|
Kyphoscoliosis
Kyphoscoliosis describes an abnormal curvature of the spine in both a coronal and sagittal plane. It is a combination of kyphosis and scoliosis. This musculoskeletal disorder often leads to other issues in patients, such as under-ventilation of lungs, pulmonary hypertension, difficulty in performing day-to-day activities, psychological issues emanating from anxiety about acceptance among peers, especially in young patients. It can also be seen in syringomyelia, Friedreich's ataxia, spina bifida, kyphoscoliotic Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (kEDS), and Duchenne muscular dystrophy due to asymmetric weakening of the paraspinal muscles. Signs and symptoms The following are clear signs of Kyphoscoliosis: * Abnormal hunch along with a presence of S or C-like shape. * * Presence of associated disorders like hypertension, neurological disorders * Abnormal gait Kyphosis Kyphosis by itself refers to an excessive convex curvature of the spine occurring in the thoracic and sacral regions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ehlers–Danlos Syndromes
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of 13 genetic connective-tissue disorders in the current classification, with the latest type discovered in 2018. Symptoms include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Complications may include aortic dissection, joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic pain, or early osteoarthritis. EDS occurs due to variations of more than 19 genes that are present at birth. The specific gene affected determines the type of EDS. Some cases result from a new variation occurring during early development, while others are inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner. Typically, these variations result in defects in the structure or processing of the protein collagen. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and confirmed by genetic testing or skin biopsy, but people may initially be misdiagnosed with hypochondriasis, depression, or chronic fatigue syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Familial Dysautonomia
Familial dysautonomia (FD), also known as Riley-Day Syndrome, is a rare, progressive, recessive genetic disorder of the autonomic nervous system that affects the development and survival of sensory, sympathetic and some parasympathetic neurons in the autonomic and sensory nervous system. FD results in variable symptoms, including insensitivity to pain, inability to produce tears, poor growth and labile blood pressure (episodic hypertension and postural hypotension). People with FD have frequent vomiting crises, pneumonia, problems with speech and movement, difficulty swallowing, inappropriate perception of heat, pain and taste as well as unstable blood pressure and gastrointestinal dysmotility. Originally reported by Drs. Conrad Milton Riley and Richard Lawrence Day in 1949, FD is one example of a group of disorders known as hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathies ( HSAN). All HSAN are characterized by widespread sensory dysfunction and variable autonomic dysfunction cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lordosis
Lordosis is historically defined as an ''abnormal'' inward curvature of the lumbar spine. However, the terms ''lordosis'' and ''lordotic'' are also used to refer to the normal inward curvature of the lumbar and cervical regions of the human spine. Similarly, kyphosis historically refers to ''abnormal'' convex curvature of the spine. The normal outward (convex) curvature in the thoracic and sacral regions is also termed ''kyphosis'' or ''kyphotic''. The term comes from the Greek lordōsis, from ''lordos'' ("bent backward"). Lordosis in the human spine makes it easier for humans to bring the bulk of their mass over the pelvis. This allows for a much more efficient walking gait than that of other primates, whose inflexible spines cause them to resort to an inefficient forward leaning "bent-knee, bent-waist" gait. As such, lordosis in the human spine is considered one of the primary physiological adaptations of the human skeleton that allows for human gait to be as energeticall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FKBP14
FKBP14 is a gene which codes for a structural protein named FKBP prolyl isomerase 14. This protein is believed to aid in the process of procollagen folding and is located in the endoplasmic reticulum that functions to process and transport proteins. Procollagens are collagen precursors located in the extracellular matrix that give tissues elasticity, strength, and support. This gene is involved in patterning the collagen structure. FKBP prolyl isomerase 14 may also be involved in altering other factors in the extracellular matrix. Mutations of this gene are associated with the kyphoscoliotic type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. This condition is characterized by a high range of joint movement, muscle atrophy, curved spine, and delicate cardiovascular vessels. These symptoms are brought about by a loss of the protein which results in a disruption of endoplasmic reticulum activities and extracellular matrix organization. FKBP14 mRNA levels are found higher in ovarian cancer tissues than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a type of degenerative joint disease that results from breakdown of joint cartilage and underlying bone which affects 1 in 7 adults in the United States. It is believed to be the fourth leading cause of disability in the world. The most common symptoms are joint pain and stiffness. Usually the symptoms progress slowly over years. Initially they may occur only after exercise but can become constant over time. Other symptoms may include joint swelling, decreased range of motion, and, when the back is affected, weakness or numbness of the arms and legs. The most commonly involved joints are the two near the ends of the fingers and the joint at the base of the thumbs; the knee and hip joints; and the joints of the neck and lower back. Joints on one side of the body are often more affected than those on the other. The symptoms can interfere with work and normal daily activities. Unlike some other types of arthritis, only the joints, not internal organs, are af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Disorders
Bone disease refers to the medical conditions which affect the bone. Terminology A bone disease is also called an "osteopathy", but because the term osteopathy is often used to refer to an alternative health-care philosophy, use of the term can cause some confusion. Bone and cartilage disorders Osteochondrodysplasia is a general term for a disorder of the development of bone and cartilage. List A * Ambe * Avascular necrosis or Osteonecrosis * Arthritis B * Bone spur (Osteophytes) C * Craniosynostosis * Coffin–Lowry syndrome * Copenhagen disease F * Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva * Fibrous dysplasia * Fong disease (or Nail–patella syndrome) * Fracture G * Giant cell tumor of bone * Greenstick fracture * Gout H * Hypophosphatasia * Hereditary multiple exostoses K * Klippel–Feil syndrome M * Metabolic bone disease * Multiple myeloma N * Nail–patella syndrome O * Osteitis * Osteitis deformans (or Paget's disease of bone) * Osteitis fibr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pott's Disease
Pott disease is tuberculosis of the spine, usually due to haematogenous spread from other sites, often the lungs. The lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebrae areas of the spine are most often affected. It causes a kind of tuberculous arthritis of the intervertebral joints. The infection can spread from two adjacent vertebrae into the adjoining intervertebral disc An intervertebral disc (or intervertebral fibrocartilage) lies between adjacent vertebrae in the vertebral column. Each disc forms a fibrocartilaginous joint (a symphysis), to allow slight movement of the vertebrae, to act as a ligament to hold t ... space. If only one vertebra is affected, the disc is normal, but if two are involved, the disc, which is avascular, cannot receive nutrients, and collapses. In a process called caseous necrosis, the disc tissue dies, leading to vertebral narrowing and eventually to vertebral collapse and spinal damage. A dry soft-tissue mass often forms and superinfection is rare. Spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
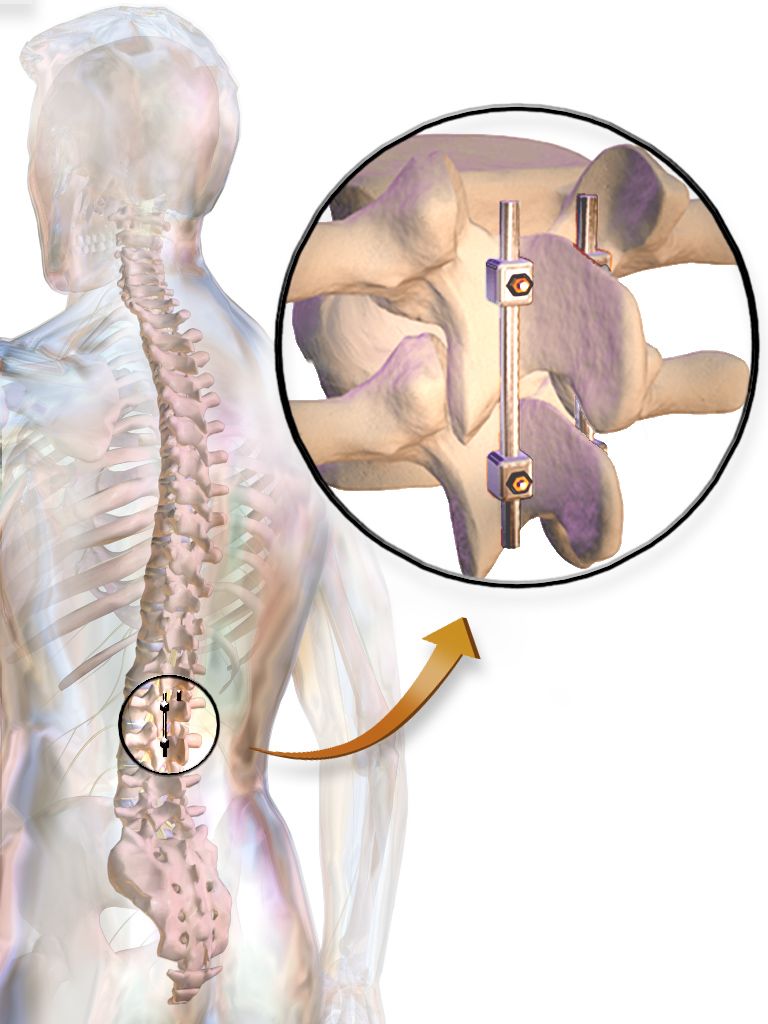
Harrington Rod
The Harrington rod (or Harrington implant) is a stainless steel Stainless steel is an alloy of iron that is resistant to rusting and corrosion. It contains at least 11% chromium and may contain elements such as carbon, other nonmetals and metals to obtain other desired properties. Stainless steel's corros ... surgical device. Historically, this rod was implanted along the spinal column to treat, among other conditions, a lateral or coronal-plane curvature of the spine, or scoliosis. Up to one million people had Harrington rods implanted for scoliosis between the early 1960s and the late 1990s. History The Harrington implant was developed in 1953 by Paul Randall Harrington, Paul Harrington, a professor of orthopedic surgery at Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, Texas. Harrington rods were intended to provide a means to reduce the curvature and to provide more stability to a spinal fusion. Before the Harrington rod was invented, scoliosis patients had their spines fused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoxemia
Hypoxemia is an abnormally low level of oxygen in the blood. More specifically, it is oxygen deficiency in arterial blood. Hypoxemia has many causes, and often causes hypoxia as the blood is not supplying enough oxygen to the tissues of the body. Definition ''Hypoxemia'' refers to the low level of oxygen in blood, and the more general term ''hypoxia'' is an abnormally low oxygen content in any tissue or organ, or the body as a whole. Hypoxemia can cause hypoxia (hypoxemic hypoxia), but hypoxia can also occur via other mechanisms, such as anemia. Hypoxemia is usually defined in terms of reduced partial pressure of oxygen (mm Hg) in arterial blood, but also in terms of reduced content of oxygen (ml oxygen per dl blood) or percentage saturation of hemoglobin (the oxygen-binding protein within red blood cells) with oxygen, which is either found singly or in combination. While there is general agreement that an arterial blood gas measurement which shows that the partial pressure of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Back Brace
A back brace is a device designed to limit the motion of the spine in cases of bone fracture or in post-operative spinal fusiona, as well as a preventative measure against some progressive conditions or to correct patient posture. Common back braces include: * Rigid (hard) braces : These braces are form-fitting plastic molds (historically leather) and rigid (typically metal) supports that significantly restrict motion by between 50 and 65% while rotation is limited by up to 70%. * Soft braces : Elastic braces that limit the forward motion of the spine and assist in setting spinal fusions or supporting the spine during occasions of stress (for example, employment requiring the lifting of heavy loads) * Semi rigid braces : Semi-rigid braces combine elements of flexible and rigid braces within one overall design. This is done by adding rigid supports or additional stiff padding and straps to the body of a flexible brace. Sometimes these added rigid supports are removable, allowing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Specimen Of Adult Female Showing Kyphoscoliosis (curvature Of The Spine), 1830-1860 - NCP 3358
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body, and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal skeleton supported by fluid pressure. Vertebrates are animals with a vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bone and cartilage. Invertebrates are animals that lack a vertebral column. The skeletons of invertebrates vary, including hard exoskeleton shells, plated endoskeletons, or spicules. Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invertebrates. Etymology The term ''skeleton'' comes . ''Sceleton'' is an archaic form of the word. Classification Skeletons can be defined by several attributes. Solid skeletons consist of hard substances, such as bone, cartilage, or cuticle. These can be further divided by locat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |