|
Longphort
A longphort (Ir. plur. ''longphuirt'') is a term used in Ireland for a Viking ship enclosureConnolly S.J (1998). The Oxford Companion to Irish History. Oxford University Press. p. 580 or shore fortress. Although these ''longphorts'' were used as bases for Viking raids, the term had additional meanings and these sites had multiple purposes.Valante, Mary A. The Vikings in Ireland: Settlement, Trade, and Urbanization. Dublin: Four Courts Press, 2008. The reason it cannot be assumed that ''longphorts'' were solely for military purposes as that would assume that there were always large numbers of Vikings at these settlements, which is not true. These camps were fortified areas along rivers, usually at a tributary where both sides were protected such that the Vikings could port ships. The sites were easily defended, sheltered, and gave immediate access to the sea. These camps would be of great importance to the Vikings during their raids of Ireland, which included attacks on many churches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longford Town
Longford () is the county town of County Longford in Ireland. It has a population of 10,008 according to the 2016 census. It is the biggest town in the county and about one third of the county's population lives there. Longford lies at the meeting of Ireland's N4 and N5 National Primary Route roads, which means that traffic travelling between Dublin and County Mayo, or north County Roscommon passes around the town. Longford railway station, on the Dublin-Sligo line, is used heavily by commuters. History The town is built at a fording point on the banks of the River Camlin (), which is a tributary of the River Shannon. According to several sources, the name Longford is an Anglicization of the Irish , referring to a fortress or fortified house. The area came under the sway of the local clan which controlled the south and middle of the County of Longford (historically called or ) and hence, the town was known as (fort/stronghold of O'Farrell). A Dominican priory was founde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Ireland (800–1169)
The history of Ireland 800–1169 covers the period in the history of Ireland from the first Viking raids to the Norman invasion. The first two centuries of this period are characterised by Viking raids and the subsequent Norse settlements along the coast. Viking ports were established at Dublin, Wexford, Waterford, Cork and Limerick, which became the first large towns in Ireland. Ireland consisted of many semi-independent territories ( túatha), and attempts were made by various factions to gain political control over the whole of the island. For the first two centuries of this period, this was mainly a rivalry between putative High Kings of Ireland from the northern and southern branches of the Uí Néill. The one who came closest to being de facto king over the whole of Ireland, however, was Brian Boru, the first high king in this period not belonging to the Uí Néill. Following Brian's death at the Battle of Clontarf in 1014, the political situation became more complex with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
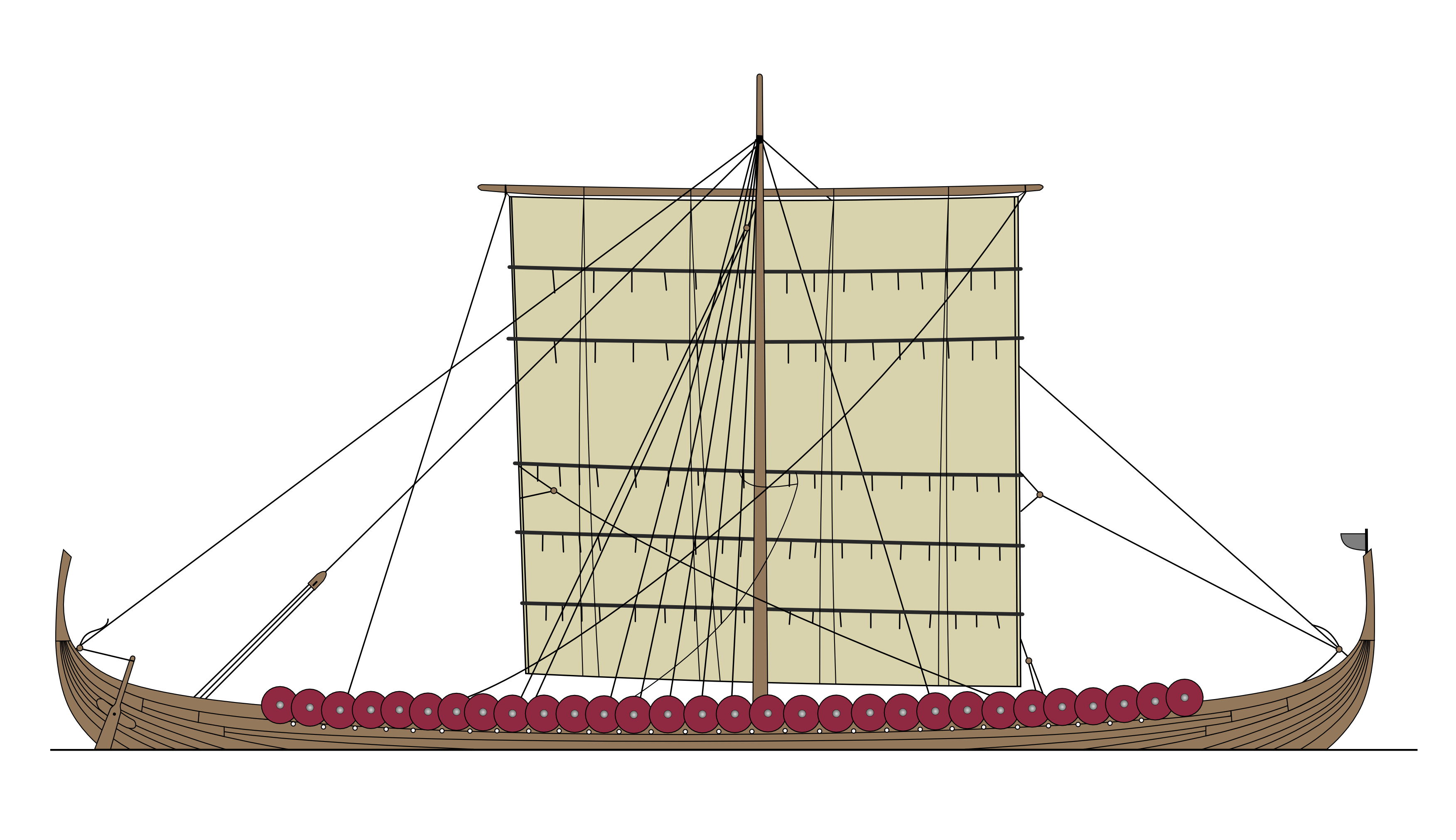
Longship
Longships were a type of specialised Scandinavian warships that have a long history in Scandinavia, with their existence being archaeologically proven and documented from at least the fourth century BC. Originally invented and used by the Norsemen (commonly known as the Vikings) for commerce, exploration, and warfare during the Viking Age, many of the longship's characteristics were adopted by other cultures, like Anglo-Saxons, and continued to influence shipbuilding for centuries. The longship's design evolved over many centuries, and continuing up until the sixth century with clinker-built ships like Nydam. The longship appeared in its complete form between the ninth and 13th centuries. The character and appearance of these ships have been reflected in Scandinavian boatbuilding traditions to the present day. The particular skills and methods employed in making longships are still used worldwide, often with modern adaptations. They were all made out of wood, with cloth sails ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Ulster
The ''Annals of Ulster'' ( ga, Annála Uladh) are annals of medieval Ireland. The entries span the years from 431 AD to 1540 AD. The entries up to 1489 AD were compiled in the late 15th century by the scribe Ruaidhrí Ó Luinín, under his patron Cathal Óg Mac Maghnusa, on the island of ''Senadh-Mic-Maghnusa'', also known as ''Senad'' or Ballymacmanus Island (now known as Belle Isle, where Belle Isle Castle is located), near Lisbellaw, on Lough Erne in the kingdom of ''Fir Manach'' ( Fermanagh). Later entries (up to AD 1540) were added by others. Entries up to the mid-6th century are retrospective, drawing on earlier annalistic and historical texts, while later entries were contemporary, based on recollection and oral history. T. M. Charles-Edwards has claimed that the main source for its records of the first millennium A.D. is a now lost Armagh continuation of the '' Chronicle of Ireland''. The Annals used the Irish language, with some entries in Latin. Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of St
Annals ( la, annāles, from , "year") are a concise historical record in which events are arranged chronologically, year by year, although the term is also used loosely for any historical record. Scope The nature of the distinction between annals and history is a subject based on divisions established by the ancient Romans. Verrius Flaccus is quoted by Aulus Gellius as stating that the etymology of ''history'' (from Greek , , equated with Latin , "to inquire in person") properly restricts it to primary sources such as Thucydides's which have come from the author's own observations, while annals record the events of earlier times arranged according to years. White distinguishes annals from chronicles, which organize their events by topics such as the reigns of kings, and from histories, which aim to present and conclude a narrative implying the moral importance of the events recorded. Generally speaking, annalists record events drily, leaving the entries unexplained and equally w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linn Duachaill
Linn Duachaill (; "Duachall's pool") is the name of a Viking longphort near the village of Annagassan, County Louth, Ireland. The settlement was built in 841 CE, the same time as the settlement of ''Dubh Linn'', or Dublin. In contrast to Dublin, the settlement was abandoned. It has been argued that possibly because of changing tidal patterns, it lacked continuous access to the sea. The tides would have made access to the water difficult for a number of hours per day. History The longphort of Linn Duachaill is first mentioned in Irish annals of the 840s. A certain Tergeis or Turgesius, as he is called in the annals, is said to have founded forts at Dubh Linn and Linn Duachaill, from which the "surrounding territories and churches were plundered and preyed." Walter Alison Phillips, ed., ''History of the Church of Ireland: From the Earliest Times to the Present Day'', Volume 2 ''Movement Towards Rome: The Medieval Church and the Reformation'', Oxford University Press, 1934, OCLC 6061 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Dublin
Vikings invaded the territory around Dublin in the 9th century, establishing the Norse Kingdom of Dublin, the earliest and longest-lasting Norse kingdom in Ireland. Its territory corresponded to most of present-day County Dublin. The Norse referred to the kingdom as ''Dyflin'', which is derived . The first reference to the Vikings comes from the ''Annals of Ulster'' and the first entry for 841 AD reads: "Pagans still on Lough Neagh". It is from this date onward that historians get references to ship fortresses or longphorts being established in Ireland. It may be safe to assume that the Vikings first over-wintered in 840–841 AD. The actual location of the longphort of Dublin is still a hotly debated issue. Norse rulers of Dublin were often co-kings, and occasionally also Kings of Jórvík in what is now Yorkshire. Under their rule, Dublin became the biggest slave port in Western Europe. Over time, the settlers in Dublin became increasingly Gaelicized. They began to exhibit a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Waterford
Waterford city is situated in south eastern Ireland, on the river Suir ronounced Shureabout from where the river enters the sea. Practically the entire city is built on the south bank of the river. The "Old town", now the business centre, clusters behind the broad quay-front on a low-lying strip of land left behind by a gentle loop of the river at this point. From this, the land rises sharply to the east and opposite to the west while remaining level in between. The eastern slopes are almost entirely occupied by private residential estates, while the western and southwestern prominences are largely given over to local council housing development. There are corresponding elevations on the north bank eastwards towards Christendom and westwards towards Mount Misery nothing. The rocks which form the base of the city all belong to the Palaeozoic Group – principally Ordovician shales underlying sandstone. On the East side of the city, the rock is crossed by an alluvial bank runnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Limerick
The history of Limerick stretches back to its establishment by Vikings as a walled city on King's Island, Limerick, King's Island (an island in the River Shannon) in 812, and to the granting of Limerick's city charter in 1197. John, King of England, King John ordered the building (1200) of King John's Castle (Limerick), a great castle. The city was Sieges of Limerick (other), besieged three times in the 17th century, culminating in the famous 1691 Treaty of Limerick and the Flight of the Wild Geese, flight of the defeated Catholic leaders Irish diaspora, abroad. Much of the city was built during the following Georgian era, Georgian prosperity, which ended abruptly with the Act of Union 1800, Act of Union in 1800. Today the city has a growing multicultural population. Name ''Luimneach'' originally referred to the general area along the banks of the Shannon Estuary, which was known as ''Loch Luimnigh''. The original pre-Viking and Viking era settlement on Kings Island w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uí Ímair
The Uí Ímair (; meaning ‘''scions of Ivar’''), also known as the Ivar Dynasty or Ivarids was a royal Norse-Gael dynasty which ruled much of the Irish Sea region, the Kingdom of Dublin, the western coast of Scotland, including the Hebrides and some part of Northern England, from the mid 9th century. The dynasty lost control of York in the mid 10th century, but reigned over the other domains at variously disputed times, depending on which rulers may be counted among their descendants. This has proved a difficult question for scholars to determine, because reliable pedigrees do not survive. Additionally, for between three and four decades, the Uí Ímair were overkings of the Kingdom of Scotland itself, distinct from the Kingdom of Strathclyde, of which they may also have been overkings, and later briefly the Irish province of Munster, dominated from Waterford, and later still, briefly the English kingdom of Mercia. In the west of Ireland, the Uí Ímair also supplied at leas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Cork
Cork, located on Ireland's south coast, is the second largest city within the Republic of Ireland after Dublin and the third largest on the island of Ireland after Dublin and Belfast. Cork City is the largest city in the province of Munster. Its history dates back to the sixth century. Origins Cork began as a monastic settlement, founded by St Finbar in the sixth century. However the ancestor of the modern city was founded between 915 and 922, when Viking settlers established a trading community. The Viking leader Ottir Iarla is particularly associated with raiding and conquests in the province of Munster. The ''Cogad Gáedel re Gallaib'' connects this with the earliest Viking settlement of Cork. The Norse phase of Cork's history left a legacy of family names, such as Cotter and Coppinger, peculiar to Cork which are claimed to have Norse origins. In the twelfth century, this settlement was taken over by invading Anglo-Norman settlers. The Norsemen of Cork fought against the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woodstown
Woodstown ( ga, Baile na Coille, IPA: �bˠalʲəˈnˠaˈkɛl̪ʲə is home to a historic settlement measuring 1.5 km by 0.5 km, located on the southern bank of the River Suir, about 5.5 km west of Waterford City in the southeast of Ireland. This site should not be confused with Woodstown beach which is on the western side of Waterford Harbour near the fishing port of Dunmore East. Discovery The National Roads Authority had planned to build a road over the site which showed no evidence of a historical monument. Investigation ditch and gulley across the road route led to the discovery of the site. In 2005 the site was declared a national monument and the motorway bypassed the site. The NRA, who have no responsibility for the site in the future, published reports, based on excavations in April and August 2003. These suggest that the site found at Woodstown was a defended, riverside settlement with evidence of industrial activity, most likely dating from the period - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |