|
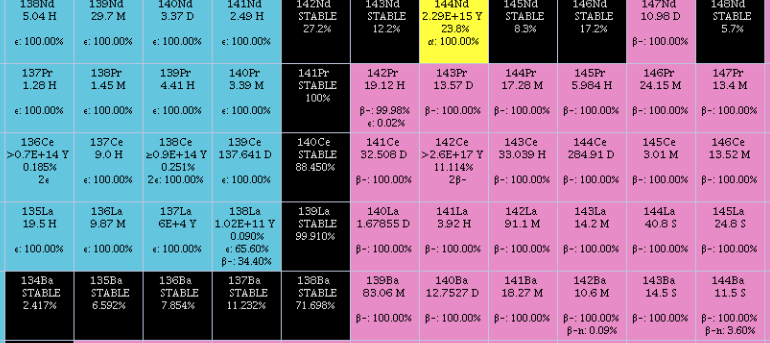
Lanthanum Bromide
Lanthanum(III) bromide (LaBr3) is an inorganic halide salt of lanthanum. When pure, it is a colorless white powder. The single crystals of LaBr3 are hexagonal crystals with melting point of 783 °C. It is highly hygroscopic and water-soluble. There are several hydrates, La3Br·x H2O, of the salt also known. It is often used as a source of lanthanum in chemical synthesis and as a scintillation material in certain applications. Lanthanum bromide scintillation detector The scintillator material cerium activated lanthanum bromide (LaBr3:Ce) was first produced in 2001. LaBr3:Ce-based radiation detectors offer improved energy resolution, fast emission and excellent temperature and linearity characteristics. Typical energy resolution at 662 keV is 3% as compared to sodium iodide detectors at 7%. The improved resolution is due to a photoelectron yield that is 160% greater than is achieved with sodium iodide. Another advantage of LaBr3:Ce is the nearly flat photo emission over a 70&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hygroscopic
Hygroscopy is the phenomenon of attracting and holding water molecules via either absorption or adsorption from the surrounding environment, which is usually at normal or room temperature. If water molecules become suspended among the substance's molecules, adsorbing substances can become physically changed, e.g., changing in volume, boiling point, viscosity or some other physical characteristic or property of the substance. For example, a finely dispersed hygroscopic powder, such as a salt, may become clumpy over time due to collection of moisture from the surrounding environment. ''Deliquescent'' materials are sufficiently hygroscopic that they absorb so much water that they become liquid and form an aqueous solution. Etymology and pronunciation The word ''hygroscopy'' () uses combining forms of '' hygro-'' and '' -scopy''. Unlike any other ''-scopy'' word, it no longer refers to a viewing or imaging mode. It did begin that way, with the word ''hygroscope'' referring in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum Bromide
Lanthanum(III) bromide (LaBr3) is an inorganic halide salt of lanthanum. When pure, it is a colorless white powder. The single crystals of LaBr3 are hexagonal crystals with melting point of 783 °C. It is highly hygroscopic and water-soluble. There are several hydrates, La3Br·x H2O, of the salt also known. It is often used as a source of lanthanum in chemical synthesis and as a scintillation material in certain applications. Lanthanum bromide scintillation detector The scintillator material cerium activated lanthanum bromide (LaBr3:Ce) was first produced in 2001. LaBr3:Ce-based radiation detectors offer improved energy resolution, fast emission and excellent temperature and linearity characteristics. Typical energy resolution at 662 keV is 3% as compared to sodium iodide detectors at 7%. The improved resolution is due to a photoelectron yield that is 160% greater than is achieved with sodium iodide. Another advantage of LaBr3:Ce is the nearly flat photo emission over a 70&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphors And Scintillators
A phosphor is a substance that exhibits the phenomenon of luminescence; it emits light when exposed to some type of radiant energy. The term is used both for fluorescent or phosphorescent substances which glow on exposure to ultraviolet or visible light, and cathodoluminescent substances which glow when struck by an electron beam (cathode rays) in a cathode-ray tube. When a phosphor is exposed to radiation, the orbital electrons in its molecules are excited to a higher energy level; when they return to their former level they emit the energy as light of a certain color. Phosphors can be classified into two categories: fluorescent substances which emit the energy immediately and stop glowing when the exciting radiation is turned off, and phosphorescent substances which emit the energy after a delay, so they keep glowing after the radiation is turned off, decaying in brightness over a period of milliseconds to days. Fluorescent materials are used in applications in which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bromides
A bromide ion is the negatively charged form (Br−) of the element bromine, a member of the halogens group on the periodic table. Most bromides are colorless. Bromides have many practical roles, being found in anticonvulsants, flame-retardant materials, and cell stains. Although uncommon, chronic toxicity from bromide can result in bromism, a syndrome with multiple neurological symptoms. Bromide toxicity can also cause a type of skin eruption, see potassium bromide. The bromide ion has an ionic radius of 196 pm. Natural occurrence Bromide is present in typical seawater (35 PSU) with a concentration of around 65 mg/L, which is about 0.2% of all dissolved salts. Seafood and deep sea plants generally have higher levels than land-derived foods. Bromargyrite—natural, crystalline silver bromide—is the most common bromide mineral known but is still very rare. In addition to silver, bromine is also in minerals combined with mercury and copper. Formation and react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanthanum Compounds
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57. It is a soft, ductile, silvery-white metal that tarnishes slowly when exposed to air. It is the eponym of the lanthanide series, a group of 15 similar elements between lanthanum and lutetium in the periodic table, of which lanthanum is the first and the prototype. Lanthanum is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements. Like most other rare earth elements, the usual oxidation state is +3. Lanthanum has no biological role in humans but is essential to some bacteria. It is not particularly toxic to humans but does show some antimicrobial activity. Lanthanum usually occurs together with cerium and the other rare earth elements. Lanthanum was first found by the Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1839 as an impurity in cerium nitrate – hence the name ''lanthanum'', from the Ancient Greek (), meaning 'to lie hidden'. Although it is classified as a rare earth element, lanthanum is the 28th most abund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Isotope
A medical isotope is an isotope used in medicine. The first uses of isotopes in medicine were in radiopharmaceuticals, and this is still the most common use. However more recently, separated stable isotopes have also come into use. Examples of non-radioactive medical isotopes are: * Deuterium in deuterated drugs * Carbon-13 used in liver function Liver function tests (LFTs or LFs), also referred to as a hepatic panel, are groups of blood tests that provide information about the state of a patient's liver. These tests include prothrombin time (PT/INR), activated partial thromboplastin tim ... and metabolic tests Radioactive isotopes used Radioactive isotopes are used in medicine for both treatment and diagnostic scans. The most common isotope used in diagnostic scans is Tc-99m (Technetium-99m), being used in approximately 85% of all nuclear medicine diagnostic scans worldwide. It is used for diagnoses involving a large range of body parts and diseases such as cancers and n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homeland Security
Homeland security is an American national security term for "the national effort to ensure a homeland that is safe, secure, and resilient against terrorism and other hazards where American interests, aspirations, and ways of life can thrive" to the "national effort to prevent terrorist attacks within the United States, reduce the vulnerability of the U.S. to terrorism, and minimize the damage from attacks that do occur." According to an official work published by the Congressional Research Service in 2013, the "Homeland security" term's definition has varied over time. Homeland security is not constrained to terrorist incidents. Terrorism is violent, criminal acts committed by individuals and/or groups to further ideological goals stemming from influences, such as those of a political, religious, social, racial, or environmental nature. Within the US, an all-hazards approach exists regarding homeland security endeavors. In this sense, homeland security encompasses both natural d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioisotope
A radionuclide (radioactive nuclide, radioisotope or radioactive isotope) is a nuclide that has excess nuclear energy, making it unstable. This excess energy can be used in one of three ways: emitted from the nucleus as gamma radiation; transferred to one of its electrons to release it as a conversion electron; or used to create and emit a new particle (alpha particle or beta particle) from the nucleus. During those processes, the radionuclide is said to undergo radioactive decay. These emissions are considered ionizing radiation because they are energetic enough to liberate an electron from another atom. The radioactive decay can produce a stable nuclide or will sometimes produce a new unstable radionuclide which may undergo further decay. Radioactive decay is a random process at the level of single atoms: it is impossible to predict when one particular atom will decay. However, for a collection of atoms of a single nuclide the decay rate, and thus the half-life (''t''1/2) for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamma Spectroscopy
Gamma-ray spectroscopy is the quantitative study of the energy spectra of gamma-ray sources, such as in the nuclear industry, geochemical investigation, and astrophysics. Most radioactive sources produce gamma rays, which are of various energies and intensities. When these emissions are detected and analyzed with a spectroscopy system, a gamma-ray energy spectrum can be produced. A detailed analysis of this spectrum is typically used to determine the identity and quantity of gamma emitters present in a gamma source, and is a vital tool in radiometric assay. The gamma spectrum is characteristic of the gamma-emitting nuclides contained in the source, just like in an optical spectrometer, the optical spectrum is characteristic of the material contained in a sample. Gamma ray characteristics Gamma rays are the highest-energy form of electromagnetic radiation, being physically the same as all other forms (e.g., X-rays, visible light, infrared, radio) but having (in general) higher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Photomultiplier
Silicon photomultipliers, often called "SiPM" in the literature, are solid-state single-photon-sensitive devices based on Single-photon avalanche diode (SPAD) implemented on common silicon substrate. The dimension of each single SPAD can vary from 10 to 100 micrometres, and their density can be up to 10000 per square millimeter. Every SPAD in SiPM operates in Geiger mode and is coupled with the others by a metal or polysilicon quenching resistor. Although the device works in digital/switching mode, most of SiPM are an analog device because all the microcells are read in parallel, making it possible to generate signals within a dynamic range from a single photon to 1000 photons for a device with just a square-millimeter area. More advanced readout schemes are utilized for the lidar applications. The supply voltage (''V''b) depends on APD technology used and typically varies between 20 V and 100 V, thus being from 15 to 75 times lower than the voltage required for a traditional pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Drift Detector
Silicon drift detectors (SDDs) are X-ray radiation detectors used in x-ray spectrometry ( XRF and EDS) and electron microscopy. Their chief characteristics compared with other X-ray detectors are: *high count rates *comparatively high energy resolution (e.g. 125 eV for Mn Kα wavelength) *Peltier cooling Working principle Like other solid state X-ray detectors, silicon drift detectors measure the energy of an incoming photon by the amount of ionization it produces in the detector material. This varying ionization produces varying charge, which the detector electronics measure for each incoming photon. In the SDD, this material is high purity silicon with a very low leakage current. The high purity allows for the use of Peltier cooling instead of the traditional liquid nitrogen. The major distinguishing feature of a SDD is the transversal field generated by a series of ring electrodes that causes charge carriers to 'drift' to a small collection electrode. The 'drift' concept of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photomultiplier
A photomultiplier is a device that converts incident photons into an electrical signal. Kinds of photomultiplier include: * Photomultiplier tube, a vacuum tube converting incident photons into an electric signal. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs for short) are members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically vacuum phototubes, which are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. ** Magnetic photomultiplier, developed by the Soviets in the 1930s. ** Electrostatic photomultiplier, a kind of photomultiplier tube demonstrated by Jan Rajchman of RCA Laboratories in Princeton, NJ in the late 1930s which became the standard for all future commercial photomultipliers. The first mass-produced photomultiplier, the Type 931, was of this design and is still commercially produced today. * Silicon photomultiplier, a solid-state device converting incident photons into an electric signal. Silicon photomultiplie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |