|
Labyrinthine Artery
The labyrinthine artery (auditory artery, internal auditory artery) is a branch of either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery or the basilar artery. It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) through the internal acoustic meatus. It supplies blood to the internal ear. Structure The labyrinthine artery is a branch of either the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) or the basilar artery. It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) through the internal acoustic meatus. It divides into a cochlear branch and a labyrinthine (or anterior vestibular) branch. Function The labyrinthine artery supplies blood to the inner ear. It also supplies the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) along its length. Clinical significance The labyrinthine artery may become occluded. This can cause loss of hearing and balance on the affected side. History The labyrinthine artery may also be known as the internal auditory artery or the auditory artery. See also * Intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) is one of three pairs of arteries that supplies blood to the cerebellum. It arises from the basilar artery on each side at the level of the junction between the medulla oblongata and the pons in the brainstem. It has a variable course, passing backward to be distributed to the anterior part of the undersurface of the cerebellum, anastomosing with both the posterior inferior cerebellar (PICA) branch of the vertebral artery and the superior cerebellar artery. It also gives off the internal auditory or labyrinthine artery in most cases; however, the labyrinthine artery can less commonly emerge as a branch of the basilar artery. The amount of tissue supplied by the AICA is variable, depending upon whether the PICA is more or less dominant, but usually includes the anteroinferior surface of the cerebellum, the flocculus, middle cerebellar peduncle and inferolateral portion of the pons. Clinical significance Occlusion of AICA is conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilar Artery
The basilar artery () is one of the arteries that supplies the brain with oxygen-rich blood. The two vertebral arteries and the basilar artery are known as the vertebral basilar system, which supplies blood to the posterior part of the circle of Willis and joins with blood supplied to the anterior part of the circle of Willis from the internal carotid arteries. Structure The basilar artery arises from the union of the two vertebral arteries at the junction between the medulla oblongata and the pons between the abducens nerves (CN VI). The diameter of the basilar artery range from 1.5 to 6.6 mm. It ascends superiorly in the basilar sulcus of the ventral pons and divides at the junction of the midbrain and pons into the posterior cerebral arteries. Its branches from caudal to rostral include: *anterior inferior cerebellar artery *labyrinthine artery (<15% of people, usually branches from the anterior inferior cerebellar artery) * |
Internal Auditory Veins
The veins of the vestibule and semicircular canals accompany the arteries, and, receiving those of the cochlea at the base of the modiolus, unite to form the internal auditory veins (or veins of labyrinth) which end in the posterior part of the superior petrosal sinus or in the transverse sinus The transverse sinuses (left and right lateral sinuses), within the human head, are two areas beneath the brain which allow blood to drain from the back of the head. They run laterally in a groove along the interior surface of the occipital bone. .... References Veins of the head and neck {{Portal bar, Anatomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
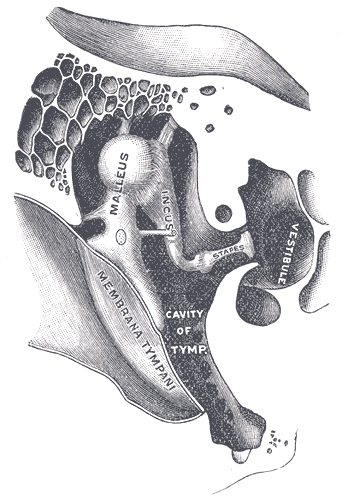
Inner Ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts: * The cochlea, dedicated to hearing; converting sound pressure patterns from the outer ear into electrochemical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve. * The vestibular system, dedicated to balance The inner ear is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear is innervated by the eighth cranial nerve in all vertebrates. Structure The labyrinth can be divided by layer or by region. Bony and membranous labyrinths The bony labyrinth, or osseous labyrinth, is the network of passages with bony walls lined with periosteum. The three major parts of the bony labyrinth are the vestib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
The anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) is one of three pairs of arteries that supplies blood to the cerebellum. It arises from the basilar artery on each side at the level of the junction between the medulla oblongata and the pons in the brainstem. It has a variable course, passing backward to be distributed to the anterior part of the undersurface of the cerebellum, anastomosing with both the posterior inferior cerebellar (PICA) branch of the vertebral artery and the superior cerebellar artery. It also gives off the internal auditory or labyrinthine artery in most cases; however, the labyrinthine artery can less commonly emerge as a branch of the basilar artery. The amount of tissue supplied by the AICA is variable, depending upon whether the PICA is more or less dominant, but usually includes the anteroinferior surface of the cerebellum, the flocculus, middle cerebellar peduncle and inferolateral portion of the pons. Clinical significance Occlusion of AICA is conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibulocochlear Nerve
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain. Through olivocochlear fibers, it also transmits motor and modulatory information from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem to the cochlea. Structure The vestibulocochlear nerve consists mostly of bipolar neurons and splits into two large divisions: the cochlear nerve and the vestibular nerve. Cranial nerve 8, the vestibulocochlear nerve, goes to the middle portion of the brainstem called the pons (which then is largely composed of fibers going to the cerebellum). The 8th cranial nerve runs between the base of the pons and medulla oblongata (the lower portion of the brainstem). This junction between the pons, medulla, and cerebellum that contains the 8th nerve is called the cerebellopontine angle. The vestibulocochlear nerv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Acoustic Meatus
The internal auditory meatus (also meatus acusticus internus, internal acoustic meatus, internal auditory canal, or internal acoustic canal) is a canal within the petrous part of the temporal bone of the skull between the posterior cranial fossa and the inner ear. Structure The opening to the meatus is called the porus acusticus internus or internal acoustic opening. It is located inside the posterior cranial fossa of the skull, near the center of the posterior surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone. The size varies considerably. Its outer margins are smooth and rounded. The canal which comprises the internal auditory meatus is short (about 1 cm) and runs laterally into the bone. The lateral (outer) aspect of the canal is known as the fundus. The fundus is subdivided by two thin crests of bone to form three separate canals, through which course the facial and vestibulocochlear nerve branches. The falciform crest first divides the meatus into superior and inferior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Ear
{{disambig ...
Internal may refer to: *Internality as a concept in behavioural economics *Neijia, internal styles of Chinese martial arts *Neigong or "internal skills", a type of exercise in meditation associated with Daoism *''Internal (album)'' by Safia, 2016 See also * *Internals (other) *External (other) External may refer to: * External (mathematics), a concept in abstract algebra * Externality In economics, an externality or external cost is an indirect cost or benefit to an uninvolved third party that arises as an effect of another party' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Press
Academic Press (AP) is an academic book publisher founded in 1941. It was acquired by Harcourt, Brace & World in 1969. Reed Elsevier bought Harcourt in 2000, and Academic Press is now an imprint of Elsevier. Academic Press publishes reference books, serials and online products in the subject areas of: * Communications engineering * Economics * Environmental science * Finance * Food science and nutrition * Geophysics * Life sciences * Mathematics and statistics * Neuroscience * Physical sciences * Psychology Well-known products include the ''Methods in Enzymology'' series and encyclopedias such as ''The International Encyclopedia of Public Health'' and the ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience''. See also * Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft (AVG) — the German predecessor, founded in 1906 by Leo Jolowicz (1868–1940), the father of Walter Jolowicz Walter may refer to: People * Walter (name), both a surname and a given name * Little Walter, American blues harmonica player Marion Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterworth-Heinemann
Butterworth–Heinemann is a British publishing company specialised in professional information and learning materials for higher education and professional training, in printed and electronic forms. It was formed in 1990 by the merger of Heinemann Professional Publishing and Butterworths Scientific, both subsidiaries of Reed International. With its earlier constituent companies, the founding dates back to 1923. It has publishing units in Oxford (UK) and Waltham, Massachusetts (United States). As of 2006, it is an imprint of Elsevier. See also *LexisNexis Butterworths LexisNexis is a part of the RELX corporation that sells data analytics products and various databases that are accessed through online portals, including portals for computer-assisted legal research (CALR), newspaper search, and consumer informa ... References External links * Book publishing companies of the United Kingdom Elsevier imprints {{publish-corp-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inner Ear
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the temporal bone of the skull with a system of passages comprising two main functional parts: * The cochlea, dedicated to hearing; converting sound pressure patterns from the outer ear into electrochemical impulses which are passed on to the brain via the auditory nerve. * The vestibular system, dedicated to balance The inner ear is found in all vertebrates, with substantial variations in form and function. The inner ear is innervated by the eighth cranial nerve in all vertebrates. Structure The labyrinth can be divided by layer or by region. Bony and membranous labyrinths The bony labyrinth, or osseous labyrinth, is the network of passages with bony walls lined with periosteum. The three major parts of the bony labyrinth are the vestib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ... through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting Vibration, vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduction (physiology), transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |