|
Largest Known Prime Number
The largest known prime number is , a number which has 41,024,320 digits when written in the decimal system. It was found on October 12, 2024, on a cloud-based virtual machine volunteered by Luke Durant, a 36-year-old researcher from San Jose, California, to the Great Internet Mersenne Prime Search (GIMPS). A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 with no divisors other than 1 and itself. Euclid's theorem proves that for any given prime number, there will always be a higher one, and thus there are infinitely many; there is no largest prime. Many of the largest known primes are Mersenne primes, numbers that are one less than a power of two, because they can utilize a Lucas–Lehmer primality test, specialized primality test that is faster than the general one. , the seven largest known primes are Mersenne primes. The last eighteen record primes were Mersenne primes. The Binary number, binary representation of any Mersenne prime is Repunit, composed of all ones, since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
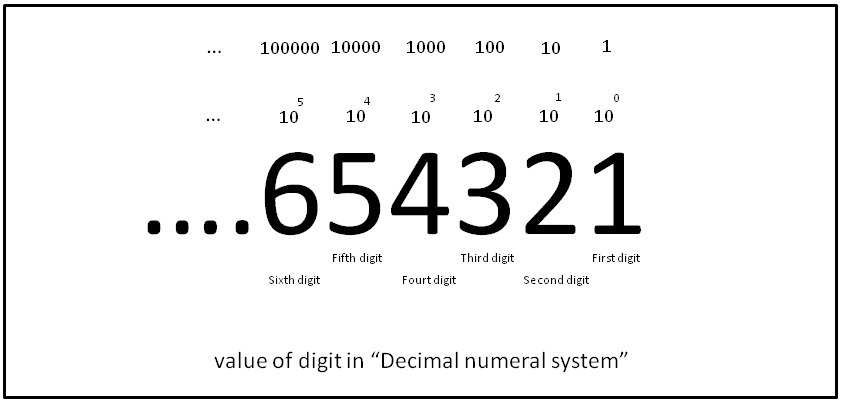
Decimal
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers (''decimal fractions'') of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. The way of denoting numbers in the decimal system is often referred to as ''decimal notation''. A decimal numeral (also often just ''decimal'' or, less correctly, ''decimal number''), refers generally to the notation of a number in the decimal numeral system. Decimals may sometimes be identified by a decimal separator (usually "." or "," as in or ). ''Decimal'' may also refer specifically to the digits after the decimal separator, such as in " is the approximation of to ''two decimals''". Zero-digits after a decimal separator serve the purpose of signifying the precision of a value. The numbers that may be represented in the decimal system are the decimal fractions. That is, fractions of the form , w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cooperative Computing Award
The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) is an American international non-profit digital rights group based in San Francisco, California. It was founded in 1990 to promote Internet civil liberties. It provides funds for legal defense in court, presents ''amicus curiae'' briefs, defends individuals and new technologies from what it considers abusive legal threats, works to expose government malfeasance, provides guidance to the government and courts, organizes political action and mass mailings, supports some new technologies which it believes preserve personal freedoms and online civil liberties, maintains a database and web sites of related news and information, monitors and challenges potential legislation that it believes would infringe on personal liberties and fair use, and solicits a list of what it considers are abusive patents with intentions to defeat those that it considers are without merit. History Foundation The Electronic Frontier Foundation was formed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
David Wheeler (computer Scientist)
David John Wheeler (9 February 1927 – 13 December 2004) was an English computer scientist and professor of computer science at the University of Cambridge. Education Wheeler was born in Birmingham, England, the second of the three children of (Agnes) Marjorie, ''née'' Gudgeon, and Arthur Wheeler, a press tool maker, engineer, and proprietor of a small shopfitting firm. He was educated at a local primary school in Birmingham and then went on to King Edward VI Camp Hill School after winning a scholarship in 1938. His education was disrupted by World War II, and he completed his sixth form studies at Hanley High School. In 1945 he gained a scholarship to study the Cambridge Mathematical Tripos at Trinity College, Cambridge, graduating in 1948. He was awarded the world's first PhD in computer science in 1951. Career Wheeler's contributions to the field included work on the Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Calculator (EDSAC) in the 1950s and the Burrows–Wheeler tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Édouard Lucas
__NOTOC__ François Édouard Anatole Lucas (; 4 April 1842 – 3 October 1891) was a French mathematician. Lucas is known for his study of the Fibonacci sequence. The related Lucas sequences and Lucas numbers are named after him. Biography Lucas was born in Amiens and educated at the École Normale Supérieure. He worked in the Paris Observatory and later became a professor of mathematics at the Lycée Saint Louis and the Lycée Charlemagne in Paris. Lucas served as an artillery officer in the French Army during the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871. In 1875, Lucas posed a challenge to prove that the only solution of the Diophantine equation :\sum_^ n^2 = M^2\; with ''N'' > 1 is when ''N'' = 24 and ''M'' = 70. This is known as the cannonball problem, since it can be visualized as the problem of taking a square arrangement of cannonballs on the ground and building a square pyramid out of them. It was not until 1918 that a proof (using elliptic functions) was found for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |