckel's cartilage. It is innervated by the mandibular nerve In neuroanatomy, the mandibular nerve (V) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V). Unlike the other divisions of the trigeminal nerve ( ophthalmic nerve, maxillary nerve) which contain only .... References External links * Embryology {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Pharyngeal Arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arches. In the human embryo, the arches are first seen during the fourth week of development. They appear as a series of outpouchings of mesoderm on both sides of the developing pharynx. The vasculature of the pharyngeal arches is known as the aortic arches. In fish, the branchial arches support the gills. Structure In vertebrates, the pharyngeal arches are derived from all three germ layers (the primary layers of cells that form during embryogenesis). Neural crest cells enter these arches where they contribute to features of the skull and facial skeleton such as bone and cartilage. However, the existence of pharyngeal structures before neural crest cells evolved is indicated by the existence of neural crest-independent mechanisms of pharyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depressor Labii Inferioris Muscle
The depressor labii inferioris (or quadratus labii inferioris) is a facial muscle. It helps to lower the bottom lip. Structure The depressor labii inferioris muscle arises from the lateral surface of the mandible. This is below the mental foramen, and the origin may be around 3 cm wide. It inserts on the skin of the lower lip, blending in with the orbicularis oris muscle around 2 cm wide. At its origin, depressor labii is continuous with the fibers of the platysma muscle. Some yellow fat is intermingled with the fibers. Nerve supply The depressor labii inferioris muscle is supplied by the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve. Function The depressor labii inferioris muscle helps to depress and everts the lower lip. It is the most important of the muscles of the lower lip for this function. It is an antagonist of the orbicularis oris muscle. It is needed to expose the mandibular (lower) teeth during smiling. Clinical significance Resection The depressor labi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Of The Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from '' mandere'' "to chew" and ''-bula'' (ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

