|
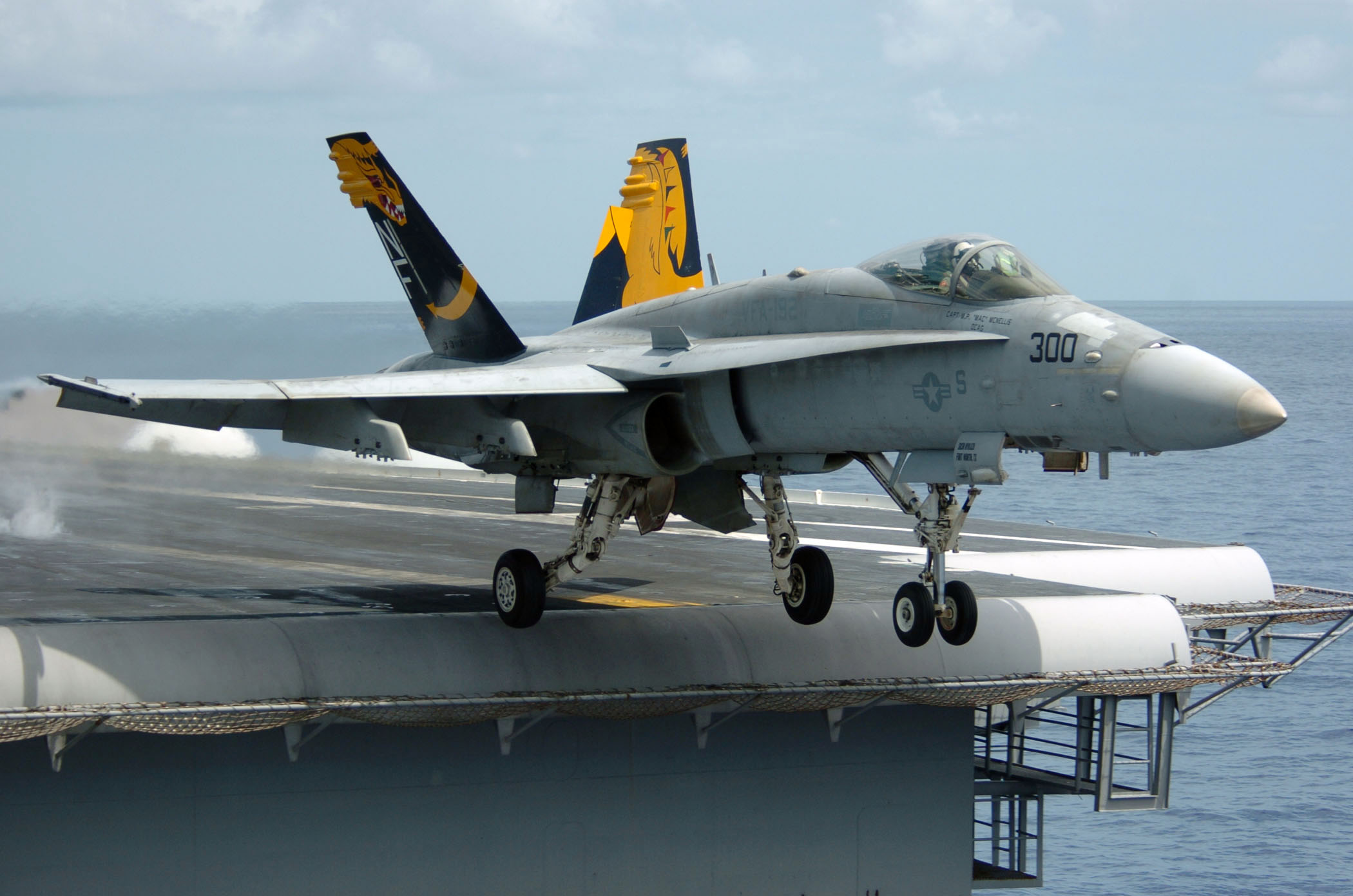
Landing Signal Officer
A landing signal officer or landing safety officer (LSO), also informally known as paddles (United States Navy) or batsman (Royal Navy), is a naval aviator specially trained to facilitate the "safe and expeditious recovery" of naval aircraft aboard aircraft carriers. LSOs aboard smaller air capable ships that launch and recover helicopters are informally known as deck. Originally LSOs were responsible for bringing aircraft aboard ship using hand-operated signals. Since the introduction of optical landing systems in the 1950s, LSOs assist pilots by giving information via radio handsets. History In the United States Navy, aircraft carrier operations began with USS ''Langley'' (CV-1) in 1922, and it served as a platform to experiment and develop aircraft launch and recovery procedures.Tate, Jackson R., RADM USN "We Rode the Covered Wagon" ''United States Naval Institute Proceedings'' October 1978 p.66-68 The first pilots had no signaling system for assistance from shipboard pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-4B Of VF-21 Returns To USS Midway (CVA-41) Off Vietnam In 1965
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American Tandem#Aviation, tandem two-seat, twinjet, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic aircraft, supersonic jet interceptor aircraft, interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed by McDonnell Aircraft for the United States Navy.Swanborough and Bowers 1976, p. 301. Proving highly adaptable, it entered service with the Navy in 1961 before it was adopted by the United States Marine Corps and the United States Air Force, and by the mid-1960s it had become a major part of their air arms. Phantom production ran from 1958 to 1981 with a total of 5,195 aircraft built, making it the List of most produced aircraft, most produced American supersonic military aircraft in history, and cementing its position as an iconic combat aircraft of the Cold War. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martlet Landing On HMS Indomitable (92)
A martlet in English heraldry is a mythical bird without feet that never roosts from the moment of its drop-birth until its death fall; martlets are proposed to be continuously on the wing. It is a compelling allegory for continuous effort, expressed in heraldic charge depicting a stylised bird similar to a swift or a house martin, without feet. It should be distinguished from the ''merlette'' of French heraldry, which is a duck-like bird with a swan-neck and chopped-off beak and legs. The Common Swift rarely lands outside breeding season, and sleeps while airborne. Etymology The word "martlet" is derived from the bird known as the martin, with the addition of the diminutive suffix "-let"; thus martlet means "little martin". The origin of the name martin is obscure, though it may refer to the festival Martinmas, which occurs around the same time martins begin their migration from Europe to Africa. Description These mythical birds are shown properly in English heraldry with two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
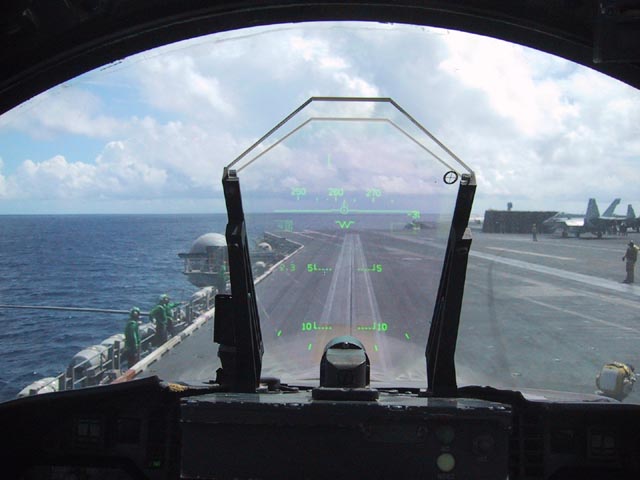
Head-up Display
A head-up display, or heads-up display, also known as a HUD (), is any transparent display that presents data without requiring users to look away from their usual viewpoints. The origin of the name stems from a pilot being able to view information with the head positioned "up" and looking forward, instead of angled down looking at lower instruments. A HUD also has the advantage that the pilot's eyes do not need to refocus to view the outside after looking at the optically nearer instruments. Although they were initially developed for military aviation, HUDs are now used in commercial aircraft, automobiles, and other (mostly professional) applications. Head-up displays were a precursor technology to augmented reality (AR), incorporating a subset of the features needed for the full AR experience, but lacking the necessary registration and tracking between the virtual content and the user's real-world environment. Overview A typical HUD contains three primary components: a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port (nautical)
Port and starboard are nautical terms for watercraft and aircraft, referring respectively to the left and right sides of the vessel, when aboard and facing the bow (front). Vessels with bilateral symmetry have left and right halves which are mirror images of each other. One asymmetric feature is where access to a boat, ship, or aircraft is at the side, it is usually only on the port side (hence the name). Side Port and starboard unambiguously refer to the left and right side of the vessel, not the observer. That is, the port side of the vessel always refers to the same portion of the vessel's structure, and does not depend on which way the observer is facing. The port side is the side of the vessel which is to the left of an observer aboard the vessel and , that is, facing forward towards the direction the vehicle is heading when underway, and starboard side is to the right of such an observer. This convention allows orders and information to be given unambiguously, without ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landing Signal Officers Aboard USS Harry S
Landing is the last part of a flight, where a flying animal, aircraft, or spacecraft returns to the ground. When the flying object returns to water, the process is called alighting, although it is commonly called "landing", "touchdown" or "splashdown" as well. A normal aircraft flight would include several parts of flight including taxi, takeoff, climb, cruise, descent and landing. Aircraft Aircraft usually land at an airport on a firm runway or helicopter landing pad, generally constructed of asphalt concrete, concrete, gravel or grass. Aircraft equipped with pontoons (floatplane) or with a boat hull-shaped fuselage (a flying boat) are able to land on water. Aircraft also sometimes use skis to land on snow or ice. To land, the airspeed and the rate of descent are reduced such that the object descends at a low enough rate to allow for a gentle touch down. Landing is accomplished by slowing down and descending to the runway. This speed reduction is accomplished by redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Aviator
Naval aviation is the application of military air power by navies, whether from warships that embark aircraft, or land bases. Naval aviation is typically projected to a position nearer the target by way of an aircraft carrier. Carrier-based aircraft must be sturdy enough to withstand demanding carrier operations. They must be able to launch in a short distance and be sturdy and flexible enough to come to a sudden stop on a pitching flight deck; they typically have robust folding mechanisms that allow higher numbers of them to be stored in below-decks hangars and small spaces on flight decks. These aircraft are designed for many purposes, including air-to-air combat, surface attack, submarine attack, search and rescue, matériel transport, weather observation, reconnaissance and wide area command and control duties. Naval helicopters can be used for many of the same missions as fixed-wing aircraft while operating from aircraft carriers, helicopter carriers, destroyers and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NAS Oceana
Naval Air Station (NAS) Oceana or NAS Oceana is a United States Navy Naval Air Station located in Virginia Beach, Virginia. Nowadays, the station is located on 23.9 km2. It has total of 250 aircraft deployed and buildings valued at $800 million in plant replacement value. The total Navy community (which includes spouses) count for around 20.000 people. The base is under the jurisdiction of Navy Region Mid-Atlantic and is the headquarters of Strike Fighter Wing Atlantic and Carrier Air Wing 1, Carrier Air Wings 1, Carrier Air Wing Three, 3, Carrier Air Wing Seven, 7 and Carrier Air Wing Eight, 8. As home to all East Coast strike fighter jet squadrons, the Naval Air Station is classified as a master jet base. The airfield is known as Apollo Soucek Field, named after Lieutenant (later Admiral) Apollo Soucek, a Navy test pilot who set the global altitude record in 1930 by flying a Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company, Curtiss ''"Hawk"'' biplane to an altitude of 43,166 feet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angled Flight Deck
The flight deck of an aircraft carrier is the surface from which its aircraft take off and land, essentially a miniature airfield at sea. On smaller naval ships which do not have aviation as a primary mission, the landing area for helicopters and other VTOL aircraft is also referred to as the flight deck. The official U.S. Navy term for these vessels is "air-capable ships". Flight decks have been in use upon ships since 1910, the American pilot Eugene Ely being the first individual to take off from a warship. Initially consisting of wooden ramps built over the forecastle of capital ships, a number of battlecruisers, including the British and , the American and , and the Japanese Akagi and battleship Kaga, were converted to aircraft carriers during the interwar period. The first aircraft carrier to feature a full-length flight deck, akin to the configuration of the modern vessels, was the converted liner . The armoured flight deck was another innovation pioneered by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Landing System, Day, Aboard USS John F
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light. Because light is an electromagnetic wave, other forms of electromagnetic radiation such as X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves exhibit similar properties. Most optical phenomena can be accounted for by using the classical electromagnetic description of light. Complete electromagnetic descriptions of light are, however, often difficult to apply in practice. Practical optics is usually done using simplified models. The most common of these, geometric optics, treats light as a collection of rays that travel in straight lines and bend when they pass through or reflect from surfaces. Physical optics is a more comprehensive model of light, which includes wave effects such as diffraction and interference that cannot be acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
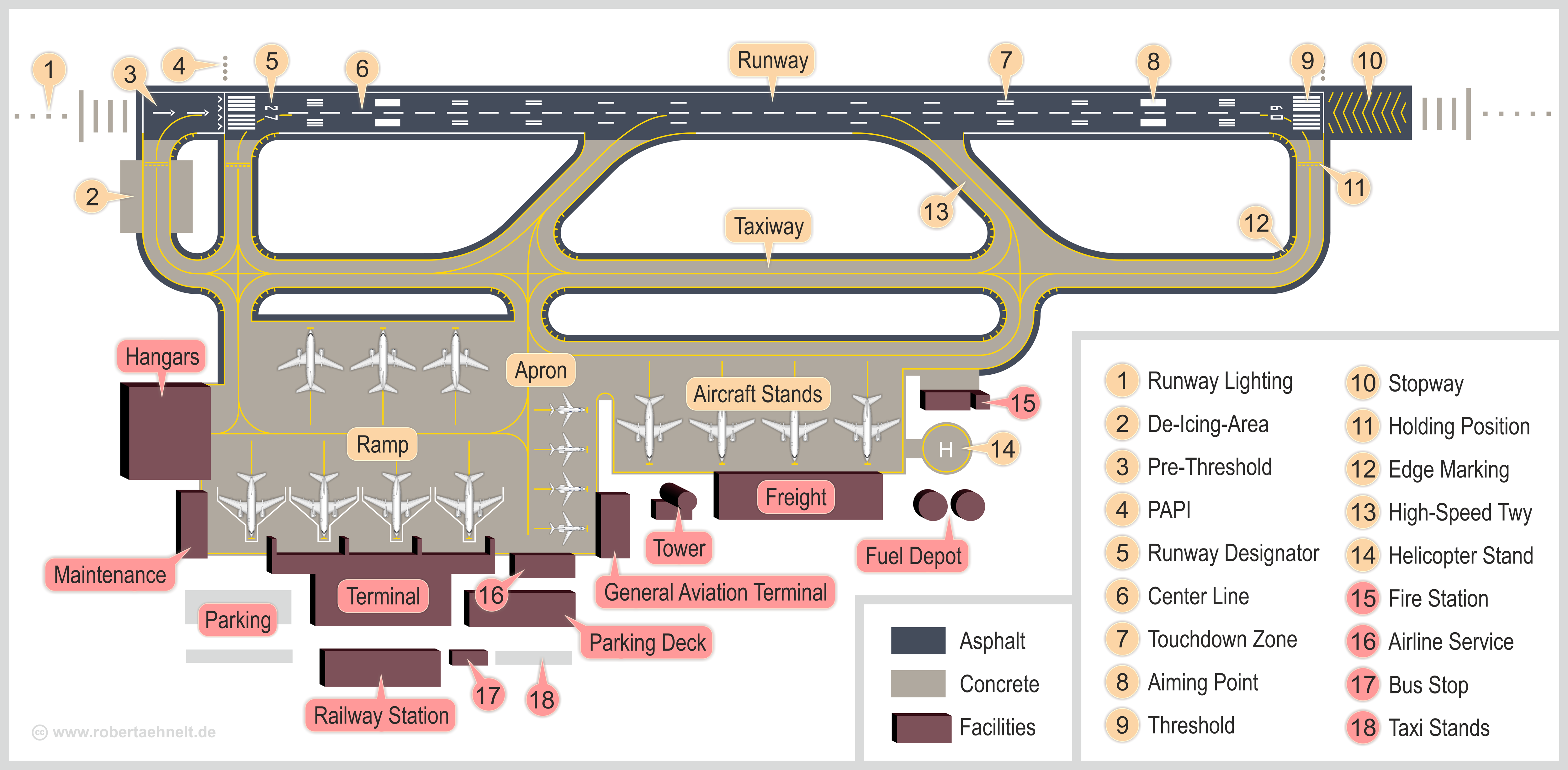
Airports
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface such as a runway for a plane to take off and to land or a helipad, and often includes adjacent utility buildings such as control towers, hangars and terminals, to maintain and monitor aircraft. Larger airports may have airport aprons, taxiway bridges, air traffic control centres, passenger facilities such as restaurants and lounges, and emergency services. In some countries, the US in particular, airports also typically have one or more fixed-base operators, serving general aviation. Operating airports is extremely complicated, with a complex system of aircraft support services, passenger services, and aircraft control services contained within the operation. Thus airports can be major employers, as well as important hubs for tourism a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)