|
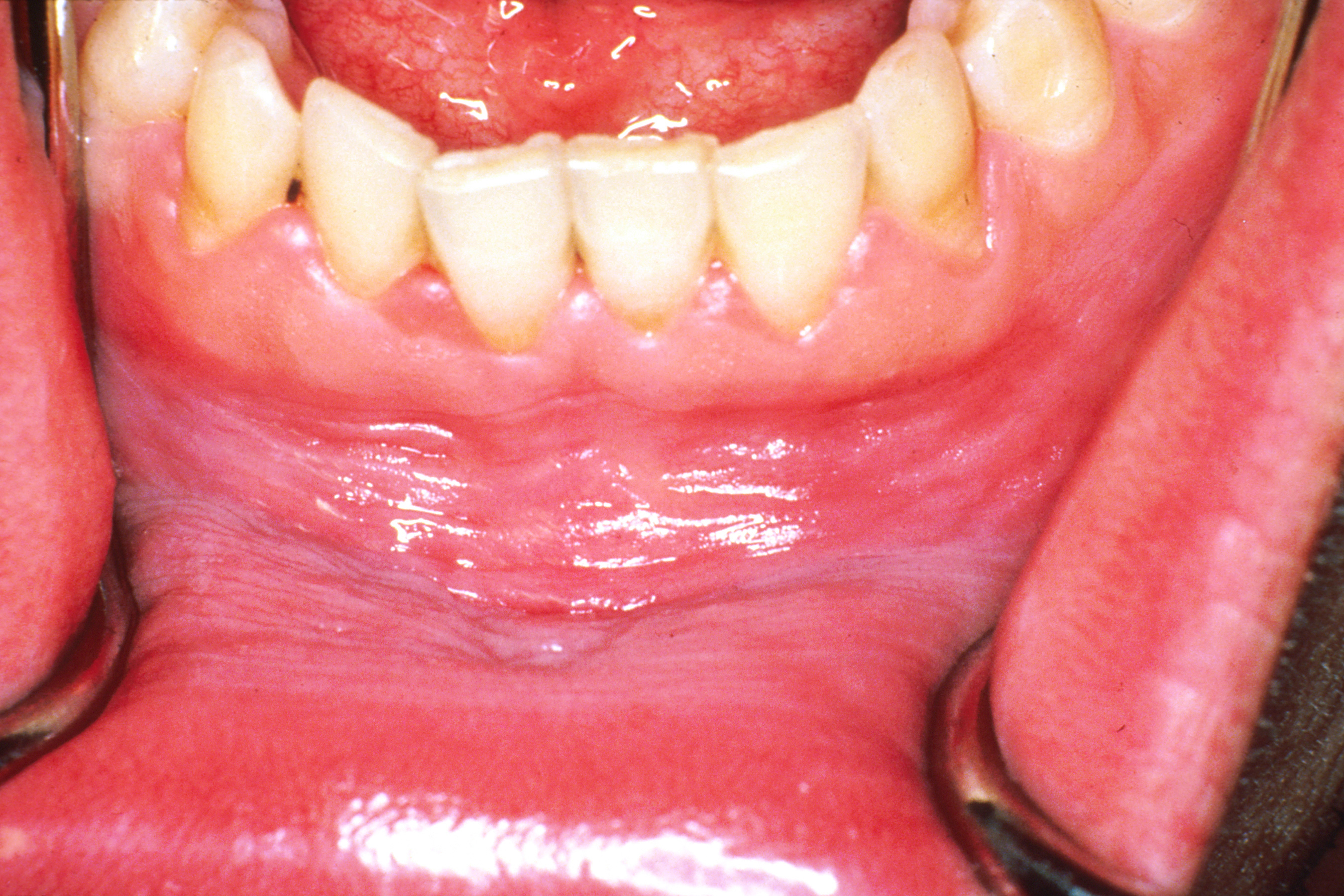
Leukoplakia
Oral leukoplakia is a ''potentially malignant disorder'' affecting the oral mucosa. It is defined as "essentially an oral mucosal white lesion that cannot be considered as any other definable lesion." Oral leukoplakia is a white patch or plaque that develops in the oral cavity and is strongly associated with smoking. Leukoplakia is a firmly attached white patch on a mucous membrane which is associated with increased risk of cancer. The edges of the lesion are typically abrupt and the lesion changes with time. Advanced forms may develop red patches. There are generally no other symptoms. It usually occurs within the mouth, although sometimes mucosa in other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, or genitals may be affected. The cause of leukoplakia is unknown. Risk factors for formation inside the mouth include smoking, chewing tobacco, excessive alcohol, and use of betel nuts. One specific type is common in HIV/AIDS. It is a precancerous lesion, a tissue alteration i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukoplakia
Oral leukoplakia is a ''potentially malignant disorder'' affecting the oral mucosa. It is defined as "essentially an oral mucosal white lesion that cannot be considered as any other definable lesion." Oral leukoplakia is a white patch or plaque that develops in the oral cavity and is strongly associated with smoking. Leukoplakia is a firmly attached white patch on a mucous membrane which is associated with increased risk of cancer. The edges of the lesion are typically abrupt and the lesion changes with time. Advanced forms may develop red patches. There are generally no other symptoms. It usually occurs within the mouth, although sometimes mucosa in other parts of the gastrointestinal tract, urinary tract, or genitals may be affected. The cause of leukoplakia is unknown. Risk factors for formation inside the mouth include smoking, chewing tobacco, excessive alcohol, and use of betel nuts. One specific type is common in HIV/AIDS. It is a precancerous lesion, a tissue alteration i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Candidiasis
Oral candidiasis, also known as oral thrush among other names, is candidiasis that occurs in the mouth. That is, oral candidiasis is a mycosis (yeast/fungal infection) of ''Candida'' species on the mucous membranes of the mouth. ''Candida albicans'' is the most commonly implicated organism in this condition. ''C. albicans'' is carried in the mouths of about 50% of the world's population as a normal component of the oral microbiota. This candidal carriage state is not considered a disease, but when ''Candida'' species become pathogenic and invade host tissues, oral candidiasis can occur. This change usually constitutes an opportunistic infection by normally harmless micro-organisms because of local (i.e., mucosal) or systemic factors altering host immunity. Classification Oral candidiasis is a mycosis (fungal infection). Traditionally, oral candidiasis is classified using the Lehner system, originally described in the 1960s, into acute and chronic forms (see table). Some of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lichen Planus
Lichen planus (LP) is a chronic inflammatory and immune-mediated disease that affects the skin, nails, hair, and mucous membranes. It is not an actual lichen, and is only named that because it looks like one. It is characterized by polygonal, flat-topped, violaceous papules and plaques with overlying, reticulated, fine white scale ( Wickham's striae), commonly affecting dorsal hands, flexural wrists and forearms, trunk, anterior lower legs and oral mucosa. The hue may be gray-brown in people with darker skin. Although there is a broad clinical range of LP manifestations, the skin and oral cavity remain as the major sites of involvement. The cause is unknown, but it is thought to be the result of an autoimmune process with an unknown initial trigger. There is no cure, but many different medications and procedures have been used in efforts to control the symptoms. The term lichenoid reaction (lichenoid eruption or lichenoid lesion) refers to a lesion of similar or identical histopa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
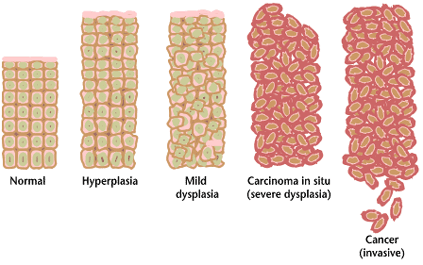
Precancerous
A precancerous condition is a condition, tumor or lesion involving abnormal cells which are associated with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Clinically, precancerous conditions encompass a variety of abnormal tissues with an increased risk of developing into cancer. Some of the most common precancerous conditions include certain colon polyps, which can progress into colon cancer, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, which can progress into multiple myeloma or myelodysplastic syndrome. and cervical dysplasia, which can progress into cervical cancer. Bronchial premalignant lesions can progress to squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Pathologically, precancerous tissue can range from benign neoplasias, which are tumors which don't invade neighboring normal tissues or spread to distant organs, to dysplasia, a collection of highly abnormal cells which, in some cases, has an increased risk of progressing to anaplasia and invasive cancer which is life-threate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperkeratosis
Hyperkeratosis is thickening of the stratum corneum (the outermost layer of the epidermis, or skin), often associated with the presence of an abnormal quantity of keratin,Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease'' (7th ed.). Saunders. Page 1230. . and also usually accompanied by an increase in the granular layer. As the corneum layer normally varies greatly in thickness in different sites, some experience is needed to assess minor degrees of hyperkeratosis. It can be caused by vitamin A deficiency or chronic exposure to arsenic. Hyperkeratosis can also be caused by B-Raf inhibitor drugs such as Vemurafenib and Dabrafenib.Niezgoda, Anna; Niezgoda, Piotr; Czajkowski, Rafal (2015) ''Novel Approaches to Treatment of Advanced Melanoma: A Review of Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy'' BioMed Research International It can be treated with urea-containing creams, which dissolve the intercellular matrix of the cells of the stratum co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Medicine
An oral medicine or stomatology doctor (or stomatologist) has received additional specialized training and experience in the diagnosis and management of oral mucosal abnormalities (growths, ulcers, infection, allergies, immune-mediated and autoimmune disorders) including oral cancer, salivary gland disorders, temporomandibular disorders (e.g.: problems with the TMJ) and facial pain (due to musculoskeletal or neurologic conditions), taste and smell disorders; and recognition of the oral manifestations of systemic and infectious diseases. It lies at the interface between medicine and dentistry. An oral medicine doctor is trained to diagnose and manage patients with disorders of the orofacial region, essentially as a "physician of the mouth." History The importance of the mouth in medicine has been recognized since the earliest known medical writings. For example, Hippocrates, Galen and others considered the tongue to be a "barometer" of health, and emphasized the diagnostic and prog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Common types include: * Squamous-cell skin cancer: A type of skin cancer * Squamous-cell carcinoma of the lung: A type of lung cancer * Squamous-cell thyroid carcinoma: A type of thyroid cancer * Esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma: A type of esophageal cancer * Squamous-cell carcinoma of the vagina: A type of vaginal cancer Despite sharing the name "squamous-cell carcinoma", the SCCs of different body sites can show differences in their presented symptoms, natural history, prognosis, and response to treatment. By body location Human papillomavirus infection has been associated with SCCs of the oropharynx, lung, fingers, and anogenital region. Head and neck cancer About 90% of cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chewing Tobacco
Chewing tobacco is a type of smokeless tobacco product that is placed between the cheek and lower gum to draw out its flavor. Some users chew it, others do not. It consists of coarsely chopped aged tobacco that is flavored and often sweetened; it is not ground fine like dipping tobacco. Unwanted juices are then spat. Chewing tobacco may be left as loose leaf or compressed into a small rectangular "plug". Nearly all modern chewing tobaccos are produced by a process of leaf curing, cutting, fermentation, and processing, which may include sweetening and flavoring. Historically, many American chewing-tobacco brands popular during the American Civil War era were made with cigar clippings. Chewing tobacco is a source of nicotine. History Chewing is one of the oldest methods of consuming tobacco. Indigenous peoples of the Americas in both North and South America chewed the leaves of the plant long before the arrival of Europeans. The Southern United States was distinctive for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinomas (SCCs), also known as epidermoid carcinomas, comprise a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Common types include: * Squamous-cell skin cancer: A type of skin cancer * Squamous-cell carcinoma of the lung: A type of lung cancer * Squamous-cell thyroid carcinoma: A type of thyroid cancer * Esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma: A type of esophageal cancer * Squamous-cell carcinoma of the vagina: A type of vaginal cancer Despite sharing the name "squamous-cell carcinoma", the SCCs of different body sites can show differences in their presented symptoms, natural history, prognosis, and response to treatment. By body location Human papillomavirus infection has been associated with SCCs of the oropharynx, lung, fingers, and anogenital region. Head and neck cancer About 90% of cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |