|
Lakes Of Rotorua
The region around the city of Rotorua, in New Zealand's North Island, contains several lakes. From biggest to smallest, these are Lake Rotorua (Second Lake), Lake Tarawera, Lake Rotoiti (Small Lake), Lake Rotoma (White Lake), Lake Okataina, Lake Rotoehu (Muddy Lake), Lake Rotomahana (Warm Lake), Lake Rerewhakaaitu, Lake Rotokakahi (Green Lake), Lake Okareka and Lake Tikitapu (Blue lake). There are also four smaller lakes: Lake Okaro/Ngakaro, Lake Rotokawa (not to be confused with Lake Rotokawa near Taupo), Lake Rotokawau and Lake Rotongata (Mirror Lake). Most of the lakes have formed due to volcanic activity. The region is part of the Taupo Volcanic Zone, the world's most active area of explosive silicic volcanic activity in geologically recent time. Geographic statistics Lake Rotorua Lake Rotorua is the largest of the lakes with Lake Tarawera close behind, it is also the second largest lake in the North Island by surface area and covers 79.8 square kilometers. With a ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotorua
Rotorua () is a city in the Bay of Plenty region of New Zealand's North Island. The city lies on the southern shores of Lake Rotorua, from which it takes its name. It is the seat of the Rotorua Lakes District, a territorial authority encompassing Rotorua and several other nearby towns. Rotorua has an estimated resident population of , making it the country's 12th largest urban area, and the Bay of Plenty's second largest urban area behind Tauranga. Rotorua is a major destination for both domestic and international tourists; the tourism industry is by far the largest industry in the district. It is known for its geothermal activity, and features geysers – notably the Pōhutu Geyser at Whakarewarewa – and hot mud pools. This thermal activity is sourced to the Rotorua Caldera, in which the town lies. Rotorua is home to the Toi Ohomai Institute of Technology. History The name Rotorua comes from the Māori language, where the full name for the city and lake is . ''Roto'' m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Okareka
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotorua Lakes District
Rotorua Lakes District or Rotorua District is a Territorial authorities of New Zealand, territorial authority district in the North Island of New Zealand. It has one urban area of significant size, the city of Rotorua. The district is governed by Rotorua Lakes Council, which is headquartered in Rotorua and is headed by a mayor. The district falls within two Regions of New Zealand, regional council areas, with the majority of the area and Rotorua city in the Bay of Plenty region and the rest in the Waikato region. Tania Tapsell has been the mayor of Rotorua since the 2022 local elections. History Rotorua has an unusual history as the town was built by the Government as a tourist destination in the 1880s. Through the Rotorua Borough Act 1922, which achieved royal assent on 28 September 1922, the Rotorua Borough was formed. The inaugural elections for mayor were held in February 1923 and Cecil Clinkard was successful. In 1962, Rotorua was proclaimed a city. In 1979, the status was c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pumice
Pumice (), called pumicite in its powdered or dust form, is a volcanic rock that consists of highly vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which may or may not contain crystals. It is typically light-colored. Scoria is another vesicular volcanic rock that differs from pumice in having larger vesicles, thicker vesicle walls, and being dark colored and denser.Jackson, J.A., J. Mehl, and K. Neuendorf (2005) ''Glossary of Geology'' American Geological Institute, Alexandria, Virginia. 800 pp. McPhie, J., M. Doyle, and R. Allen (1993) ''Volcanic Textures A guide to the interpretation of textures in volcanic rocks'' Centre for Ore Deposit and Exploration Studies, University of Tasmania, Hobart, Tasmania..198 pp. Pumice is created when super-heated, highly pressurized rock is violently ejected from a volcano. The unusual foamy configuration of pumice happens because of simultaneous rapid cooling and rapid depressurization. The depressurization creates bubbles by lowering the solubi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent to granite. Rhyolitic magma is extremely viscous, due to its high silica content. This favors explosive eruptions over effusive eruptions, so this type of magma is more often erupted as pyroclastic rock than as lava flows. Rhyolitic ash-flow tuffs are among the most voluminous of continental igneous rock formations. Rhyolitic tuff has been extensively used for construction. Obsidian, which is rhyolitic volcanic glass, has been used for tools from prehistoric times to the present day because it can be shaped to an extremely sharp edge. Rhyolitic pumice finds use as an abrasive, in concrete, and as a soil amendment. Description Rhyolite i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Tarawera
Mount Tarawera is a volcano on the North Island of New Zealand within the older but volcanically productive Ōkataina Caldera. Located 24 kilometres southeast of Rotorua, it consists of a series of rhyolitic lava domes that were fissured down the middle by an explosive basaltic eruption in 1886. This eruption was one of New Zealand's largest historical eruptions, and killed an estimated 120 people. The fissures run for about northeast-southwest. The volcano's component domes include Ruawahia Dome (the highest at 1,111 metres), Tarawera Dome and Wahanga Dome. It is surrounded by several lakes, most of which were created or drastically altered by the 1886 eruption. These lakes include Lakes Tarawera, Rotomahana, Rerewhakaaitu, Ōkataina, Ōkareka, Tikitapu / Blue and Rotokākahi / Green. The Tarawera River runs northeastwards across the northern flank of the mountain from Lake Tarawera. In 2000, the mountain was ceded to the Ngāti Rangitihi sub-tribe of Te Araw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bay Of Plenty
The Bay of Plenty ( mi, Te Moana-a-Toi) is a region of New Zealand, situated around a bight of the same name in the northern coast of the North Island. The bight stretches 260 km from the Coromandel Peninsula in the west to Cape Runaway in the east. The Bay of Plenty Region, governed by the Bay of Plenty Regional Council, incorporates several large islands in the bay, in addition to the mainland area. Called ''Te Moana-a-Toi'' (the Sea of Toi) in the Māori language after Toi, an early ancestor, the name 'Bay of Plenty' was bestowed by James Cook in 1769 when he noticed the abundant food supplies at several Māori villages there, in stark contrast to observations he had made earlier in Poverty Bay. History According to local Māori traditions, the Bay of Plenty was the landing point of several migration canoes that brought Māori settlers to New Zealand. These include the ''Mātaatua'', ''Nukutere'', ''Tākitimu'', '' Arawa'' and ''Tainui'' canoes. Many of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
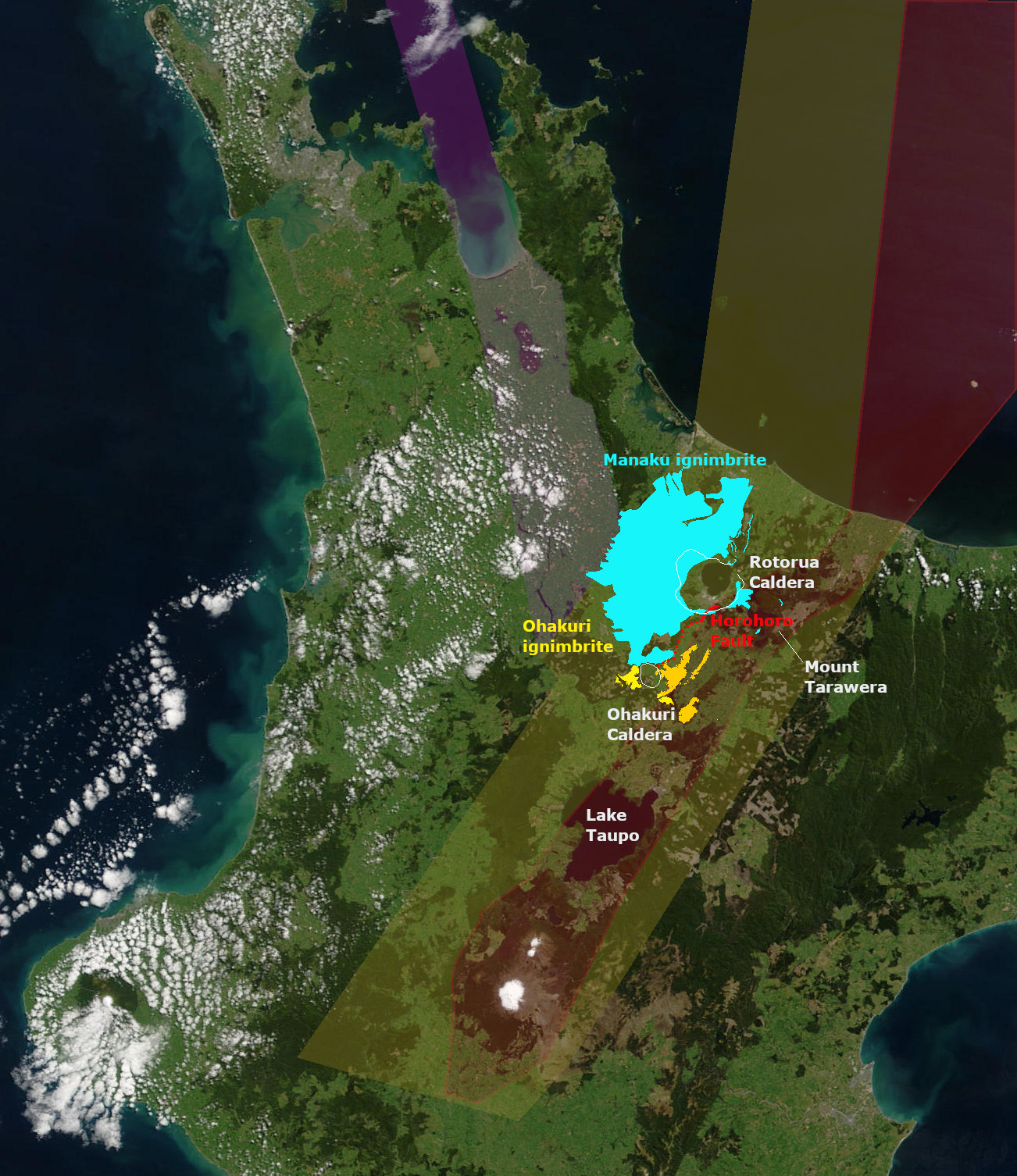
Rotorua Caldera
The Rotorua Caldera, now in filled with Lake Rotorua, is a large rhyolitic caldera. It is one of several large volcanoes located in the Taupō Volcanic Zone on the North Island of New Zealand. Geography The major regional settlement of Rotorua is located in the caldera. There is geothermal activity in the city of Rotorua and the geothermal areas of Tikitere and Whakarewarewa are associated with the caldera. These areas are still associated with small hydrothermal eruptions. Geology Eruption history The caldera was formed in a single event paired List of large volcanic eruptions, major eruption, that lasted only weeks, is now dated about 240,000 years ago, and which ejected more than of rhyolitic Mamaku ignimbrite giving it a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 7. The eruption has been reinterpreted as a paired eruption with a very slightly later, slightly smaller southerly eruption from the same mush body feeding the Ohakuri Caldera. Ignimbrite, up to thick covering about , was depo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Tikitapu
Lake Tikitapu, more commonly known as Blue Lake, is the smallest of four small lakes lying between Lake Rotorua and Lake Tarawera in the Bay of Plenty Region of New Zealand's North Island. The other three are Lake Rotokakahi (Green Lake), Lake Okareka, and Lake Okataina. Lake Tikitapu gets its name, Blue Lake, for its aqua colour. Its stunning blue colour can be attributed to the pumice and rhyolite that lies on the lake bed. Lake Tikitapu was formed 13,300 years ago as the result of a lava dam. The lake has a flat bed and, as a collapsed volcanic crater, it only has a maximum depth of 27.5m. The lake is approximately 150 hectares in size, with a catchment size of 620 hectares. Activities and Leisure There are plenty of activities to do on and surrounding the lake. On the lake, swimming, boating, trout fishing and watersports are popular activities. Both rainbow trout and brook trout reside in the lake, making it very popular with experienced and recreational fishers. Popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Rotokakahi
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle. Lakes are distinct from lagoons, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zones, and areas with ongoing glaciation. Other lakes are found in endorheic basins or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_2020.jpg)