|
Laser Scanner
Laser scanning is the controlled deflection of laser beams, visible or invisible. Scanned laser beams are used in some 3-D printers, in rapid prototyping, in machines for material processing, in laser engraving machines, in ophthalmological laser systems for the treatment of presbyopia, in confocal microscopy, in laser printers, in laser shows, in Laser TV, and in barcode scanners. Applications specific to mapping and 3D object reconstruction are known as ''3D laser scanner''. Technology Scanning mirrors Most laser scanners use moveable mirrors to steer the laser beam. The steering of the beam can be ''one-dimensional'', as inside a laser printer, or ''two-dimensional'', as in a laser show system. Additionally, the mirrors can lead to a ''periodic'' motion - like the rotating ''polygon mirrror'' in a barcode scanner or so-called ''resonant galvanometer'' scanners - or to a ''freely addressable'' motion, as in servo-controlled galvanometer scanners. One also uses the terms ''r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deflection (physics)
In physics, deflection is a change in a moving object's velocity, hence its trajectory, as a consequence of contact (collision) with a surface or the influence of a non-contact force field. Examples of the former include a ball bouncing off the ground or a bat; examples of the latter include a beam of electrons used to produce a picture, or the relativistic bending of light due to gravity. Deflective efficiency An object's deflective efficiency can never equal or surpass 100%, for example: *a mirror will never reflect exactly the same amount of light cast upon it, though it may concentrate the light which is reflected into a narrower beam. *on hitting the ground, a ball previously in free-fall (meaning no force other than gravity acted upon it) will never bounce back up to the place where it first started to descend. This transfer of some energy into heat or other radiation is a consequence of the theory of thermodynamics, where, for every such interaction, some energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates with a reversed flow of power, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Electric motors can be powered by direct current (DC) sources, such as from batteries, or rectifiers, or by alternating current (AC) sources, such as a power grid, inverters or electrical generators. Electric motors may be classified by considerations such as power source type, construction, application and type of motion output. They can be powered by AC or DC, be brushed or brushless, single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase, axial or radial flux, and may be air-cooled or liquid-cooled. Standardized motors provide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Speed Mobile Laser Scanning System
High may refer to: Science and technology * Height * High (atmospheric), a high-pressure area * High (computability), a quality of a Turing degree, in computability theory * High (tectonics), in geology an area where relative tectonic uplift took or takes place * Substance intoxication, also known by the slang description "being high" * Sugar high, a misconception about the supposed psychological effects of sucrose Music Performers * High (musical group), a 1974–1990 Indian rock group * The High, an English rock band formed in 1989 Albums * ''High'' (The Blue Nile album) or the title song, 2004 * ''High'' (Flotsam and Jetsam album), 1997 * ''High'' (New Model Army album) or the title song, 2007 * ''High'' (Royal Headache album) or the title song, 2015 * ''High'' (EP), by Jarryd James, or the title song, 2016 Songs * "High" (Alison Wonderland song), 2018 * "High" (The Chainsmokers song), 2022 * "High" (The Cure song), 1992 * "High" (David Hallyday song), 1988 * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical-cavity Surface-emitting Laser
The vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser, or VCSEL , is a type of semiconductor laser diode with laser beam emission perpendicular from the top surface, contrary to conventional edge-emitting semiconductor lasers (also ''in-plane'' lasers) which emit from surfaces formed by cleaving the individual chip out of a wafer. VCSELs are used in various laser products, including computer mice, fiber optic communications, laser printers, Face ID, and smartglasses. Production advantages There are several advantages to producing VCSELs, in contrast to the production process of edge-emitting lasers. Edge-emitters cannot be tested until the end of the production process. If the edge-emitter does not function properly, whether due to bad contacts or poor material growth quality, the production time and the processing materials have been wasted. VCSELs however, can be tested at several stages throughout the process to check for material quality and processing issues. For instance, if t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
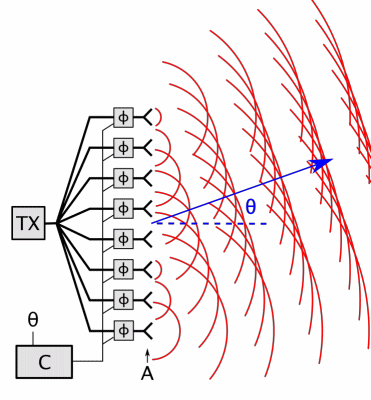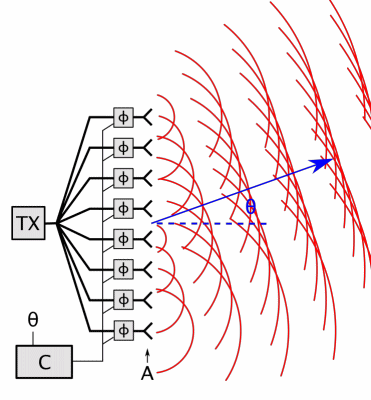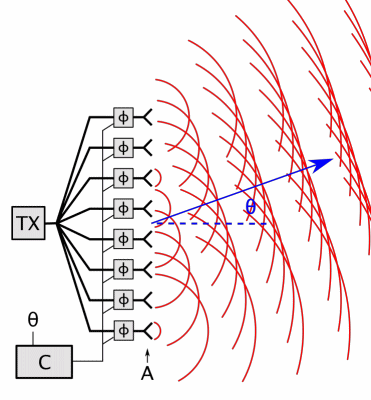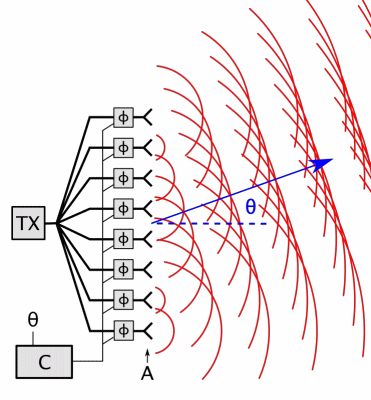
Phased Array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called '' phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser TV
Laser color television (laser TV), or laser color video display, is a type of television that utilizes two or more individually modulated optical (laser) rays of different colors to produce a combined spot that is scanned and projected across the image plane by a polygon-mirror system or less effectively by optoelectronic means to produce a color-television display. The systems work either by scanning the entire picture a dot at a time and modulating the laser directly at high frequency, much like the electron beams in a cathode ray tube, or by optically spreading and then modulating the laser and scanning a line at a time, the line itself being modulated in much the same way as with digital light processing (DLP). The special case of one ray reduces the system to a monochrome display as, for example, in black and white television. This principle applies to a direct view display as well as to a (front or rear) laser projector system. Laser TV technology began to appear in the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electro-optics
Electro–optics is a branch of electrical engineering, electronic engineering, materials science, and material physics involving components, electronic devices such as lasers, laser diodes, LEDs, waveguides, etc. which operate by the propagation and interaction of light with various tailored materials. It is closely related to the branch of optics, involving application of generation of photons, called photonics. It is not only concerned with the " electro–optic effect", since it deals with the interaction between the electromagnetic ( optical) and the electrical ( electronic) states of materials. Electro-optical devices The electro-optic effect is a change in the optical properties of an optically active material due to interaction with light. This interaction usually results in a change in the birefringence Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acousto-optic Modulator
An acousto-optic modulator (AOM), also called a Bragg cell or an acousto-optic deflector (AOD), uses the acousto-optic effect to diffract and shift the frequency of light using sound waves (usually at radio-frequency). They are used in lasers for Q-switching, telecommunications for signal modulation, and in spectroscopy for frequency control. A piezoelectric transducer is attached to a material such as glass. An oscillating electric signal drives the transducer to vibrate, which creates sound waves in the material. These can be thought of as moving periodic planes of expansion and compression that change the index of refraction. Incoming light scatters (see Brillouin scattering) off the resulting periodic index modulation and interference occurs similar to Bragg diffraction. The interaction can be thought of as a three-wave mixing process resulting in Sum-frequency generation or Difference-frequency generation between phonons and photons. Principles of operation A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prism (optics)
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled — elements with two parallel surfaces are ''not'' prisms. The most familiar type of optical prism is the triangular prism, which has a triangular base and rectangular sides. Not all optical prisms are geometric prisms, and not all geometric prisms would count as an optical prism. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic and fluorite. A dispersive prism can be used to break white light up into its constituent spectral colors (the colors of the rainbow) as described in the following section. Other types of prisms noted below can be used to reflect light, or to split light into components with different polarizations. Types Dispersive ''Dispersive prisms'' are used to break up light into its constituent spectral col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handheld Projector
A handheld projector (also known as a pocket projector, mobile projector, pico projector or mini beamer) is an image projector in a handheld device. It was developed as a computer display device for compact portable devices such as mobile phones, personal digital assistants, and digital cameras, which have sufficient storage capacity to handle presentation materials but are too small to accommodate a display screen that an audience can see easily. Handheld projectors involve miniaturized hardware, and software that can project digital images onto a nearby viewing surface. The system comprises five main parts: the battery, the electronics, the laser or LED light sources, the combiner optic, and in some cases, scanning micromirror devices. First, the electronics system turns the image into an electronic signal. Next, the electronic signals drive laser or LED light sources with different colors and intensities down different paths. In the combiner optic, the different ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |