|
Levoketoconazole
Levoketoconazole, sold under the brand name Recorlev, is a steroidogenesis inhibitor that is used for the treatment of Cushing's syndrome. Levoketoconazole was approved for medical use in the United States in December 2021. Levoketoconazole is the levorotatory or (2''S'',4''R'') enantiomer of ketoconazole, and it is an enzyme inhibitor, inhibitor of the enzymes CYP11B1 (11β-hydroxylase), CYP17A1 (17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase), and CYP21A2 (21-hydroxylase). It inhibits glucocorticoid biosynthesis and hence circulating levels of glucocorticoids, thereby treating Cushing's syndrome. In addition to its increased potency, the drug is 12-fold less potent than racemic ketoconazole in inhibiting CYP7A1 (cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase), theoretically resulting in further reduced interference with bile acid production and metabolite elimination and therefore less risk of hepatotoxicity. Levoketoconazole has also been found to inhibit CYP11A1 (cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme) and CYP51 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole, sold under the brand name Nizoral among others, is an antiandrogen and antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. Applied to the skin it is used for fungal skin infections such as tinea, cutaneous candidiasis, pityriasis versicolor, dandruff, and seborrheic dermatitis. Taken by mouth it is a less preferred option and only recommended for severe infections when other agents cannot be used. Other uses include treatment of excessive male-patterned hair growth in women and Cushing's syndrome. Common side effects when applied to the skin include redness. Common side effects when taken by mouth include nausea, headache, and liver problems. Liver problems may result in death or the need for a liver transplantation. Other severe side effects when taken by mouth include QT prolongation, adrenocortical insufficiency, and anaphylaxis. It is an imidazole and works by hindering the production of ergosterol required for the fungal cell membrane, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP7A1
Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase also known as cholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase or cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene which has an important role in cholesterol metabolism. It is a cytochrome P450 enzyme, which belongs to the oxidoreductase class, and converts cholesterol to 7-alpha-hydroxycholesterol, the first and rate limiting step in bile acid synthesis. The inhibition of cholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) represses bile acid biosynthesis. Evolution Sequence comparisons indicated a huge similarity between cytochromes P450 identified in man and bacteria, and suggested that the superfamily cytochrome P450 first originated from a common ancestral gene some three billion years ago. The superfamily cytochrome P450 was named in 1961, because of the 450-nm spectral peak pigment that cytochrome P450 has when reduced and bound to carbon monoxide. In the early 1960s, P450 was thought to be one enzyme, and by the mid 1960s it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7α-Hydroxylase Inhibitors
Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase also known as cholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase or cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the gene which has an important role in cholesterol metabolism. It is a cytochrome P450 enzyme, which belongs to the oxidoreductase class, and converts cholesterol to 7-alpha-hydroxycholesterol, the first and rate limiting step in bile acid synthesis. The inhibition of cholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) represses bile acid biosynthesis. Evolution Sequence comparisons indicated a huge similarity between cytochromes P450 identified in man and bacteria, and suggested that the superfamily cytochrome P450 first originated from a common ancestral gene some three billion years ago. The superfamily cytochrome P450 was named in 1961, because of the 450-nm spectral peak pigment that cytochrome P450 has when reduced and bound to carbon monoxide. In the early 1960s, P450 was thought to be one enzyme, and by the mid 1960s it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP51A1
Lanosterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51A1) is the animal version of a cytochrome P450 enzyme that is involved in the conversion of lanosterol to 4,4-dimethylcholesta-8(9),14,24-trien-3β-ol. The cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are a conserved group of proteins that serve as key players in the metabolism of organic substances and the biosynthesis of important steroids, lipids, and vitamins in eukaryotes. As a member of this family, lanosterol 14α-demethylase is responsible for an essential step in the biosynthesis of sterols. In particular, this protein catalyzes the removal of the C-14α-methyl group from lanosterol. This demethylation step is regarded as the initial checkpoint in the transformation of lanosterol to other sterols that are widely used within the cell. Evolution The structural and functional properties of the cytochrome P450 superfamily have been subject to extensive diversification over the course of evolution. Recent estimates indicate that there are currently 10 class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanosterol 14α-demethylase Inhibitors
Lanosterol is a tetracyclic triterpenoid and is the compound from which all animal and fungal steroids are derived. By contrast plant steroids are produced via cycloartenol. Role in biosynthesis of other steroids Elaboration of lanosterol under enzyme catalysis leads to the core structure of steroids. 14-Demethylation of lanosterol by CYP51 eventually yields cholesterol. Biosynthesis Research Lanosterol has been identified as a key component in maintaining eye lens clarity. Pre-clinical research has identified Lanosterol as a possible agent for the reversal and prevention of cataracts. In vivo experiments on dogs showed significant reversal of cataracts within 6 weeks of lanosterol injection. In 2018, Lanosterol was shown to improve lens clarity in cells with lens clouding due to aging or physical stressors. A subsequent study found positive results on the optics of the lens in mice with cataracts (Wang, Hoshino,Uesugi, Yagi, Pierscionek and Andley (2022). Use Lanosterol is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiopure Drugs
An enantiopure drug is a pharmaceutical that is available in one specific enantiomeric form. Most biological molecules (proteins, sugars, etc.) are present in only one of many chiral forms, so different enantiomers of a chiral drug molecule bind differently (or not at all) to target receptors. Chirality can be observed when the geometric properties of an object is not superimposable with its mirror image. Two forms of a molecule are formed (both mirror images) from a chiral carbon, these two forms are called enantiomers. One enantiomer of a drug may have a desired beneficial effect while the other may cause serious and undesired side effects, or sometimes even beneficial but entirely different effects. The desired enantiomer is known as an eutomer while the undesired enantiomer is known as the distomer. When equal amounts of both enantiomers are found in a mixture, the mixture is known as a racemic mixture. If a mixture for a drug does not have a 1:1 ratio of its enantiomers it is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
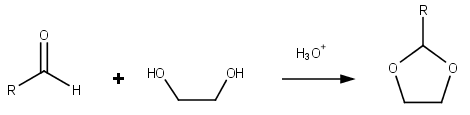
Dioxolanes
Dioxolane is a heterocyclic acetal with the chemical formula (CH2)2O2CH2. It is related to tetrahydrofuran by interchange of one oxygen for a CH2 group. The corresponding saturated 6-membered C4O2 rings are called dioxanes. The isomeric 1,2-dioxolane (wherein the two oxygen centers are adjacent) is a peroxide. 1,3-dioxolane is used as a solvent and as a comonomer in polyacetals. As a class of compounds Dioxolanes are a group of organic compounds containing the dioxolane ring. Dioxolanes can be prepared by acetalization of aldehydes and ketalization of ketones with ethylene glycol. (+)-''cis''-Dioxolane is the trivial name for which is a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor agonist. Protecting groups Organic compounds containing carbonyl groups sometimes need protection so that they do not undergo reactions during transformations of other functional groups that may be present. A variety of approaches to protection and deprotection of carbonyls including as dioxolanes are known. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP17A1 Inhibitors
A CYP17A1 inhibitor is a type of drug which inhibits the enzyme CYP17A1. It may inhibit both of the functions of the enzyme, 17α-hydroxylase and 17,20-lyase, or may be selective for inhibition of one of these two functions (generally 17,20-lyase). These drugs prevent the conversion of pregnane steroids into androgens like testosterone and therefore are androgen biosynthesis inhibitors and functional antiandrogens. Examples of CYP17A1 inhibitors include the older drug ketoconazole and the newer drugs abiraterone acetate, orteronel, galeterone, and seviteronel. The CYP17A1 inhibitors that have been marketed, like abiraterone acetate, are used mainly in the treatment of prostate cancer. CYP17A1 inhibitors that are not selective for inhibition of 17,20-lyase must be combined with a glucocorticoid such as prednisone in order to avoid adrenal insufficiency and mineralocorticoid excess caused by prevention of cortisol production. See also * Steroidogenic enzyme * Steroidogenesis inhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme. While many drugs are deactivated by CYP3A4, there are also some drugs which are ''activated'' by the enzyme. Some substances, such as some drugs and furanocoumarins present in grapefruit juice, interfere with the action of CYP3A4. These substances will therefore either amplify or weaken the action of those drugs that are modified by CYP3A4. CYP3A4 is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of oxidizing enzymes. Several other members of this family are also involved in drug metabolism, but CYP3A4 is the most common and the most versatile one. Like all members of this family, it is a hemoprotein, i.e. a protein containing a heme group with an iron atom. In humans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholesterol Side-chain Cleavage Enzyme Inhibitors
Cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme is commonly referred to as P450scc, where "scc" is an acronym for side-chain cleavage. P450scc is a mitochondrial enzyme that catalyzes conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone. This is the first reaction in the process of steroidogenesis in all mammalian tissues that specialize in the production of various steroid hormones. P450scc is a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily of enzymes (family 11, subfamily A, polypeptide 1) and is encoded by the gene. Nomenclature The systematic name of this enzyme class is cholesterol, reduced-adrenal-ferredoxin:oxygen oxidoreductase (side-chain-cleaving). Other names include: * C27-side-chain cleavage enzyme * cholesterol 20-22-desmolase * cholesterol C20-22 desmolase * cholesterol desmolase * cholesterol side-chain cleavage enzyme * cholesterol side-chain-cleaving enzyme * cytochrome P-450scc * desmolase, steroid 20-22 * enzymes, cholesterol side-chain-cleaving * steroid 20-22 desmolas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroarenes
In organic chemistry, an aryl halide (also known as haloarene) is an aromatic compound in which one or more hydrogen atoms, directly bonded to an aromatic ring are replaced by a halide. The haloarene are different from haloalkanes because they exhibit many differences in methods of preparation and properties. The most important members are the aryl chlorides, but the class of compounds is so broad that there are many derivatives and applications. Preparation The two main preparatory routes to aryl halides are direct halogenation and via diazonium salts. Direct halogenation In the Friedel-Crafts halogenation, Lewis acids serve as catalysts. Many metal chlorides are used, examples include iron(III) chloride or aluminium chloride. The most important aryl halide, chlorobenzene is produced by this route. Monochlorination of benzene is always accompanied by formation of the dichlorobenzene derivatives. Arenes with electron donating groups react with halogens even in the absence of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |