|
LinuxConf
Linuxconf is a system configuration tool for the Linux operating system. It features different user interfaces: a text interface or a graphical user interface in the form of a Web page or native application. Most Linux distributions consider it deprecated compared to other tools such as Webmin, the system-config-* tools on Red Hat Enterprise Linux/Fedora, drakconf on Mandriva, YaST on openSUSE and so on. Linuxconf was deprecated from Red Hat Linux in version 7.1 in April 2001. It was created by Jacques Gélinas of Solucorp, a company based in Québec. It is licensed under the terms of the GNU General Public License The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the Four Freedoms (Free software), four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was th .... References External links Linuxconf home page Free system software Linux configuration utilities Unix configurat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which includes the kernel and supporting system software and libraries, many of which are provided by the GNU Project. Many Linux distributions use the word "Linux" in their name, but the Free Software Foundation uses the name "GNU/Linux" to emphasize the importance of GNU software, causing some controversy. Popular Linux distributions include Debian, Fedora Linux, and Ubuntu, the latter of which itself consists of many different distributions and modifications, including Lubuntu and Xubuntu. Commercial distributions include Red Hat Enterprise Linux and SUSE Linux Enterprise. Desktop Linux distributions include a windowing system such as X11 or Wayland, and a desktop environment such as GNOME or KDE Plasma. Distributions intended for ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine from the human end, while the machine simultaneously feeds back information that aids the operators' decision-making process. Examples of this broad concept of user interfaces include the interactive aspects of computer operating systems, hand tools, heavy machinery operator controls and process controls. The design considerations applicable when creating user interfaces are related to, or involve such disciplines as, ergonomics and psychology. Generally, the goal of user interface design is to produce a user interface that makes it easy, efficient, and enjoyable (user-friendly) to operate a machine in the way which produces the desired result (i.e. maximum usability). This generally means that the operator needs to provide minimal input ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linux Distribution
A Linux distribution (often abbreviated as distro) is an operating system made from a software collection that includes the Linux kernel and, often, a package management system. Linux users usually obtain their operating system by downloading one of the Linux distributions, which are available for a wide variety of systems ranging from embedded devices (for example, OpenWrt) and personal computers (for example, Linux Mint) to powerful supercomputers (for example, Rocks Cluster Distribution). A typical Linux distribution comprises a Linux kernel, GNU tools and libraries, additional software, documentation, a window system (the most common being the X Window System, or, more recently, Wayland), a window manager, and a desktop environment. Most of the included software is free and open-source software made available both as compiled binaries and in source code form, allowing modifications to the original software. Usually, Linux distributions optionally include some proprietary so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deprecation
In several fields, especially computing, deprecation is the discouragement of use of some terminology, feature, design, or practice, typically because it has been superseded or is no longer considered efficient or safe, without completely removing it or prohibiting its use. Typically, deprecated materials are not completely removed to ensure legacy compatibility or back up practice in case new methods are not functional in an odd scenario. It can also imply that a feature, design, or practice will be removed or discontinued entirely in the future. Etymology In general English usage, the infinitive "to deprecate" means "to express disapproval of (something)". It derives from the Latin verb ''deprecari'', meaning "to ward off (a disaster) by prayer". In current technical usage, for one to state that a feature is deprecated is merely a recommendation against using it. It is still possible to produce a program or product without heeding the deprecation. Software While a deprecated so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Webmin
Webmin is a powerful and flexible web-based server management control panel for Unix-like systems. Webmin allows the user to configure operating system internals, such as users, disk quotas, services or configuration files, as well as modify and control open-source apps, such as BIND, Apache HTTP Server, PHP or MySQL. General description Webmin is largely based on Perl, running as its own process and web server. It defaults to TCP port 10000 for communicating, and can be configured to use SSL if OpenSSL is installed with additional required Perl Modules. Webmin is built around modules, which have an interface to the configuration files and the Webmin server, which makes it simple to add new functionality. Due to Webmin's modular design, it is possible for anyone who is interested to write plugins for desktop configuration. Webmin allows for controlling many machines through a single interface, or seamless login on other Webmin hosts on the same subnet or LAN. Webmin is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) is a commercial open-source Linux distribution developed by Red Hat for the commercial market. Red Hat Enterprise Linux is released in server versions for x86-64, Power ISA, ARM64, and IBM Z and a desktop version for x86-64. Fedora Linux serves as its upstream source. All of Red Hat's official support and training, together with the Red Hat Certification Program, focuses on the Red Hat Enterprise Linux platform. The first version of Red Hat Enterprise Linux to bear the name originally came onto the market as "Red Hat Linux Advanced Server". In 2003, Red Hat rebranded Red Hat Linux Advanced Server to "Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS" and added two more variants, Red Hat Enterprise Linux ES and Red Hat Enterprise Linux WS. Red Hat uses strict trademark rules to restrict free re-distribution of their officially supported versions of Red Hat Enterprise Linux but still freely provides its source code. Third-party derivatives can be built and redistribut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fedora (operating System)
Fedora Linux is a Linux distribution developed by the Fedora Project. Fedora contains software distributed under various free and open-source licenses and aims to be on the leading edge of open-source technologies. Fedora is the upstream (software development), upstream source for Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Since the release of Fedora 35, six different editions are made available tailored to personal computer, server (computing), server, cloud computing, Container (computing), container and Internet of Things installations. A new version of Fedora Linux is released every six months. , Fedora Linux has an estimated 1.2 million users, including Linus Torvalds (), creator of the Linux kernel. Features Fedora has a reputation for focusing on innovation, integrating new technologies early on and working closely with Upstream (software development), upstream Linux communities. Making changes upstream instead of specifically for Fedora Linux ensures that the changes are available t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drakconf
drakconf, or the Mandriva Control Center, is a computer program written in Perl for the configuration of Mandriva Linux, a Linux distribution. It is a tool that allows easy configuration of Mandriva. It is licensed under the open-source GNU General Public License. It is also used by Mageia, a fork of Mandriva, where it is called Mageia Control Center. It is part of the so-called drakxtools and is specifically designed for this Linux distribution for running under command-line or X Window System environment. However the source code is available, so it could be ported to other distributions. This tool is a key feature in Mandriva Linux because it puts many configuration tools together in one place, and it is easier for a user who is new to Linux Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandriva
Mandriva S.A. was a public software company specializing in Linux and open-source software. Its corporate headquarters was in Paris, and it had development centers in Metz, France and Curitiba, Brazil. Mandriva, S.A. was the developer and maintainer of a Linux distribution called Mandriva Linux, as well as various enterprise software products. Mandriva was a founding member of the Desktop Linux Consortium. History Mandriva, S.A. began as MandrakeSoft in 1998. In February 2004, following lengthy litigation with the Hearst Corporation over the name "Mandrake" (the Hearst Corporation owned a comic strip called ''Mandrake the Magician''), MandrakeSoft was required to change its name. Following the acquisition of the Brazilian Linux distribution Conectiva in February 2005, the company's name was changed on 7 April 2005 to "Mandriva" to reflect the names "MandrakeSoft" and "Conectiva." On October 4, 2004, MandrakeSoft acquired the professional support company Edge IT, which focused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
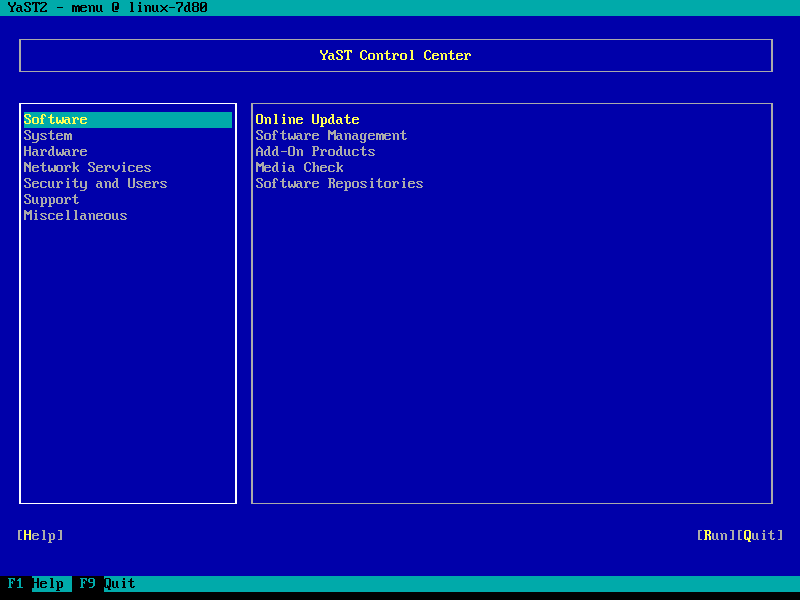
YaST
YaST (Yet another Setup Tool) is a Linux operating system setup and configuration tool. YaST is featured in the openSUSE Linux distribution, as well as in SUSE's derived commercial distributions. It is also part of the defunct United Linux. YaST features tools that can configure many aspects of the system. YaST was released first in April 1995. The first SuSE distribution that included YaST was released in May 1996. YaST was re-written in 1999 and included first in SuSE Linux 6.3 as only an installer. YaST2 was added to the desktop in SuSE Linux 6.4 and co-existed with YaST1 until YaST1's removal in SuSE Linux 8.0. Details YaST is free software that SUSE has made available under the GPL in 2004.heise.de: YaST wird freie Software (in German) It is a tool for administering and maintaining a SUSE Linux ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenSUSE
openSUSE () is a free and open-source software, free and open source RPM Package Manager, RPM-based Linux distribution developed by the openSUSE project. The initial release of the community project was a beta version of SUSE Linux 10.0. Additionally the project creates a variety of tools, such as YaST, Open Build Service, openQA, Snapper, Machinery, Portus, KIWI (openSUSE), KIWI and OSEM. Product history In the past, the SUSE Linux company had focused on releasing the SUSE Linux Personal and SUSE Linux Professional box sets which included extensive printed documentation that was available for sale in retail stores. The company's ability to sell an open source product was largely due to the closed-source development process used. Although SUSE Linux had always been free software product licensed with the GNU General Public License (GNU GPL), it was only freely possible to retrieve the source code of the next release 2 months after it was ready for purchase. SUSE Linux' strate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Québec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area and the second-largest by Population of Canada by province and territory, population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois people, Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York (state), New York in the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)