|
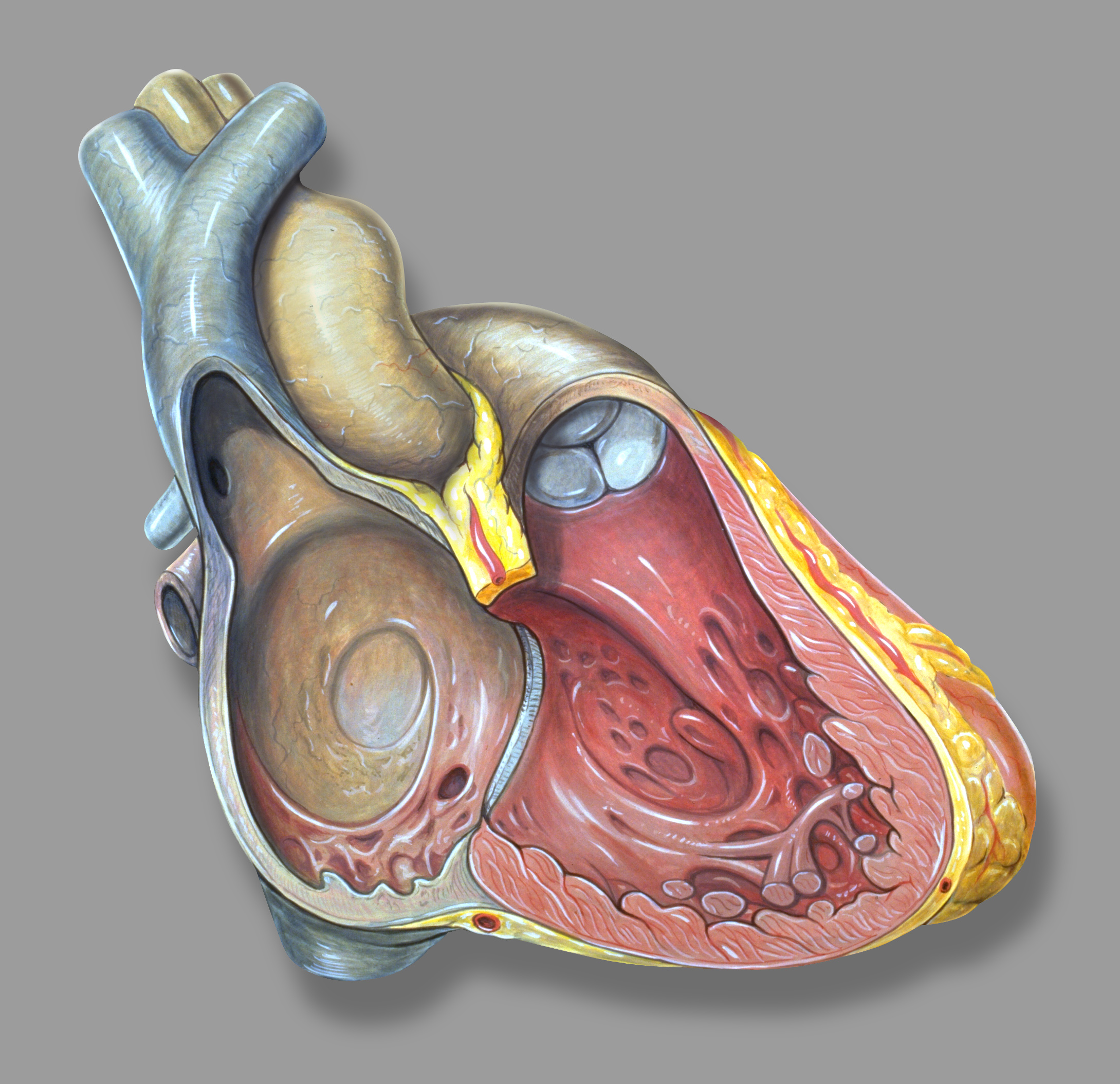
Left Atrial Enlargement
Left atrial enlargement (LAE) or left atrial dilation refers to enlargement of the left atrium (LA) of the heart, and is a form of cardiomegaly. Signs and symptoms Left atrial enlargement can be mild, moderate or severe depending on the extent of the underlying condition. Although other factors may contribute, left atrium size has been found to be a predictor of mortality due to both cardiovascular issues as well as all-cause mortality. Research suggests that left atrium size as measured by an echo-cardiograph may be linked to cardiovascular disease. However, studies that have found LAE to be a predictor for mortality recognize the need for more standardized left atrium measurements than those found in an echo-cardiogram. Causes In the general population, obesity appears to be the most important risk factor for LAE. LAE has been found to be correlated to body size, independent of obesity, meaning that LAE is more common in people with a naturally large body size. Also, a study ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Atrial Volume
The volume of the heart's left atrium (left atrial volume) is an important biomarker for cardiovascular physiology and clinical cardiology. It is usually calculated as left atrial volume index in terms of body surface area. Measurement The left atrial volume is commonly measured by echocardiography or magnetic resonance tomography. It is calculated from biplane recordings with the equation: :_=\frac\frac where ''A''4''c'' and ''A''2''c'' denote LA areas in 4- and 2-chamber views respectively, and ''L'' corresponds to the shortest long-axis length measured in either views. Usually, the volume of the left atrium is divided by the body surface area in order to provide an extensive property, which is independent from body size. The resulting index is referred to as left atrial volume index (LAVI): :LAVI=\frac Physiology LAVI between 21 and 52 mL/m2 is regarded as normal. Pathophysiologiy and clinical implications Enlargement of the left atrium is a form of cardiomegaly. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Surface Area
In physiology and medicine, the body surface area (BSA) is the measured or calculated surface area of a human body. For many clinical purposes, BSA is a better indicator of metabolic mass than body weight because it is less affected by abnormal adipose mass. Nevertheless, there have been several important critiques of the use of BSA in determining the dosage of medications with a narrow therapeutic index, such as chemotherapy. Typically there is a 4–10 fold variation in drug clearance between individuals due to differing the activity of drug elimination processes related to genetic and environmental factors. This can lead to significant overdosing and underdosing (and increased risk of disease recurrence). It is also thought to be a distorting factor in Phase I and II trials that may result in potentially helpful medications being prematurely rejected. The trend to personalized medicine is one approach to counter this weakness. Uses Examples of uses of the BSA: * Renal clearan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial ellipsoid (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordata, chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. Individual vertebrae are named according to their region and position, and can be used as anatomical landmarks in order to guide procedures such as Lumbar puncture, lumbar punctures. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord. There are about 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human vertebral column is one of the most-studied examples. Many different diseases in humans can affect the spine, with spina bifida and scoliosis being recognisable examples. The general structure of human vertebrae is fairly typical of that found in mammals, reptiles, and birds. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thoracic Cavity
The thoracic cavity (or chest cavity) is the chamber of the body of vertebrates that is protected by the thoracic wall (rib cage and associated skin, muscle, and fascia). The central compartment of the thoracic cavity is the mediastinum. There are two openings of the thoracic cavity, a superior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic inlet and a lower inferior thoracic aperture known as the thoracic outlet. The thoracic cavity includes the tendons as well as the cardiovascular system which could be damaged from injury to the back, spine or the neck. Structure Structures within the thoracic cavity include: * structures of the cardiovascular system, including the heart and great vessels, which include the thoracic aorta, the pulmonary artery and all its branches, the superior and inferior vena cava, the pulmonary veins, and the azygos vein * structures of the respiratory system, including the diaphragm, trachea, bronchi and lungs * structures of the digestive system, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echocardiogram
An echocardiography, echocardiogram, cardiac echo or simply an echo, is an ultrasound of the heart. It is a type of medical imaging of the heart, using standard ultrasound or Doppler ultrasound. Echocardiography has become routinely used in the diagnosis, management, and follow-up of patients with any suspected or known heart diseases. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging modalities in cardiology. It can provide a wealth of helpful information, including the size and shape of the heart (internal chamber size quantification), pumping capacity, location and extent of any tissue damage, and assessment of valves. An echocardiogram can also give physicians other estimates of heart function, such as a calculation of the cardiac output, ejection fraction, and diastolic function (how well the heart relaxes). Echocardiography is an important tool in assessing wall motion abnormality in patients with suspected cardiac disease. It is a tool which helps in reaching an early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
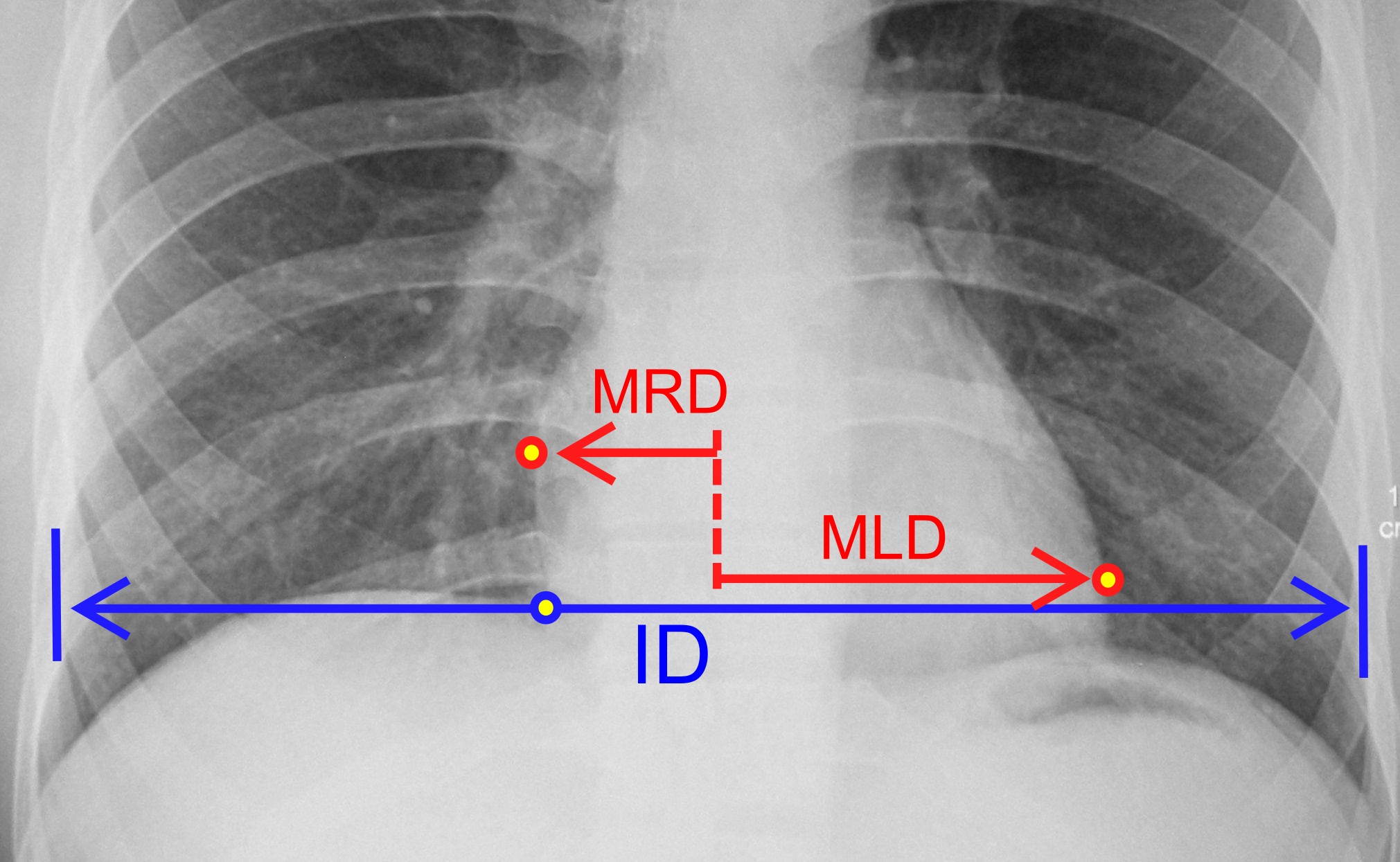
Cardiomegaly
Cardiomegaly (sometimes megacardia or megalocardia) is a medical condition in which the heart is enlarged. As such, it is more commonly referred to simply as "having an enlarged heart". It is usually the result of underlying conditions that make the heart work harder, such as obesity, heart valve disease, high blood pressure (hypertension), and coronary artery disease. Cardiomyopathy is also associated with cardiomegaly. Cardiomegaly can be serious depending on what part of the heart is enlarged, and can result in congestive heart failure. Recent studies suggest that cardiomegaly is associated with a higher risk of sudden cardiac death. Cardiomegaly may improve over time, but many people with an enlarged heart (dilated cardiomyopathy) need lifelong treatment with medication. Having an immediate family member who has or had cardiomegaly may indicate that a person is more susceptible to getting this condition. Signs and symptoms For many people, cardiomegaly is asymptomatic. For ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P Wave (electrocardiography)
The P wave on the ECG represents atrial depolarization, which results in atrial contraction, or atrial systole. Physiology The P wave is a summation wave generated by the depolarization front as it transits the atria. Normally the right atrium depolarizes slightly earlier than left atrium since the depolarization wave originates in the sinoatrial node, in the high right atrium and then travels to and through the left atrium. The depolarization front is carried through the atria along semi-specialized conduction pathways including Bachmann's bundle resulting in uniform shaped waves. Depolarization originating elsewhere in the atria (atrial ectopics) result in P waves with a different morphology from normal. Pathology Peaked P waves (> 0.25 mV) suggest right atrial enlargement, cor pulmonale, (''P pulmonale'' rhythm), but have a low predictive value (~20%). A P wave with increased amplitude can indicate hypokalemia. It can also indicate right atrial enlargement. A P wave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(cropped).jpg)