|
Life Zone
The life zone concept was developed by C. Hart Merriam in 1889 as a means of describing areas with similar plant and animal communities. Merriam observed that the changes in these communities with an increase in latitude at a constant elevation are similar to the changes seen with an increase in elevation at a constant latitude. The life zones Merriam identified are most applicable to western North America, being developed on the San Francisco Peaks, Arizona and Cascade Range of the northwestern USA. He tried to develop a system that is applicable across the North American continent, but that system is rarely referred to. The life zones that Merriam identified, along with characteristic plants, are as follows: * Lower Sonoran (low, hot desert): creosote bush, Joshua tree * Upper Sonoran (desert steppe or chaparral): sagebrush, scrub oak, Colorado pinyon, Utah juniper * Transition (open woodlands): ponderosa pine * Canadian (fir forest): Rocky Mountain Douglas fir, quaking as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotemperature
The Holdridge life zones system is a global bioclimatic scheme for the classification of land areas. It was first published by Leslie Holdridge in 1947, and updated in 1967. It is a relatively simple system based on few empirical data, giving objective criteria. A basic assumption of the system is that both soil and the climax vegetation can be mapped once the climate is known. Scheme While it was first designed for tropical and subtropical areas, the system now applies globally. The system has been shown to fit not just tropical vegetation zones,but Mediterranean zones, and boreal zones too, but is less applicable to cold oceanic or cold arid climates where moisture becomes the predominant factor. The system has found a major use in assessing the potential changes in natural vegetation patterns due to global warming. The three major axes of the barycentric subdivisions are: * precipitation (annual, logarithmic) * biotemperature (mean annual, logarithmic) * potential evapotranspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinton Hart Merriam
Clinton Hart Merriam (December 5, 1855 – March 19, 1942) was an American zoologist, mammalogist, ornithologist, entomologist, ecologist, ethnographer, geographer, naturalist and physician. He was commonly known as the 'father of mammalogy', a branch of zoology referring to the study of mammals. Early life Clinton Hart Merriam was born in New York City in 1855 to Clinton Levi Merriam, a U.S. congressman, and Caroline Hart, a judge's daughter and a graduate of Rutgers Institute. The name Clinton, shared by both father and son, was in honor of New York governor DeWitt Clinton, whom the Merriam family had connections with. To avoid confusion, the younger Merriam went by his first initial combined with his middle name, his mother's maiden name, and thus often appears as C. Hart Merriam in both the literature of his time and thereafter. Although born in New York City, where his parents were staying the winter, the family home and place where Merriam spent his boyhood days was " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engelmann Spruce
''Picea engelmannii'', with the common names Engelmann spruce, white spruce, mountain spruce, and silver spruce, is a species of spruce native to western North America. It is mostly a high-altitude mountain tree but also appears in watered canyons. Description ''Picea engelmannii'' is a medium-sized to large evergreen tree growing to tall, exceptionally to tall, and with a trunk diameter of up to . The reddish bark is thin and scaly, flaking off in small circular plates across. The crown is narrow conic in young trees, becoming cylindric in older trees. The shoots are buff-brown to orange-brown, usually densely pubescent, and with prominent pulvini. The leaves are needle-like, long, flexible, rhombic in cross-section, glaucous blue-green above with several thin lines of stomata, and blue-white below with two broad bands of stomata. The needles have a pungent odour when crushed. Purple cones of about 1 cm appear in spring, releasing yellow pollen when windy. The cones ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leslie Holdridge
Leslie Ransselaer Holdridge (September 29, 1907 – June 19, 1999) was an American botanist and climatologist. He was the father of composer Lee Holdridge as well as the father of Leslie A. Holdridge, Lorena Holdridge, Marbella Holdridge, Marly Holdridge, Marisela Holdridge, Thania Holdridge, John Holdridge, Ida Holdridge, Reuseland Holdridge, Leythy J. Holdridge and youngest son Gregory Holdridge whom he fathered with Costa Rican Clara Luz Melendez. Career In his famous 1947 paper, he defined "life zones" using three indicators: # Mean annual biotemperature (average temperature, after data values below 0 °C or above 30 °C have been eliminated) # Total annual precipitation # The ratio of mean annual potential evapotranspiration to mean total annual precipitation. Holdridge participated in the Cinchona Missions, a United States effort to search for natural sources of quinine during World War II.Steere, W. (1945). The Cinchona-Bark Industry of South America. The Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commission For Environmental Cooperation
The Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC; es, Comisión para la Cooperación Ambiental; french: Commission de coopération environnementale) was established by Canada, Mexico, and the United States to implement the North American Agreement on Environmental Cooperation (NAAEC), the environmental side accord to the North American Free Trade Agreement The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA ; es, Tratado de Libre Comercio de América del Norte, TLCAN; french: Accord de libre-échange nord-américain, ALÉNA) was an agreement signed by Canada, Mexico, and the United States that crea .... The CEC's mission is to facilitate cooperation and public participation to foster conservation, protection and enhancement of the North American environment for the benefit of present and future generations, in the context of increasing economic, trade and social links among Canada, Mexico and the United States. Origins and structure The Commission for Environmental Cooperati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ecoregions In North America (CEC)
This list of ecoregions of North America provides an overview of North American ecoregions designated by the Commission for Environmental Cooperation (CEC) in its North American Environmental Atlas. It should not be confused with Wikipedia articles based on the classification system developed by the World Wildlife Fund, such as List of ecoregions (WWF) and Lists of ecoregions by country. The commission was established in 1994 by the member states of Canada, Mexico, and the United States to address regional environmental concerns under the North American Agreement on Environmental Cooperation (NAAEC), the environmental side accord to the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). The commission's 1997 report, ''Ecological Regions of North America'', provides a framework that may be used by government agencies, non-governmental organizations, and academic researchers as a basis for risk analysis, resource management, and environmental study of the continent's ecosystems. Eco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Wide Fund For Nature
The World Wide Fund for Nature Inc. (WWF) is an international non-governmental organization founded in 1961 that works in the field of wilderness preservation and the reduction of human impact on the environment. It was formerly named the World Wildlife Fund, which remains its official name in Canada and the United States. WWF is the world's largest conservation organization, with over five million supporters worldwide, working in more than 100 countries and supporting around 3,000 conservation and environmental projects. They have invested over $1 billion in more than 12,000 conservation initiatives since 1995. WWF is a foundation with 65% of funding from individuals and bequests, 17% from government sources (such as the World Bank, DFID, and USAID) and 8% from corporations in 2020. WWF aims to "stop the degradation of the planet's natural environment and to build a future in which humans live in harmony with nature." The Living Planet Report has been published every tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Terrestrial Ecoregions (WWF)
This is a list of terrestrial ecoregions as compiled by the World Wildlife Fund (WWF). The WWF identifies terrestrial, freshwater Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ..., and marine ecoregions. The terrestrial scheme divides the Earth's land surface into 8 biogeographic realms, containing 867 smaller ecoregions. Each ecoregion is classified into one of 14 major habitat types, or biomes. In 2017 the WWF team revised ecosystem names and boundaries in the Arabian Peninsula, drier African regions, and Southeastern United States.Eric Dinerstein, David Olson, et al. (2017). An Ecoregion-Based Approach to Protecting Half the Terrestrial Realm, BioScience, Volume 67, Issue 6, June 2017, Pages 534–545, Additional ecoregions for Antarctic Realm are currently being incor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The West (U
West is a cardinal direction or compass point. West or The West may also refer to: Geography and locations Global context * The Western world * Western culture and Western civilization in general * The Western Bloc, countries allied with NATO during the Cold War * The Occident, an early-modern term originated with geographical divisions mirroring the cultural divide between the Hellenistic east and Latin West, and the political divide between the Western and Eastern Roman empires Regional contexts * West River (other) * The American frontier, also called "The Old West" or "The Wild West", an American process of westward movement from 1600 to 1920 * The Western Regions, a historical term for regions of Chinese suzerainty in Central Asia * Western Territories (''Ziemie Zachodnie'') or Recovered Territories (''Ziemie Odzyskane''), Former eastern territories of Germany annexed to Poland * West (Cornish hundred) or West Wivelshire, a county subdivision of Cornwall, Engla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
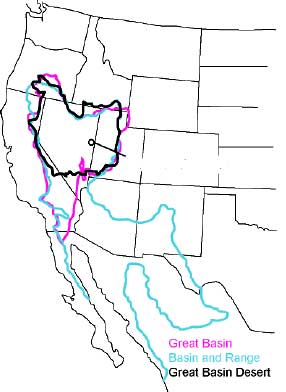
Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California. It is noted for both its arid climate and the basin and range topography that varies from the North American low point at Badwater Basin in Death Valley to the highest point of the contiguous United States, less than away at the summit of Mount Whitney. The region spans several physiographic divisions, biomes, ecoregions, and deserts. Definition The term "Great Basin" is applied to hydrographic, biological, floristic, physiographic, topographic, and ethnographic geographic areas. The name was originally coined by John C. Frémont, who, based on information gleaned from Joseph R. Walker as well as his own travels, recognized the hydrographic nature of the landform as "having no connection to the ocean". The hydrographic definition is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |