|
Laghu
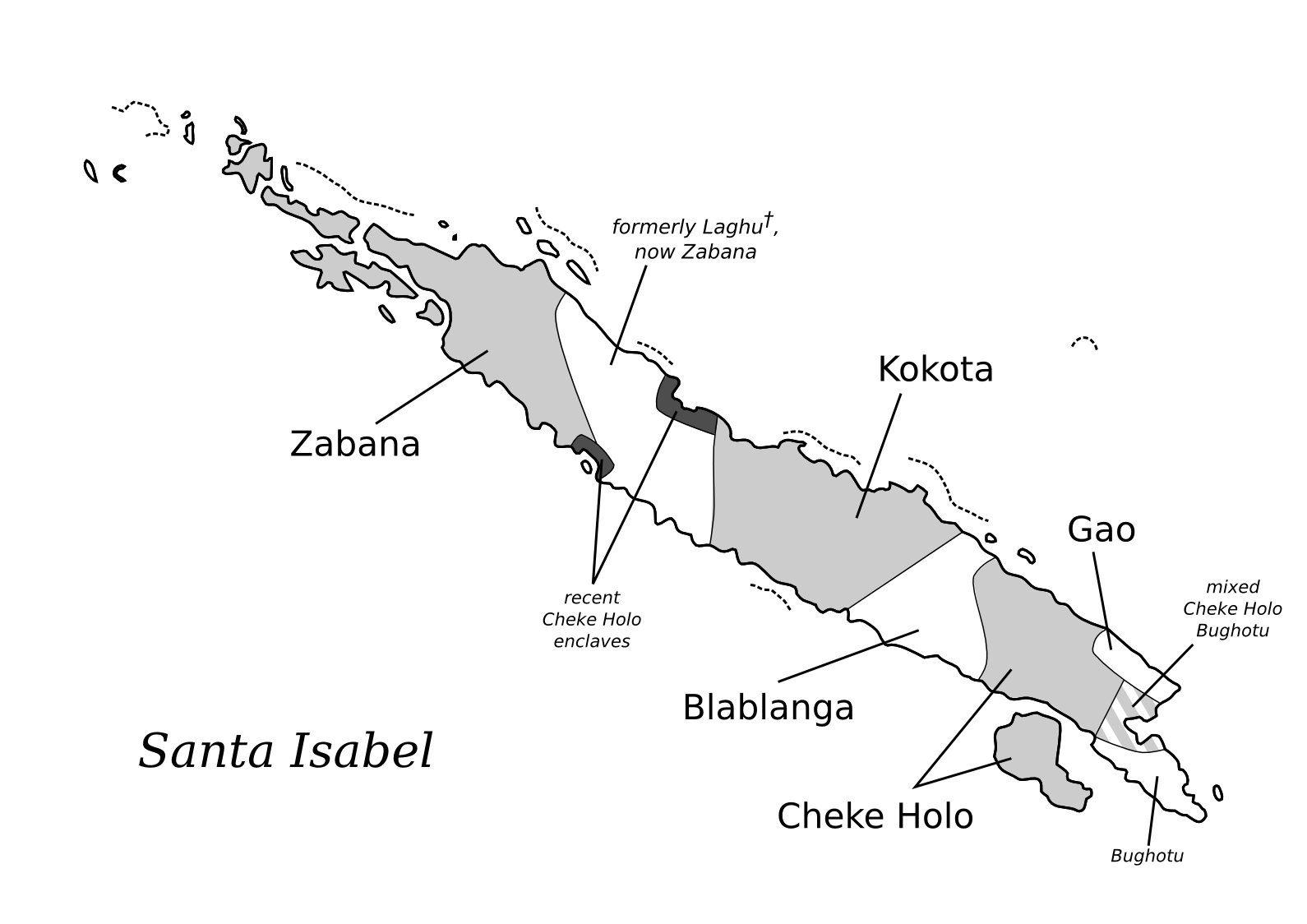
Laghu (pronounced ), also known as Hoatana or Katova, is an extinct language of Santa Isabel in the Solomon Islands. Its last speaker died in 1984. People in the villages of Baolo and Samasodu, where it used to be spoken, now speak the neighboring Zabana language, which is more widely spoken and still expanding (Palmer 2009:1-2). References * Palmer, Bill. 2009. ''Kokota Grammar.'' Oceanic Linguistics Special Publication No. 35. Honolulu: University of Hawaii Press. . Languages of the Solomon Islands Extinct languages of the Solomon Islands Languages extinct in the 1980s Ysabel languages {{MesoMelanesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laghuu
Laghuu ( vi, Xá Phó, Phù Lá Lão) is a Loloish language spoken in northwestern Vietnam.Raymond G. Gordon Jr., ed. 2005. ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World''. 15th edition. Dallas: Summer Institute of Linguistics. In Nậm Sài, Sa Pa Town, the speakers' autonym is ', while in Sơn La Province it is ' (Edmondson 1999). The people are also called the by the Vietnamese. Edmondson considers Laghuu to be related to but not part of the Yi language complex of China. Jamin Pelkey (2011) considers Laghuu to be a Southeastern Loloish language. Distribution Laghuu is spoken in the following locations by a total of about 1,000 people (Edmondson 1999 & 2002). *Lào Cai Province ** Văn Bàn District ** Bảo Thắng District **Bát Xát District ***A Lù **Sa Pa Town ***Nậm Sài **Cam Đường (near Lào Cai city) *Yên Bái Province ** Văn Yên *Sơn La Sơn La (; Tai Dam: ) is a city in the north-west region of Vietnam. It is the capital of Sơn La Province. It is bordered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Isabel Island
Santa Isabel Island (also known as Isabel, Ysabel and Mahaga) is the longest in Solomon Islands, the third largest in terms of surface area, and the largest in the group of islands in Isabel Province. Location and geographic data Choiseul lies to the north-west, Malaita to the south-east. The Pacific Ocean lies to the north, and Guadalcanal (Isatabu) to the south. The highest point in Santa Isabel is Mount Sasari, . The Marutho river runs down Mount Sasari to the ocean at Hofi. Almost all the rivers or streams run from that centre point except for those at the other tip of the island on the Katova side. The administrative centre is Buala. The nearest airport is Fera Airport on neighbouring Fera Island. History The first European landing in the Solomon Islands archipelago was made at Santa Isabel Island, by the Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña on 7 February 1568. It was charted as ''Santa Isabel de la Estrella'' (St. Elizabeth of the Star of Bethlehem in Spanish). A set ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Solomonic Languages
The family of Northwest Solomonic languages is a branch of the Oceanic languages. It includes the Austronesian languages of Bougainville and Buka in Papua New Guinea, and of Choiseul, New Georgia, and Santa Isabel (excluding Bugotu) in Solomon Islands. The unity of Northwest Solomonic and the number and composition of its subgroups, along with its relationship to other Oceanic groups, was established in pioneering work by Malcolm Ross. Languages Northwest Solomonic languages group as follows: * Nehan – North Bougainville linkage ** Nehan (Nissan) **Saposa–Tinputz: Hahon, Ratsua, Saposa (Taiof)– Teop, Tinputz **Buka: Halia– Hakö, Petats ** Papapana ** Solos * Piva–Bannoni family: Piva (Lawunuia), Bannoni * Mono–Uruavan family: Mono-Alu, Torau, Uruava *Choiseul linkage: Babatana (including Sisingga)– Ririo, Vaghua– Varisi *New Georgia – Ysabel family **New Georgia linkage: Simbo (Simbo Island), Roviana– Kusaghe, Marovo, Hoava, Vangunu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ysabel Languages
The family of Northwest Solomonic languages is a branch of the Oceanic languages. It includes the Austronesian languages of Bougainville and Buka in Papua New Guinea, and of Choiseul, New Georgia, and Santa Isabel (excluding Bugotu) in Solomon Islands. The unity of Northwest Solomonic and the number and composition of its subgroups, along with its relationship to other Oceanic groups, was established in pioneering work by Malcolm Ross. Languages Northwest Solomonic languages group as follows: * Nehan – North Bougainville linkage ** Nehan (Nissan) **Saposa–Tinputz: Hahon, Ratsua, Saposa (Taiof)– Teop, Tinputz **Buka: Halia– Hakö, Petats ** Papapana ** Solos * Piva–Bannoni family: Piva (Lawunuia), Bannoni * Mono–Uruavan family: Mono-Alu, Torau, Uruava *Choiseul linkage: Babatana (including Sisingga)– Ririo, Vaghua– Varisi *New Georgia – Ysabel family **New Georgia linkage: Simbo (Simbo Island), Roviana– Kusaghe, Marovo, Hoava, Vangunu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capital, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous Region of Bougainville (currently a part of Papua New Guinea), but excludes the Santa Cruz Islands. The islands have been settled since at least some time between 30,000 and 28,800 BCE, with later waves of migrants, notably the Lapita people, mixing and producing the modern indigenous Solomon Islanders population. In 1568, the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña was the first European to visit them. Though not named by Mendaña, it is believed that the islands were called ''"the Solomons"'' by those who later receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zabana Language
Zabana is an Oceanic language spoken almost exclusively in the Kia district on the northern part of Santa Isabel Island in the Solomon Islands. Zabana is considered a developing language (EGIDS 5) which means that the language is in vigorous use, with literature in a standardized form being used by some though this is not yet widespread or sustainable. It is one of the most spoken languages on Santa Isabel Island, competing with Cheke Holo. There is a 30% to 60% literacy rate in Zabana as a first language and a 25% to 50% literacy rate in Zabana as a second language. Location Zabana is almost exclusively spoken on Santa Isabel Island which is the largest island in the Isabel provenience and the third largest island in the Solomon Island chain. Zabana is one of the eight different languages spoken on Santa Isabel island. Out of the other seven different languages spoken on the island, Zabana shares major similarities with Kokota and Cheke Holo (also known as Maringe.) A combina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Hawaii Press
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of The Solomon Islands
Between 60 and 70 languages are spoken in the Solomon Islands Archipelago which covers a broader area than the nation state of Solomon Islands, and includes the island of Bougainville, which is an autonomous province of Papua New Guinea (PNG). The lingua franca of the archipelago is Pidgin, and the official language in both countries is English. Language families Most of the languages in the Solomon Islands are Austronesian languages. The Central Solomon languages such as Lavukaleve constitute an independent family. Two other language families are represented on Bougainville, which is geographically part of the Solomon Islands, if not within the national boundaries. The status of the Reefs – Santa Cruz languages were once thought to be non-Austronesian, but further research found them to be divergent Austronesian languages. The neighbouring languages of Vanikoro are also heavily relexified Austronesian languages. An indigenous sign language, Rennellese Sign Language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Languages Of The Solomon Islands
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, mam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Extinct In The 1980s
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of methods, including spoken, sign, and written language. Many languages, including the most widely-spoken ones, have writing systems that enable sounds or signs to be recorded for later reactivation. Human language is highly variable between cultures and across time. Human languages have the properties of productivity and displacement, and rely on social convention and learning. Estimates of the number of human languages in the world vary between and . Precise estimates depend on an arbitrary distinction (dichotomy) established between languages and dialects. Natural languages are spoken, signed, or both; however, any language can be encoded into secondary media using auditory, visual, or tactile stimuli – for example, writing, whis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
