|
Lichun
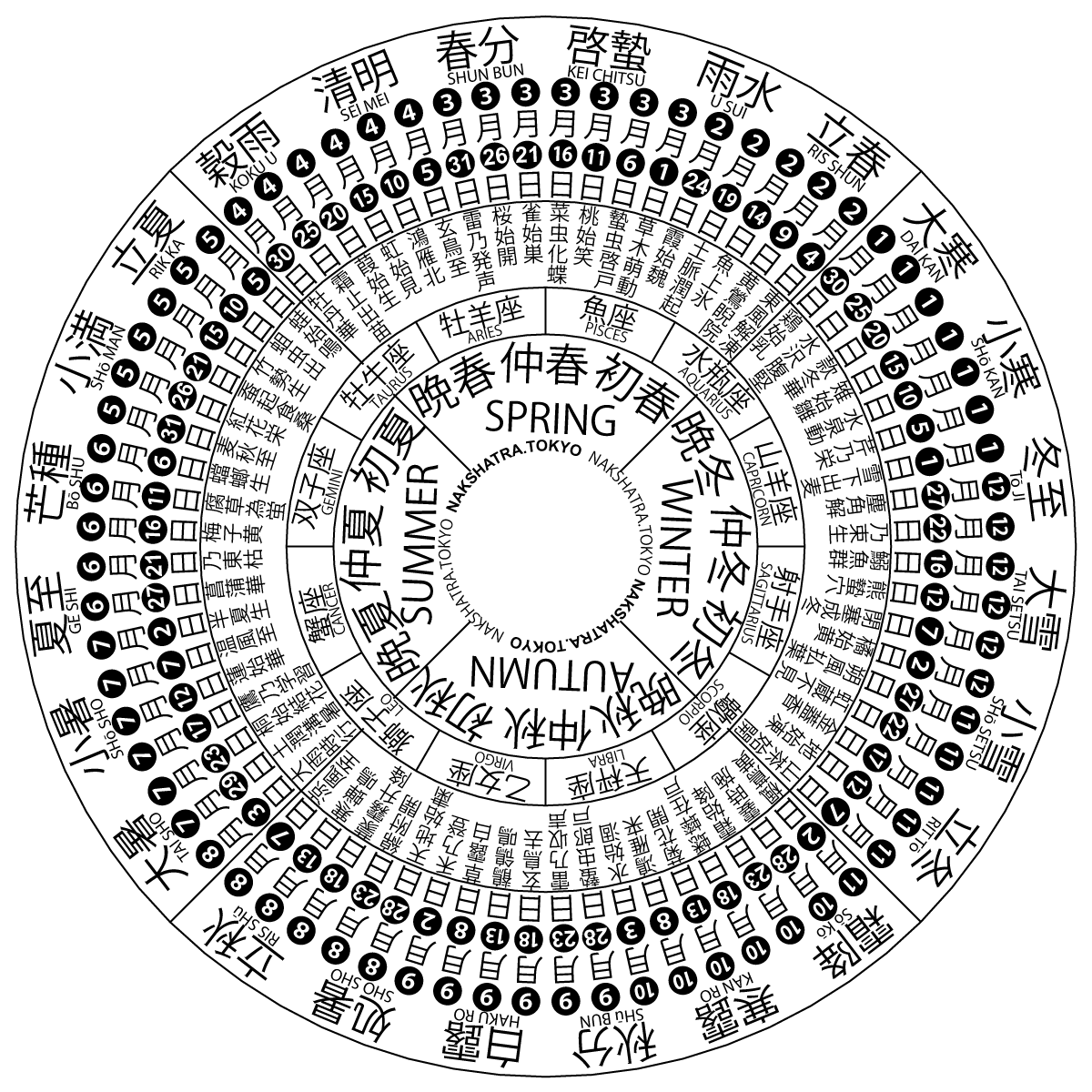
Traditional Chinese calendar divides a year into 24 solar terms. ''Lìchūn'', ''Risshun'', ''Ipchun'', or ''Lập xuân'' is the 1st solar term. It begins when the Sun reaches the celestial longitude of 315° and ends when it reaches the longitude of 330°. It more often refers in particular to the day when the Sun is exactly at the celestial longitude of 315°. In the Gregorian calendar, it usually begins around February 4 and ends around February 18 (February 19 East Asia time). It's also the beginning of a sexagenary cycle. Lichun signifies the beginning of spring in East Asian cultures. Pentads Each solar term can be divided into 3 pentads (候). They are: first pentad (初候), second pentad (次候) and last pentad (末候). Pentads in Lichun include: ; China * First pentad: Dōng Fēng Jiě Dòng () *: '' Yuè Lìng Qī Shí Èr Hòu Jí Jiě'' (月令七十二候集解) explains the name of this pentad:It is not called the 'winter ice meets the spring wind and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chūnbǐng
The spring pancake () is a traditional Chinese food unique to the northern regions. People eat spring pancakes on the day called lichun to celebrate the beginning of the spring. The spring pancake took its rise from the Jin dynasty and has prospered since the Tang dynasty. The lichun was valued by both Chinese ancient kings and civilians. Unlike kings’ great celebrations, civilians celebrated the lichun by eating spring pancakes wrapped around fresh vegetables and meat, which is called bite-the-spring. Bite-the-spring implies that civilians are praying for a good harvest year by eating fresh vegetables and meat at the beginning of spring. In the Qing dynasty, spring pancakes became a fried pancake wrapped around a filling that included ham, chicken, pork, black dates, scallions, walnuts and sugar. In addition, spring pancakes were one of the nine desserts for the regal banquet of the Qing dynasty. The spring pancake is slightly larger than the pancake that is served with Peki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese New Year
Chinese New Year is the festival that celebrates the beginning of a new year on the traditional lunisolar and solar Chinese calendar. In Chinese and other East Asian cultures, the festival is commonly referred to as the Spring Festival () as the spring season in the lunisolar calendar traditionally starts with lichun, the first of the twenty-four solar terms which the festival celebrates around the time of the Chinese New Year. Marking the end of winter and the beginning of the spring season, observances traditionally take place from New Year’s Eve, the evening preceding the first day of the year to the Lantern Festival, held on the 15th day of the year. The first day of Chinese New Year begins on the new moon that appears between 21 January and 20 February. Chinese New Year is one of the most important holidays in Chinese culture, and has strongly influenced Lunar New Year celebrations of its 56 ethnic groups, such as the Losar of Tibet (), and of China's neighbours, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yushui (solar Term)
The traditional chinese calendar divides a year into 24 solar terms. ''Yǔshuǐ'' / 雨水, ''Usui'', ''Usu'', or ''Vũ thủy'' (in vietnamese lenguage), literally meaning ''rain water'', is the 2nd one of them. It begins when the Sun reaches the celestial longitude of 330° and ends when it reaches the longitude of 345°. It more often refers in particular to the day when the Sun is exactly at the celestial longitude of 330°. In gregorian calendar The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years di ... it usually begins around 18 February (19 February of / in east Asia time) and ends around 5 March. Pentads Each solar term can be divided into three pentads (候), first (初候), second (次候) and last (末候) ones. In Yushui each pentad includes : ; in China, * first p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Term
A solar term is any of twenty-four periods in traditional Chinese calendar, Chinese lunisolar calendars that matches a particular astronomical event or signifies some natural phenomenon. The points are spaced 15° apart along the ecliptic and are used by lunisolar calendars to stay synchronized with the seasons, which is crucial for agrarian societies. The solar terms are also used to calculate Intercalation (timekeeping), intercalary months; which month is repeated depends on the position of the sun at the time. According to the ''Book of Documents'', the first determined term was Dongzhi (solar term), Dongzhi (Winter Solstice) by Duke of Zhou, Dan, the Duke of Zhou, while he was trying to locate the geological center of the Western Zhou dynasty, by measuring the length of the sun's shadow on an ancient timekeeper instrument named Tu Gui (土圭). Then four terms of seasons were set, which were soon evolved as eight terms; until 104 BC in the book Taichu Calendar, the entire twe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dahan (solar Term)
The traditional Chinese calendar divides a year into 24 solar terms.''Dàhán'', ''Daikan'', ''Daehan'', or ''Đại hàn'' () is the 24th solar term. It begins when the Sun reaches the celestial longitude of 300° and ends when it reaches the longitude of 315°. It more often refers in particular to the day when the Sun is exactly at the celestial longitude of 300°. In the Gregorian calendar The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years di ..., it usually begins around 20 January and ends around 4 February. Date and time References {{DEFAULTSORT:Dahan (Solar Term) 24 Winter time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wu Cheng (philosopher)
Wú Chéng or Wu Ch'eng (1249 – 1333) (), courtesy names Yòuqīng () and Bóqīng (), studio names Yīwúshānrén () and Caolu Xiansheng (草廬先生; lit. "Mr. Grass Hut"), was a scholar, educator, and poet who lived in the late Song dynasty and Yuan dynasty. He was one of the most influential Neo-Confucian thinkers in those eras, and his influence continued to be prominent in the Ming and Qing periods. Wu Cheng was born in 1249 in Fuzhou, Jiangxi, into a poor family with a scholarly heritage. His early training was in the Zhu Xi (1130-1200) lineage, but he was also exposed to the idea of harmonizing the Zhu Xi teachings with those of Lu Xiangshan (1139-1193), and he also had an affinity for southern Daoism. This synthetic tendency was apparent in Wu’s later writings and exerted an influence on the development of ''xinxue'' 心學 (the School of the Mind and Heart) in the Ming (1368-1644) and Qing (1644-1912) eras. He died in 1333. Failing to pass the ''jinshi'' examin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg Of Li Chun
Egg balancing is a traditional Chinese practice that has since been popularized in the United States. Although the irregular shape of eggs makes this somewhat difficult, eggshells typically have many imperfections such that the vast majority can be balanced on their broad ends with minimal effort. Folklore holds that eggs can only be balanced in this way at a particular time of year: the lunar new year in China, the Dragon Boat Festival in Taiwan or the vernal equinox in the United States. In reality, eggs will balance at any time of year, and the practice has no connection to the gravitational force of the moon or sun. History Lichun egg Egg balancing has been connected with Lichun, the solar term beginning ''Chinese'' spring () on February 4 or 5 when the sun is at the celestial longitude of 315°. On this day, fresh chicken eggs were balanced on their broad end. In Taiwan, the practice is sometimes connected with the Dragon Boat Festival instead, on the fifth day of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setsubun
is the day before the beginning of spring in the old calendar in Japan. The name literally means 'seasonal division', referring to the day just before the first day of spring in the traditional calendar, known as ; though previously referring to a wider range of possible dates, is now typically held on February 3 (in 2021 it was on 2nd February), with the day after – the first day of spring in the old calendar – known as . Both and are celebrated yearly as part of the Spring Festival () in Japan. In its association with the Lunar New Year, , though not the official New Year, was thought of as similar in its ritual and cultural associations of 'cleansing' the previous year as the beginning of the new season of spring. was accompanied by a number of rituals and traditions held at various levels to drive away the previous year's bad fortunes and evil spirits for the year to come. Origins has its origins in , a Chinese custom introduced to Japan in the 8th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shi (poetry)
''Shi'' and ''shih''Based on the Wade-Giles system formerly used by Taiwan and English-speaking countries. are romanizations of the character /, the Chinese word for all poetry generally and across all languages. In Western analysis of the styles of Chinese poetry, ''shi'' is also used as a term of art for a specific poetic tradition, modeled after the Old Chinese works collected in the Confucian ''Classic of Poetry''. This anthology included both aristocratic poems (the "Hymns" and "Eulogies") and more rustic works believed to have derived from Huaxia folk songs (the "Odes"). They are composed in ancient Chinese, mostly in four-character lines. In such analysis, "''shi''" poetry is contrasted with other forms such as the Chu-derived "'' cí''" and the Han-era "'' fu''".Watson, Burton. ''Chinese Lyricism: Shih Poetry from the Second to the Twelfth Century''. Columbia Univ. Press (New York), 1971. .Frankel, Hans. ''The Flowering Plum and the Palace Lady''. Yale Univ. Press (New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Du Fu
Du Fu (; 712–770) was a Tang dynasty poet and politician. Along with his elder contemporary and friend Li Bai (Li Po), he is frequently called the greatest of the Chinese poets.Ebrey, 103. His greatest ambition was to serve his country as a successful civil servant, but he proved unable to make the necessary accommodations. His life, like the whole country, was devastated by the An Lushan Rebellion of 755, and his last 15 years were a time of almost constant unrest. Although initially he was little-known to other writers, his works came to be hugely influential in both Chinese and Japanese literary culture. Of his poetic writing, nearly fifteen hundred poems have been preserved over the ages. He has been called the "Poet-Historian" and the "Poet-Sage" by Chinese critics, while the range of his work has allowed him to be introduced to Western readers as "the Chinese Virgil, Horace, Ovid, Shakespeare, Milton, Burns, Wordsworth, Béranger, Hugo or Baudelaire".H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luck
Luck is the phenomenon and belief that defines the experience of improbable events, especially improbably positive or negative ones. The naturalistic interpretation is that positive and negative events may happen at any time, both due to random and non-random natural and artificial processes, and that even improbable events can happen by random chance. In this view, the epithet "lucky" or "unlucky" is a descriptive label that refers to an event's positivity, negativity, or improbability. Supernatural interpretations of luck consider it to be an attribute of a person or object, or the result of a favorable or unfavorable view of a deity upon a person. These interpretations often ''prescribe'' how luckiness or unluckiness can be obtained, such as by carrying a lucky charm or offering sacrifices or prayers to a deity. Saying someone is "born lucky" may hold different meanings, depending on the interpretation: it could simply mean that they have been born into a good family or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |