|
Lidocaine
Lidocaine, also known as lignocaine and sold under the brand name Xylocaine among others, is a local anesthetic of the amino amide type. It is also used to treat ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. When used for local anaesthesia or in nerve blocks, lidocaine typically begins working within several minutes and lasts for half an hour to three hours. Lidocaine mixtures may also be applied directly to the skin or mucous membranes to numb the area. It is often used mixed with a small amount of adrenaline (epinephrine) to prolong its local effects and to decrease bleeding. If injected intravenously, it may cause cerebral effects such as confusion, changes in vision, numbness, tingling, and vomiting. It can cause low blood pressure and an irregular heart rate. There are concerns that injecting it into a joint can cause problems with the cartilage. It appears to be generally safe for use in pregnancy. A lower dose may be required in those with liver problems. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthetic Nerve Block
Nerve block or regional nerve blockade is any deliberate interruption of signals traveling along a nerve, often for the purpose of pain relief. Local anesthetic nerve block (sometimes referred to as simply "nerve block") is a short-term block, usually lasting hours or days, involving the injection of an anesthetic, a corticosteroid, and other agents onto or near a nerve. Neurolytic block, the deliberate temporary degeneration of nerve fibers through the application of chemicals, heat, or freezing, produces a block that may persist for weeks, months, or indefinitely. Neurectomy, the cutting through or removal of a nerve or a section of a nerve, usually produces a permanent block. Because neurectomy of a sensory nerve is often followed, months later, by the emergence of new, more intense pain, sensory nerve neurectomy is rarely performed. The concept of nerve block sometimes includes ''central nerve block'', which includes epidural and spinal anaesthesia. Local anesthetic nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Anesthetic
A local anesthetic (LA) is a medication that causes absence of all sensation (including pain) in a specific body part without loss of consciousness, providing local anesthesia, as opposed to a general anesthetic, which eliminates all sensation in the entire body and causes unconsciousness. Local anesthetics are most commonly used to eliminate pain during or after surgery. When it is used on specific nerve pathways ( local anesthetic nerve block), paralysis (loss of muscle function) also can be induced. Classification LAs are of 2 types: *Clinical LAs: ** amino amide LAs ** amino ester LAs *Synthetic LAs **Cocaine derivatives Synthetic cocaine-derived LAs differ from cocaine because they have a much lower abuse potential and do not cause hypertension vasoconstriction (with few exceptions). The suffix "-caine" at the ends of these medication names is derived from the word "cocaine", because cocaine was formerly used as a local anesthetic. Examples Short Duration of Act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Channel Blocker
Sodium channel blockers are drugs which impair the conduction of sodium ions (Na+) through sodium channels. Extracellular The following naturally-produced substances block sodium channels by binding to and occluding the extracellular pore opening of the channel: * Alkaloids: ** Saxitoxin (STX) ** Neosaxitoxin (NSTX) ** Tetrodotoxin (TTX) Intracellular Drugs which block sodium channels by blocking from the intracellular side of the channel include: * Local anesthetics: ''lidocaine'' * Class I antiarrhythmic agents * Various anticonvulsants: ''phenytoin, oxcarbazepine (derivative of carbamazepine)'' Unknown mechanism * Calcium has been shown to block sodium channels which explains the effects of hypercalcemia and hypocalcemia. * Lamotrigine is known to block sodium channels but it is not known whether it is extracellular or intracellular. * Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to cause inhibitory effects on sodium currents. This voltage-dependent inhibition is non-selective in natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bupivacaine
Bupivacaine, marketed under the brand name Marcaine among others, is a medication used to decrease sensation in a specific small area. In nerve blocks, it is injected around a nerve that supplies the area, or into the spinal canal's epidural space. It is available mixed with a small amount of epinephrine to increase the duration of its action. It typically begins working within 15 minutes and lasts for 2 to 8 hours. Possible side effects include sleepiness, muscle twitching, ringing in the ears, changes in vision, low blood pressure, and an irregular heart rate. Concerns exist that injecting it into a joint can cause problems with the cartilage. Concentrated bupivacaine is not recommended for epidural freezing. Epidural freezing may also increase the length of labor. It is a local anaesthetic of the amide group. Bupivacaine was discovered in 1957. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Bupivacaine is available as a generic medication. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropathic Pain
Neuropathic pain is pain caused by a lesion or disease of the somatosensory nervous system. Neuropathic pain may be associated with abnormal sensations called dysesthesia or pain from normally non-painful stimuli (allodynia). It may have continuous and/or episodic (paroxysmal) components. The latter resemble stabbings or electric shocks. Common qualities include burning or coldness, "pins and needles" sensations, numbness and itching. Up to 7–8% of the European population is affected by neuropathic pain, and in 5% of persons it may be severe. The pain may result from disorders of the peripheral nervous system or the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Neuropathic pain may occur in isolation or in combination with other forms of pain. Medical treatments focus on identifying the underlying cause and relieving pain. In cases of peripheral neuropathy, the pain may progress to insensitivity. Diagnosis Diagnosis of pain conditions relies on the character of the pain w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
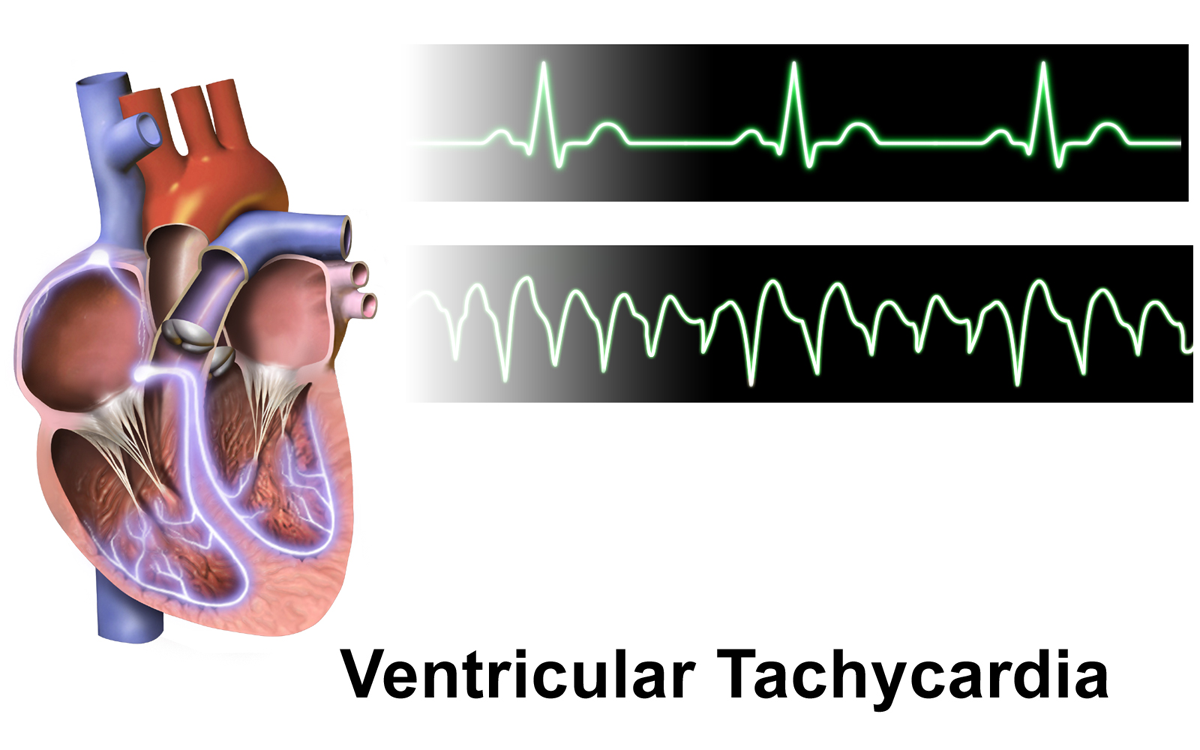
Ventricular Tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia (V-tach or VT) is a cardiovascular disorder in which fast heart rate occurs in the ventricles of the heart. Although a few seconds of VT may not result in permanent problems, longer periods are dangerous; and multiple episodes over a short period of time are referred to as an electrical storm. Short periods may occur without symptoms, or present with lightheadedness, palpitations, shortness of breath, chest pain, and decreased level of consciousness. Ventricular tachycardia may lead to coma and persistent vegetative state due to lack of blood and oxygen to the brain. Ventricular tachycardia may result in ventricular fibrillation (VF) and turn into cardiac arrest. This conversion of the VT into VF is called the degeneration of the VT. It is found initially in about 7% of people in cardiac arrest. Ventricular tachycardia can occur due to coronary heart disease, aortic stenosis, cardiomyopathy, electrolyte imbalance, or a heart attack. Diagnosis is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CYP3A4
Cytochrome P450 3A4 (abbreviated CYP3A4) () is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine, which in humans is encoded by ''CYP3A4'' gene. It organic redox reaction, oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme. While many drugs are deactivated by CYP3A4, there are also some drugs that are ''activated'' by the enzyme. Some substances, such as some drugs and furanocoumarins present in grapefruit juice, interfere with the action of CYP3A4. These substances will, therefore, either amplify or weaken the action of those drugs that are modified by CYP3A4. CYP3A4 is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of oxidizing enzymes. Several other members of this family are also involved in drug metabolism, but CYP3A4 is the most common and the most versatile one. Like all members of this family, it is a hemoprote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WHO Model List Of Essential Medicines
The WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (aka Essential Medicines List or EML), published by the World Health Organization (WHO), contains the medications considered to be most effective and safe to meet the most important needs in a health system. The list is frequently used by countries to help develop their own local lists of essential medicines. , more than 155 countries have created national lists of essential medicines based on the World Health Organization's model list. This includes both Developed country, developed and Developing country, developing countries. The list is divided into core items and complementary items. The core items are deemed to be the most cost-effective options for key health problems and are usable with little additional health care resources. The complementary items either require additional infrastructure such as specially trained health care providers or diagnostic equipment or have a lower cost–benefit ratio. About 25% of items are in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intubation
Intubation (sometimes entubation) is a medical procedure involving the insertion of a tube into the body. Most commonly, intubation refers to tracheal intubation, a procedure during which an endotracheal tube is inserted into the trachea to support patient ventilation. Other examples of intubation include balloon tamponade using a Sengstaken–Blakemore tube (a tube into the gastrointestinal tract), urinary catheterization, and nasogastric intubation using a feeding tube. Types of Intubation and Their Indications Tracheal Intubation Tracheal intubation is a procedure involving the placement of an endotracheal tube into a patient’s windpipe, also known as the trachea. This procedure may be done to treat either emergent or non-emergent conditions. Examples of emergent conditions include airway compromise, respiratory failure, allergic reactions, and trauma. An example of a non-emergent condition where tracheal intubation is performed includes surgery, during which an indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiarrhythmic Agent
Antiarrhythmic agents, also known as cardiac dysrhythmia medications, are a class of drugs that are used to suppress abnormally fast rhythms (tachycardias), such as atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia and ventricular tachycardia. Many attempts have been made to classify antiarrhythmic agents. Many of the antiarrhythmic agents have multiple modes of action, which makes any classification imprecise. Action potential The cardiac myocyte has two general types of action potentials: conduction system and working myocardium. The action potential is divided into 5 phases and shown in the diagram. The sharp rise in voltage ("0") corresponds to the influx of sodium ions, whereas the two decays ("1" and "3", respectively) correspond to the sodium-channel inactivation and the repolarizing efflux of potassium ions. The characteristic plateau ("2") results from the opening of voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Each phase utilizes different channels and it is useful to compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infiltration (medical)
Infiltration in a medical context is the process of cells or substances moving across a barrier, typically a tissue barrier, into a place they are not normally found, or in which they are typically found in lower concentrations. Infiltration may refer to normal physiological processes, such as the infiltration of certain immune cells into peripheral tissues. Infiltration may also refer to pathological processes, such as malignant tumor cells infiltrating new areas of the human body, or small particles infiltrating tissues, where they may cause damage or inflammation. Types of Infiltration The term 'infiltration' is frequently used to describe various pathologic and physiologic processes, including but not limited to: Immune Infiltration This occurs when immune cells like lymphocytes and macrophages migrate into tissues in response to infection, injury, or inflammation, aiding in defense and healing but potentially contributing to autoimmune diseases if misdirected. Immune ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidural Administration
Epidural administration (from Ancient Greek ἐπί, "upon" + '' dura mater'') is a method of medication administration in which a medicine is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord. The epidural route is used by physicians and nurse anesthetists to administer local anesthetic agents, analgesics, diagnostic medicines such as radiocontrast agents, and other medicines such as glucocorticoids. Epidural administration involves the placement of a catheter into the epidural space, which may remain in place for the duration of the treatment. The technique of intentional epidural administration of medication was first described in 1921 by the Spanish Aragonese military surgeon Fidel Pagés. Epidural anaesthesia causes a loss of sensation, including pain, by blocking the transmission of signals through nerve fibres in or near the spinal cord. For this reason, epidurals are commonly used for pain control during childbirth and surgery, for which the technique is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |