|
Left-right Asymmetry (biology)
Left-right asymmetry, (LR asymmetry) is the process in early embryonic development that breaks the normal symmetry in the bilateral embryo. In vertebrates, left-right asymmetry is established early in development at a structure called the left-right organizer (the name of which varies between species) and leads to activation of different signalling pathways on the left and right of the embryo. This in turn cause several organs in adults to develop LR asymmetry, such as the tilt of the heart, the different number lung lobes on each side of the body and the position of the stomach and spleen on the right side of the body. If this process does not occur correctly in humans it can result in the syndromes heterotaxy or situs inversus. LR asymmetry is pervasive throughout all animals, including invertebrates. Examples of invertebrate LR asymmetry include the large and small claws of the fiddler crab, asymmetrical gut coiling in ''Drosophila melanogaster,'' and dextral (clockwise) and si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryonic Development
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervous syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascidiacea
Ascidiacea, commonly known as the ascidians, tunicates (in part), and sea squirts (in part), is a polyphyletic class in the subphylum Tunicata of sac-like marine invertebrate filter feeders. Ascidians are characterized by a tough outer "tunic" made of a polysaccharide. Ascidians are found all over the world, usually in shallow water with salinities over 2.5%. While members of the Thaliacea and Larvacea (Appendicularia) swim freely like plankton, sea squirts are sessile animals after their larval phase: they then remain firmly attached to their substratum, such as rocks and shells. There are 2,300 species of ascidians and three main types: solitary ascidians, social ascidians that form clumped communities by attaching at their bases, and compound ascidians that consist of many small individuals (each individual is called a zooid) forming colonies up to several meters in diameter. Sea squirts feed by taking in water through a tube, the oral siphon. The water enters the mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symmetry Breaking And Cortical Rotation
Symmetry breaking in biology is the process by which uniformity is broken, or the number of points to view invariance are reduced, to generate a more structured and improbable state. That is to say, symmetry breaking is the event where symmetry along a particular axis is lost to establish a polarity. Polarity is a measure for a biological system to distinguish poles along an axis. This measure is important because it is the first step to building complexity. For example, during organismal development, one of the first steps for the embryo is to distinguish its dorsal-ventral axis. The symmetry-breaking event that occurs here will determine which end of this axis will be the ventral side, and which end will be the dorsal side. Once this distinction is made, then all the structures that are located along this axis can develop at the proper location. As an example, during human development, the embryo needs to establish where is ‘back’ and where is ‘front’ before compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleavage (embryo)
In embryology, cleavage is the division of cells in the early development of the embryo, following fertilization. The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with no significant overall growth, producing a cluster of cells the same size as the original zygote. The different cells derived from cleavage are called blastomeres and form a compact mass called the morula. Cleavage ends with the formation of the blastula, or of the blastocyst in mammals. Depending mostly on the concentration of yolk in the egg, the cleavage can be holoblastic (total or entire cleavage) or meroblastic (partial cleavage). The pole of the egg with the highest concentration of yolk is referred to as the vegetal pole while the opposite is referred to as the animal pole. Cleavage differs from other forms of cell division in that it increases the number of cells and nuclear mass without increasing the cytoplasmic mass. This means that with each successive subdivision, there is roughly half the cyto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically-oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachiopods, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lophotrochozoa
Lophotrochozoa (, "crest/wheel animals") is a clade of protostome animals within the Spiralia. The taxon was established as a monophyletic group based on molecular evidence. The clade includes animals like annelids, molluscs, bryozoans, brachiopods, and platyhelminthes. Groups Lophotrochozoa was defined in 1995 as the "last common ancestor of the three traditional lophophorate taxa (brachiopods, bryozoans, and phoronid worms), the mollusks and the annelids, and all of the descendants of that common ancestor". It is a cladistic definition (a node-based name), so the affiliation to Lophotrochozoa of spiralian groups not mentioned directly in the definition depends on the topology of the spiralian tree of life, and in some phylogenetic hypotheses, Lophotrochozoa may even be synonymous to Spiralia. Nemertea and Orthonectida (if not directly considered as part of Annelida) are probably lophotrochozoan phyla; Dicyemida, Gastrotricha, and Platyhelminthes may be lophotrochozoans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caenorhabditis Elegans
''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (rod-like) and Latin ''elegans'' (elegant). In 1900, Maupas initially named it '' Rhabditides elegans.'' Osche placed it in the subgenus ''Caenorhabditis'' in 1952, and in 1955, Dougherty raised ''Caenorhabditis'' to the status of genus. ''C. elegans'' is an unsegmented pseudocoelomate and lacks respiratory or circulatory systems. Most of these nematodes are hermaphrodites and a few are males. Males have specialised tails for mating that include spicules. In 1963, Sydney Brenner proposed research into ''C. elegans,'' primarily in the area of neuronal development. In 1974, he began research into the molecular and developmental biology of ''C. elegans'', which has since been extensively used as a model organism. It was the first multicellu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
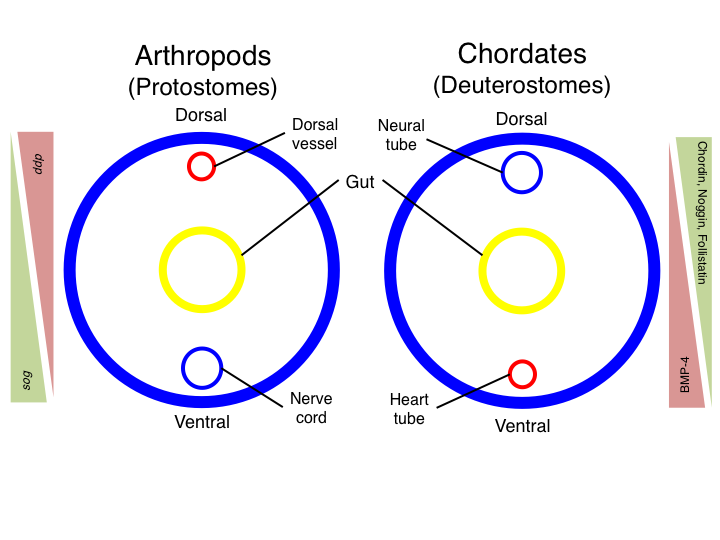
Inversion (evolutionary Biology)
In evolutionary developmental biology, inversion refers to the hypothesis that during the course of animal evolution, the structures along the dorsoventral (DV) axis have taken on an orientation opposite that of the ancestral form. Inversion was first noted in 1822 by the French zoologist Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, when he dissected a crayfish (an arthropod) and compared it with the vertebrate body plan. The idea was heavily criticised, but periodically resurfaced, and is now supported by some molecular embryologists. History As early as 1822, the French zoologist Étienne Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire noted that the organization of dorsal and ventral structures in arthropods is opposite that of mammals. Five decades later, in light of Darwin's theory of "descent with modification", German zoologist Anton Dohrn proposed that these groups arose from a common ancestor which possessed a body plan similar to that of modern annelids with a ventral nerve cord and dorsal heart. Where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protostome
Protostomia () is the clade of animals once thought to be characterized by the formation of the organism's mouth before its anus during embryonic development. This nature has since been discovered to be extremely variable among Protostomia's members, although the reverse is typically true of its sister clade, Deuterostomia. Well known examples of protostomes are arthropods, molluscs, annelids, flatworms and nematodes. They are also called schizocoelomates since schizocoely typically occurs in them. Together with the Deuterostomia and Xenacoelomorpha, these form the clade Bilateria, animals with bilateral symmetry, anteroposterior axis and three germ layers. Protostomy In animals at least as complex as earthworms, the first phase in gut development involves the embryo forming a dent on one side (the blastopore) which deepens to become its digestive tube (the archenteron). In the sister-clade, the deuterostomes (), the original dent becomes the anus while the gut eventually tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Pineapple
The sea pineapple (''Halocynthia roretzi'') is an edible ascidian (sea squirt) consumed primarily in Korea, where it is known as ''meongge'' (멍게), and to a lesser extent in Japan, where it is known as or . Sea pineapples are known for both their peculiar appearance, described by journalist Nick Tosches as "something that could exist only in a purely hallucinatory eco-system" and their peculiar taste, described as "something like iodine" and "rubber dipped in ammonia". However, aficionados claim that the taste is well suited to serving with sake. The flavor has been attributed to an unsaturated alcohol called cynthiaol, which is present in minute quantities. Sea pineapples live in shallow water, usually attached to rocks and artificial structures, an example of marine biofouling. ''Halocynthia roretzi'' is adapted to cold water: it can survive in water temperatures between , but optimum temperature is around . Aquaculture of sea pineapples first succeeded in 1982, when 39 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciona Intestinalis
''Ciona intestinalis'' (sometimes known by the common name of vase tunicate) is an ascidian (sea squirt), a tunicate with very soft tunic. Its Latin name literally means "pillar of intestines", referring to the fact that its body is a soft, translucent column-like structure, resembling a mass of intestines sprouting from a rock. It is a globally distributed cosmopolitan species. Since Linnaeus described the species, ''Ciona intestinalis'' has been used as a model invertebrate chordate in developmental biology and genomics. Studies conducted between 2005 and 2010 have shown that there are at least two, possibly four, sister species. More recently it has been shown that one of these species has already been described as ''Ciona robusta''. By anthropogenic means, the species has invaded various parts of the world and is known as an invasive species. Although Linnaeus first categorised this species as a kind of mollusk, Alexander Kovalevsky found a tadpole-like larval stage during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deuterostome
Deuterostomia (; in Greek) are animals typically characterized by their anus forming before their mouth during embryonic development. The group's sister clade is Protostomia, animals whose digestive tract development is more varied. Some examples of deuterostomes include vertebrates (and thus humans), sea stars, and crinoids. In deuterostomy, the developing embryo's first opening (the blastopore) becomes the anus, while the mouth is formed at a different site later on. This was initially the group's distinguishing characteristic, but deuterostomy has since been discovered among protostomes as well. This group is also known as enterocoelomates, because their coelom develops through enterocoely. The three major clades of deuterostomes are Chordata (e.g. vertebrates), Echinodermata (e.g. starfish), and Hemichordata (e.g. acorn worms). Together with Protostomia and their out-group Xenacoelomorpha, these compose the Bilateria, animals with bilateral symmetry and three germ layers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |