|
Latissimus Dorsi
The latissimus dorsi () is a large, flat muscle on the back that stretches to the sides, behind the arm, and is partly covered by the trapezius on the back near the midline. The word latissimus dorsi (plural: ''latissimi dorsi'') comes from Latin and means "broadest [muscle] of the back", from "latissimus" () and "dorsum" (). The pair of muscles are commonly known as "lats", especially among bodybuilders. The latissimus dorsi is responsible for Extension (kinesiology), extension, adduction, transverse extension also known as horizontal abduction (or horizontal extension), flexion from an extended position, and (medial) internal rotation of the shoulder joint. It also has a synergistic role in extension and Anatomical terms of motion, lateral flexion of the lumbar spine. Due to bypassing the scapulothoracic joints and attaching directly to the spine, the actions the latissimi dorsi have on moving the arms can also influence the movement of the scapulae, such as their downward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmented column of vertebrae that surrounds and protects the spinal cord. The vertebrae are separated by intervertebral discs in a series of cartilaginous joints. The dorsal portion of the spinal column houses the spinal canal, an elongated body cavity, cavity formed by the alignment of the vertebral neural arches that encloses and protects the spinal cord, with spinal nerves exiting via the intervertebral foramina to innervate each body segment. There are around 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human spine is one of the most-studied examples, as the general structure of human vertebrae is fairly homology (biology), typical of that found in other mammals, reptiles, and birds. The shape of the vertebral body does, howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
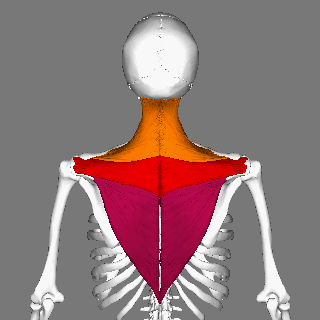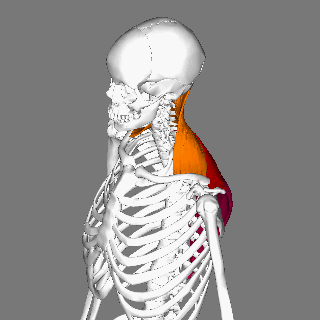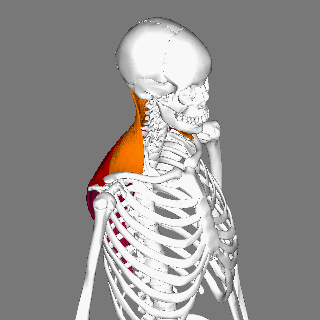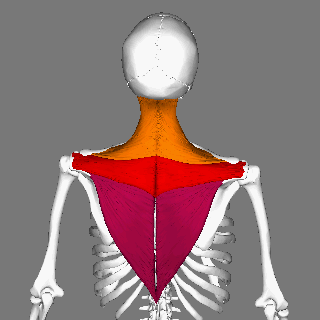
Trapezius
The trapezius is a large paired trapezoid-shaped surface muscle that extends longitudinally from the occipital bone to the lower thoracic vertebrae of the human spine, spine and laterally to the spine of the scapula. It moves the scapula and supports the arm. The trapezius has three functional parts: * an upper (descending) part which supports the weight of the arm; * a middle region (transverse), which retracts the scapula; and * a lower (ascending) part which medially rotates and depresses the scapula. Name and history The trapezius muscle resembles a trapezoid, trapezium, also known as a trapezoid, or diamond-shaped quadrilateral. The word "spinotrapezius" refers to the human trapezius, although it is not commonly used in modern texts. In other mammals, it refers to a portion of the analogous muscle. Structure The ''superior'' or ''upper'' (or descending) fibers of the trapezius originate from the spinous process of C7, the external occipital protuberance, the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
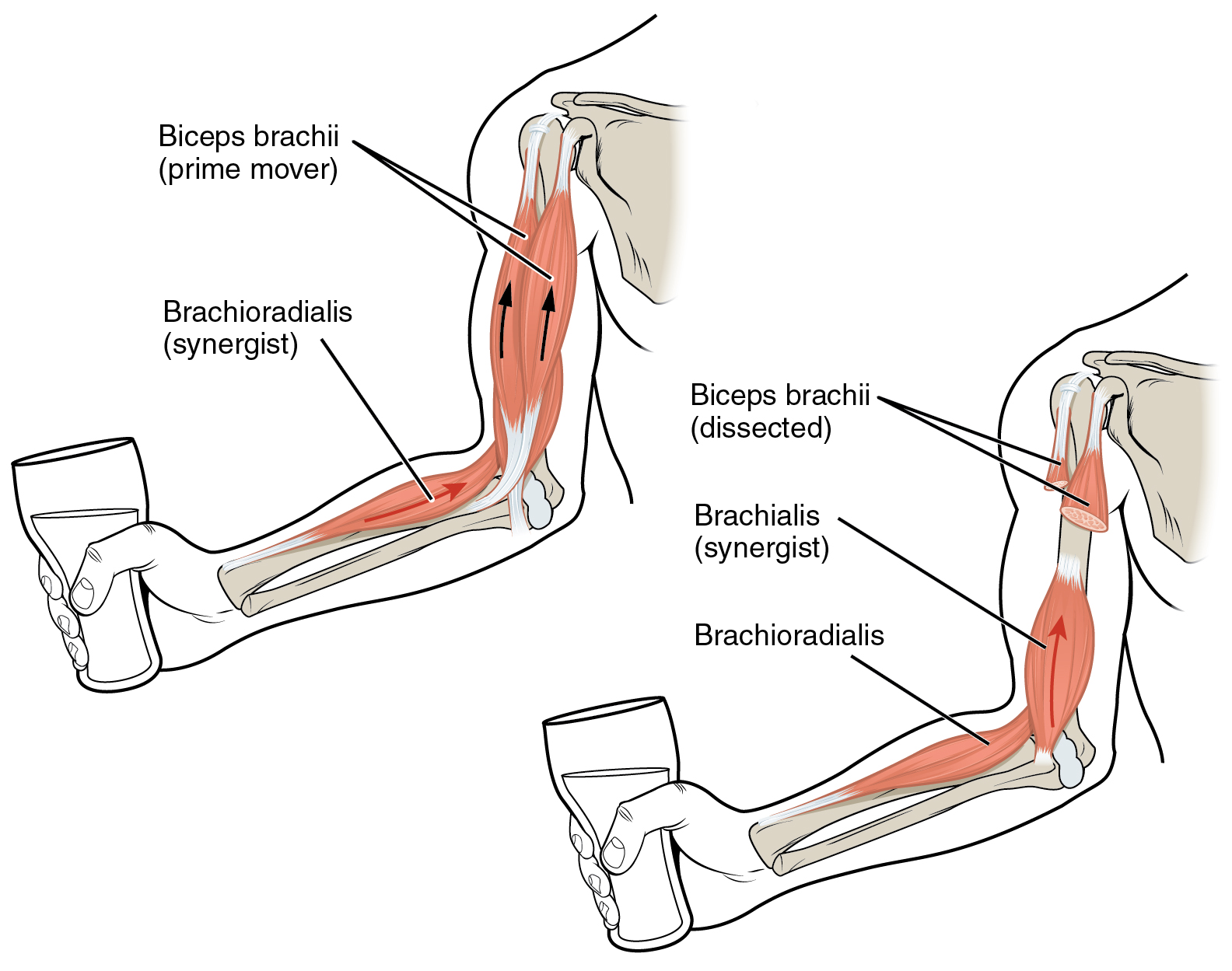
Coracobrachialis
The coracobrachialis muscle muscle in the upper medial part of the arm. It is located within the anterior compartment of the arm. It originates from the coracoid process of the scapula; it inserts onto the middle of the medial aspect of the body of the humerus. It is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve. It acts to adduct and flex the arm. Structure Origin Coracobrachialis muscle arises from the (deep surface of the) apex of the coracoid process of the scapula (a common origin with the short head of the biceps brachii). It additionally also arises from the proximal portion of tendon of origin of the biceps brachii muscle. Insertion It is inserted (by means of a flat tendon) into an impression at the middle of the medial border of the body of the humerus (shaft of the humerus) between the attachments of the medial head of the triceps brachii and the brachialis. Innervation Coracobrachialis muscle is perforated by and innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve, which ari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Slip
Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location. Types There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscle Skeletal muscle, or "voluntary muscle", is a striated muscle tissue that primarily joins to bone with tendons. Skeletal muscle enables movement of bones, and maintains posture. The widest part of a muscle that pulls on the tendons is known as the belly. Muscle slip A muscle slip is a slip of muscle that can either be an anatomical variant, or a branching of a muscle as in rib connections of the serratus anterior muscle. Smooth muscle Smooth muscle is involuntary and found in parts of the body where it conveys action without conscious intent. The majority of this type of muscle tissue is found in the digestive and urinary systems where it acts by propelling forward food, chyme, and feces in the former and ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pull Up (exercise)
A pull-up is an upper-body strength exercise. The pull-up is a closed-chain movement where the body is suspended by the hands, gripping a bar or other implement at a distance typically wider than shoulder-width, and pulled up. As this happens, the elbows flex and the shoulders adduct and extend to bring the elbows to the torso. Pull-ups build up several muscles of the upper body, including the latissimus dorsi, trapezius, and biceps brachii. A pull-up may be performed with overhand (pronated), underhand (supinated)—sometimes referred to as a chin-up—neutral, or rotating hand position. Pull-ups are used by some organizations as a component of fitness tests, and as a conditioning activity for some sports. Movement Beginning by hanging from the bar, the body is pulled up vertically. From the top position, the participant lowers their body until the arms and shoulders are fully extended. The end range of motion at the top end may be chin over bar or higher, such as ches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Motion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synergistic
Synergy is an interaction or cooperation giving rise to a whole that is greater than the simple sum of its parts (i.e., a non-linear addition of force, energy, or effect). The term ''synergy'' comes from the Attic Greek word συνεργία ' from ', , meaning "working together". Synergy is similar in concept to emergence. History The words ''synergy'' and ''synergetic'' have been used in the field of physiology since at least the middle of the 19th century: SYN'ERGY, ''Synergi'a'', ''Synenergi'a'', (F.) ''Synergie''; from ''συν'', 'with', and ''εργον'', 'work'. A correlation or concourse of action between different organs in health; and, according to some, in disease. :—Dunglison, Roble''Medical Lexicon''Blanchard and Lea, 1853 In 1896, :fr:Henri Mazel, Henri Mazel applied the term "synergy" to social psychology by writing ''La synergie sociale'', in which he argued that Darwinian theory failed to account of "social synergy" or "social love", a collective evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shoulder Joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial joint, synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule, it gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilage, cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the Biceps, biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Rotation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', describe movement above or below the horizontal plane. Many anatomica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |