|
L'Hôpital's Rule
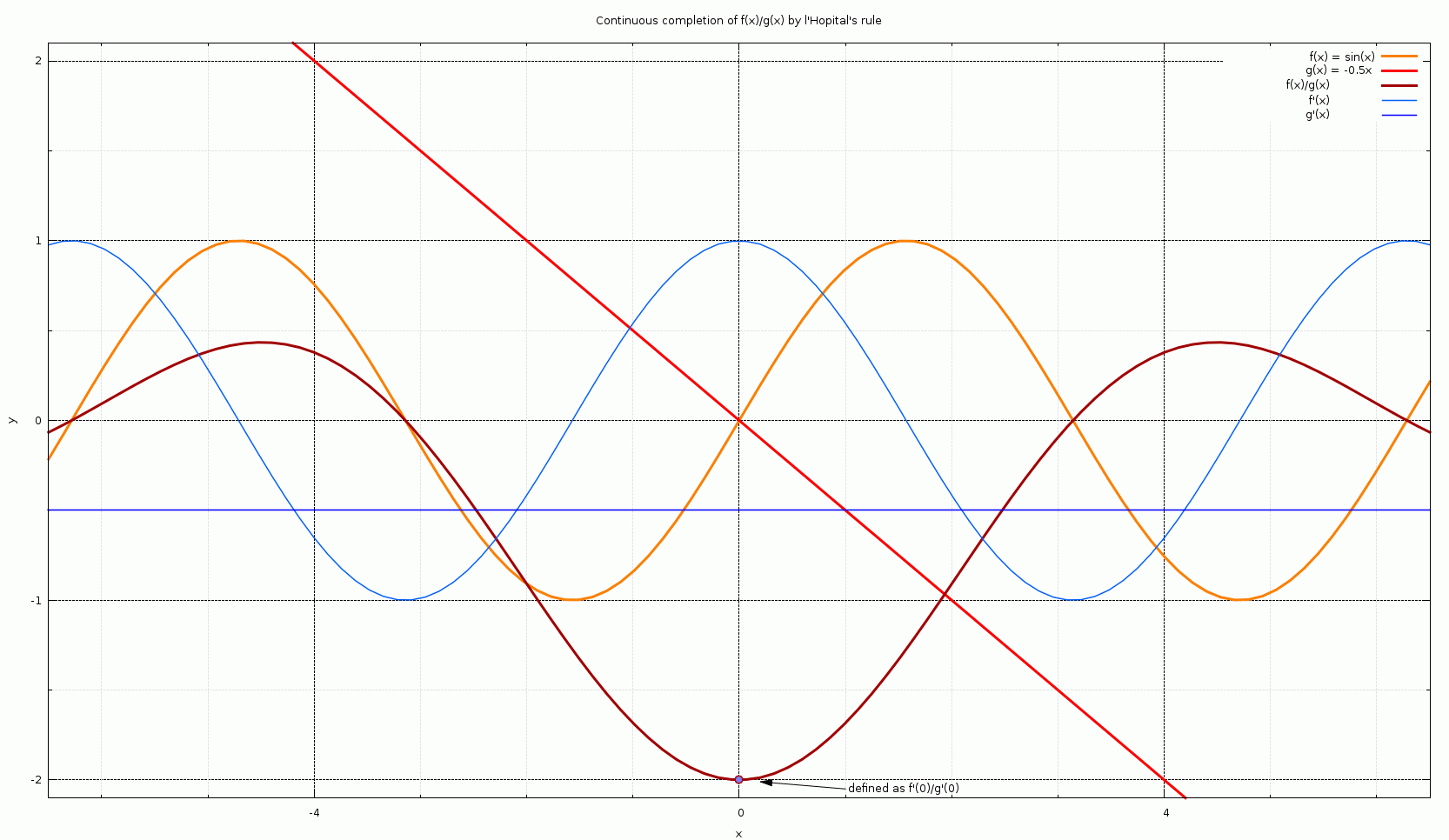
L'Hôpital's rule (, ), also known as Bernoulli's rule, is a mathematical theorem that allows evaluating limits of indeterminate forms using derivatives. Application (or repeated application) of the rule often converts an indeterminate form to an expression that can be easily evaluated by substitution. The rule is named after the 17th-century French mathematician Guillaume de l'Hôpital. Although the rule is often attributed to de l'Hôpital, the theorem was first introduced to him in 1694 by the Swiss mathematician Johann Bernoulli. L'Hôpital's rule states that for functions and which are defined on an open interval and differentiable on I\setminus \ for a (possibly infinite) accumulation point of , if \lim \limits_f(x)=\lim \limits_g(x)=0 \text\pm\infty, and g'(x)\ne 0 for all in I\setminus \, and \lim \limits_\frac exists, then :\lim_\frac = \lim_\frac. The differentiation of the numerator and denominator often simplifies the quotient or converts it to a limit t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Real Number Line
In mathematics, the extended real number system is obtained from the real number system \R by adding two elements denoted +\infty and -\infty that are respectively greater and lower than every real number. This allows for treating the potential infinities of infinitely increasing sequences and infinitely decreasing series as actual infinities. For example, the infinite sequence (1,2,\ldots) of the natural numbers increases ''infinitively'' and has no upper bound in the real number system (a potential infinity); in the extended real number line, the sequence has +\infty as its least upper bound and as its limit (an actual infinity). In calculus and mathematical analysis, the use of +\infty and -\infty as actual limits extends significantly the possible computations. It is the Dedekind–MacNeille completion of the real numbers. The extended real number system is denoted \overline, \infty,+\infty/math>, or \R\cup\left\. When the meaning is clear from context, the symbol +\inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Begging The Question
In classical rhetoric and logic, begging the question or assuming the conclusion (Latin: ) is an informal fallacy that occurs when an argument's premises assume the truth of the conclusion. Historically, begging the question refers to a fault in a dialectical argument in which the speaker assumes some premise that has not been demonstrated to be true. In modern usage, it has come to refer to an argument in which the premises assume the conclusion without supporting it. This makes it an example of circular reasoning.Herrick (2000) 248. Some examples are: *“Wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets as fall attire because wool sweaters have higher wool content". ** The claim in this quote is that wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets as fall attire. However, the justification of this claim begs the question because it ''presupposes'' that wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets: in other words, wool sweaters are better than nylon jackets because wool is better than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Reasoning
Circular reasoning (, "circle in proving"; also known as circular logic) is a fallacy, logical fallacy in which the reasoner begins with what they are trying to end with. Circular reasoning is not a formal logical fallacy, but a pragmatic defect in an argument whereby the premises are just as much in need of proof or evidence as the conclusion. As a consequence, the argument becomes a matter of faith and fails to persuade those who do not already accept it. Other ways to express this are that there is no reason to accept the premises unless one already believes the conclusion, or that the premises provide no independent ground or evidence for the conclusion. Circular reasoning is closely related to begging the question, and in modern usage the two generally refer to the same thing. Circular reasoning is often of the form: "A is true because B is true; B is true because A is true." Circularity can be difficult to detect if it involves a longer chain of propositions. An example of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortgage Calculator
Mortgage calculators are automated tools that enable users to determine the financial implications of changes in one or more variables in a mortgage financing arrangement. Mortgage calculators are used by consumers to determine monthly repayments, and by mortgage providers to determine the financial suitability of a home loan applicant. Mortgage calculators are frequently on for-profit websites, though the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau has launched its own public mortgage calculator. The major variables in a mortgage calculation include loan principal, balance, periodic compound interest rate, number of payments per year, total number of payments and the regular payment amount. More complex calculators can take into account other costs associated with a mortgage, such as local and state taxes, and insurance. Mortgage calculation capabilities can be found on financial handheld calculators such as the HP-12C or Texas Instruments TI BA II Plus. There are also multiple fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraposition
In logic and mathematics, contraposition, or ''transposition'', refers to the inference of going from a conditional statement into its logically equivalent contrapositive, and an associated proof method known as . The contrapositive of a statement has its antecedent and consequent negated and swapped. Conditional statement P \rightarrow Q. In formulas: the contrapositive of P \rightarrow Q is \neg Q \rightarrow \neg P . If ''P'', Then ''Q''. — If not ''Q'', Then not ''P''. "If ''it is raining,'' then ''I wear my coat''." — "If ''I don't wear my coat,'' then ''it isn't raining''." The law of contraposition says that a conditional statement is true if, and only if, its contrapositive is true. Contraposition ( \neg Q \rightarrow \neg P ) can be compared with three other operations: ; Inversion (the inverse), \neg P \rightarrow \neg Q:"If ''it is not raining,'' then ''I don't wear my coat''." Unlike the contrapositive, the inverse's truth value is not at all dependen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Mathematical Monthly
''The American Mathematical Monthly'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of mathematics. It was established by Benjamin Finkel in 1894 and is published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the Mathematical Association of America. It is an expository journal intended for a wide audience of mathematicians, from undergraduate students to research professionals. Articles are chosen on the basis of their broad interest and reviewed and edited for quality of exposition as well as content. The editor-in-chief An editor-in-chief (EIC), also known as lead editor or chief editor, is a publication's editorial leader who has final responsibility for its operations and policies. The editor-in-chief heads all departments of the organization and is held accoun ... is Vadim Ponomarenko ( San Diego State University). The journal gives the Lester R. Ford Award annually to "authors of articles of expository excellence" published in the journal. Editors-in-chief The following persons are or have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph P
Ralph (pronounced or ) is a male name of English origin, derived from the Old English ''Rædwulf'' and Old High German ''Radulf'', cognate with the Old Norse ''Raðulfr'' (''rað'' "counsel" and ''ulfr'' "wolf"). The most common forms are: * Ralph, the common variant form in English, which takes either of the given pronunciations. * Rafe, variant form which is less common; this spelling is always pronounced . * Raif, a very rare variant. Raif Rackstraw from H.M.S. Pinafore * Ralf, the traditional variant form in Dutch, German, Swedish, and Polish. * Ralfs, the traditional variant form in Latvian. * Raoul, the traditional variant form in French. * Raúl, the traditional variant form in Spanish. * Raul, the traditional variant form in Portuguese and Italian. * Raül, the traditional variant form in Catalan. * Rádhulbh, the traditional variant form in Irish. First name Middle Ages * Ralph the Timid (died 1057), pre-Conquest Norman earl of Hereford, England * Ralp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematische Annalen
''Mathematische Annalen'' (abbreviated as ''Math. Ann.'' or, formerly, ''Math. Annal.'') is a German mathematical research journal founded in 1868 by Alfred Clebsch and Carl Neumann. Subsequent managing editors were Felix Klein, David Hilbert, Otto Blumenthal, Erich Hecke, Heinrich Behnke, Hans Grauert, Heinz Bauer, Herbert Amann, Jean-Pierre Bourguignon, Wolfgang Lück, Nigel Hitchin, and Thomas Schick. Currently, the managing editor of Mathematische Annalen is Yoshikazu Giga (University of Tokyo). Volumes 1–80 (1869–1919) were published by Teubner. Since 1920 (vol. 81), the journal has been published by Springer. In the late 1920s, under the editorship of Hilbert, the journal became embroiled in controversy over the participation of L. E. J. Brouwer on its editorial board, a spillover from the foundational Brouwer–Hilbert controversy. Between 1945 and 1947, the journal briefly ceased publication. References External links''Mathematische Annalen''homepage a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Stolz
Otto Stolz (3 July 1842 – 23 November 1905) was an Austrian mathematician noted for his work on mathematical analysis and infinitesimals. Born in Hall in Tirol, he studied at the University of Innsbruck from 1860 and the University of Vienna from 1863, receiving his habilitation there in 1867. Two years later he studied in Berlin under Karl Weierstrass, Ernst Kummer and Leopold Kronecker, and in 1871 heard lectures in Göttingen by Alfred Clebsch and Felix Klein (with whom he would later correspond), before returning to Innsbruck permanently as a professor of mathematics. His work began with geometry (on which he wrote his thesis) but after the influence of Weierstrass it shifted to real analysis, and many small useful theorems are credited to him. For example, he proved that a continuous function ''f'' on a closed interval 'a'', ''b''with midpoint convexity, i.e., f\left(\frac2\right) \leq \frac, has left and right derivatives at each point in (''a'', ''b''). He died in 1905 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauchy's Mean Value Theorem
In mathematics, the mean value theorem (or Lagrange's mean value theorem) states, roughly, that for a given planar arc between two endpoints, there is at least one point at which the tangent to the arc is parallel to the secant through its endpoints. It is one of the most important results in real analysis. This theorem is used to prove statements about a function on an interval starting from local hypotheses about derivatives at points of the interval. History A special case of this theorem for inverse interpolation of the sine was first described by Parameshvara (1380–1460), from the Kerala School of Astronomy and Mathematics in India, in his commentaries on Govindasvāmi and Bhāskara II. A restricted form of the theorem was proved by Michel Rolle in 1691; the result was what is now known as Rolle's theorem, and was proved only for polynomials, without the techniques of calculus. The mean value theorem in its modern form was stated and proved by Augustin Louis Cauchy i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divergent Series
In mathematics, a divergent series is an infinite series that is not convergent, meaning that the infinite sequence of the partial sums of the series does not have a finite limit. If a series converges, the individual terms of the series must approach zero. Thus any series in which the individual terms do not approach zero diverges. However, convergence is a stronger condition: not all series whose terms approach zero converge. A counterexample is the harmonic series :1 + \frac + \frac + \frac + \frac + \cdots =\sum_^\infty\frac. The divergence of the harmonic series was proven by the medieval mathematician Nicole Oresme. In specialized mathematical contexts, values can be objectively assigned to certain series whose sequences of partial sums diverge, in order to make meaning of the divergence of the series. A ''summability method'' or ''summation method'' is a partial function from the set of series to values. For example, Cesàro summation assigns Grandi's divergent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |