|
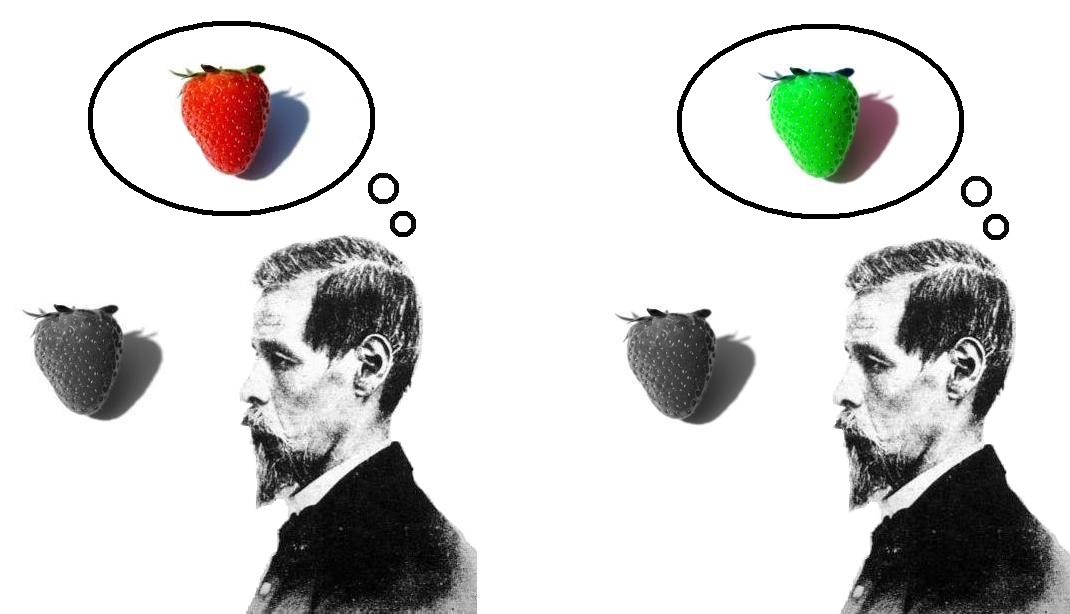
Knowledge Argument
The knowledge argument (also known as Mary's room or Mary the super-scientist) is a philosophical thought experiment proposed by Frank Jackson in his article "Epiphenomenal Qualia" (1982) and extended in "What Mary Didn't Know" (1986). The experiment describes Mary, a scientist who exists in a black and white world where she has extensive access to physical descriptions of color, but no actual human perceptual experience of color. The central question of the thought experiment is whether Mary will gain new knowledge when she goes outside the black and white world and experiences seeing in color. The experiment is intended to argue against physicalism—the view that the universe, including all that is mental, is entirely physical. The debate that emerged following its publication became the subject of an edited volume—''There's Something About Mary'' (2004)—which includes replies from such philosophers as Daniel Dennett, David Lewis, and Paul Churchland. Thought experiment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thought Experiment
A thought experiment is a hypothetical situation in which a hypothesis, theory, or principle is laid out for the purpose of thinking through its consequences. History The ancient Greek ''deiknymi'' (), or thought experiment, "was the most ancient pattern of mathematical proof", and existed before Euclidean mathematics, where the emphasis was on the conceptual, rather than on the experimental part of a thought-experiment. Johann Witt-Hansen established that Hans Christian Ørsted was the first to use the German term ' (lit. thought experiment) circa 1812. Ørsted was also the first to use the equivalent term ' in 1820. By 1883 Ernst Mach used the term ' in a different way, to denote exclusively the conduct of a experiment that would be subsequently performed as a by his students. Physical and mental experimentation could then be contrasted: Mach asked his students to provide him with explanations whenever the results from their subsequent, real, physical experiment differed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blindsight
Blindsight is the ability of people who are cortically blind to respond to visual stimuli that they do not consciously see due to lesions in the primary visual cortex, also known as the striate cortex or Brodmann Area 17. The term was coined by Lawrence Weiskrantz and his colleagues in a paper published in a 1974 issue of ''Brain''. A previous paper studying the discriminatory capacity of a cortically blind patient was published in ''Nature'' in 1973. Type classification The majority of studies on blindsight are conducted on patients who are hemianopic, i.e. blind in one half of their visual field. Following the destruction of the left or right striate cortex, patients are asked to detect, localize, and discriminate amongst visual stimuli that are presented to their blind side, often in a forced-response or guessing situation, even though they may not consciously recognize the visual stimulus. Research shows that such blind patients may achieve a higher accuracy than would be ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenomenal Concept Strategy
The phenomenal concept strategy (PCS) is an approach within philosophy of mind to provide a physicalist response to anti-physicalist arguments like the explanatory gap and philosophical zombies. The name was coined by Daniel Stoljar. As David Chalmers put it, PCS "locates the gap in the relationship between our ''concepts'' of physical processes and our ''concepts'' of consciousness, rather than in the relationship between physical processes and consciousness themselves." The idea is that if we can explain why we ''think'' there's an explanatory gap, this will defuse the motivation to question physicalism. Overview PCS advocates typically subscribe to what Chalmers has called "type-B materialism", which holds that there is an epistemic but not ontological gap between physics and subjective experience. PCS maintains that our concepts are dualistic, but reality is monistic, in a similar way as "heat" and "molecular motion" are two different concepts that refer to the same property ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martine Nida-Rümelin
Martine Nida-Rümelin (born 1957 in Munich) is a philosopher. Biography Nida-Rümelin studied philosophy, psychology, mathematics and political science at the University of Munich. In her doctoral thesis, she discusses the knowledge argument, by the Australian philosopher Frank Jackson, which is directed against a materialist conception of phenomenal consciousness. In it she presents one of the most important arguments, which is based on qualia, i.e., individual instances of subjective, conscious experience. Her transformed version of the Mary's room thought-experiment has been much discussed and coined the "Nida-Rümelin room" by John Perry. In her habilitation she developed a non- reductionist view about the identity of conscious individuals. In 2019, she won the Jean Nicod Prize. She is the daughter of the sculptor Rolf Nida-Rümelin, the granddaughter of the sculptor Wilhelm Nida-Rümelin and the sister of the philosopher and politician Julian Nida-Rümelin. Academ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Chalmers
David John Chalmers (; born 20 April 1966) is an Australian philosopher and cognitive scientist specializing in the areas of philosophy of mind and philosophy of language. He is a professor of philosophy and neural science at New York University, as well as co-director of NYU's Center for Mind, Brain and Consciousness (along with Ned Block). In 2006, he was elected a Fellow of the Australian Academy of the Humanities. In 2013, he was elected a Fellow of the American Academy of Arts & Sciences. Chalmers is best known for formulating the hard problem of consciousness. He and David Bourget cofounded PhilPapers, a database of journal articles for philosophers. Early life and education Chalmers was born in Sydney, New South Wales, in 1966, and subsequently grew up in Adelaide, South Australia, where he attended Unley High School. As a child, he experienced synesthesia. He began coding and playing computer games at age 10 on a PDP-10 at a medical center. He also performed e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroboscopic Effect
The stroboscopic effect is a visual phenomenon caused by aliasing that occurs when continuous rotational or other cyclic motion is represented by a series of short or instantaneous samples (as opposed to a continuous view) at a sampling rate close to the period of the motion. It accounts for the " wagon-wheel effect", so-called because in video, spoked wheels (such as on horse-drawn wagons) sometimes appear to be turning backwards. A strobe fountain, a stream of water droplets falling at regular intervals lit with a strobe light, is an example of the stroboscopic effect being applied to a cyclic motion that is not rotational. When viewed under normal light, this is a normal water fountain. When viewed under a strobe light with its frequency tuned to the rate at which the droplets fall, the droplets appear to be suspended in mid-air. Adjusting the strobe frequency can make the droplets seemingly move slowly up or down. Stroboscopic principles, and their ability to create an il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akinetopsia
Akinetopsia (Greek: a for "without", kine for "to move" and opsia for "seeing"), also known as cerebral akinetopsia or motion blindness, is a term introduced by Semir Zeki to describe an extremely rare neuropsychological disorder, having only been documented in a handful of medical cases, in which a patient cannot perceive motion in their visual field, despite being able to see stationary objects without issue. There are varying degrees of akinetopsia: from seeing motion as frames of a cinema reel to an inability to discriminate any motion. There is currently no effective treatment or cure for akinetopsia. Signs and symptoms Akinetopsia can be separated into two categories, "inconspicuous akinetopsia" or "gross akinetopsia", based on symptom severity and the amount the akinetopsia affects the patient's quality of life. Inconspicuous akinetopsia Inconspicuous akinetopsia is often described by seeing motion as a cinema reel or a multiple exposure photograph. This is the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip Pettit
Philip Noel Pettit (born 1945) is an Irish philosopher and political theorist. He is the Laurance S. Rockefeller University Professor of Politics and Human Values at Princeton University and also Distinguished University Professor of Philosophy at the Australian National University. Education and career Pettit was educated at Garbally College, the National University of Ireland, Maynooth (BA, LPh, MA) and Queen's University, Belfast (PhD). He has been a lecturer at University College, Dublin, a research fellow at Trinity Hall, Cambridge, and professor at the University of Bradford. He was for many years professorial fellow in social and political theory at the Research School of Social Sciences, Australian National University before becoming a visiting professor of philosophy at Columbia University for five years, then moving to Princeton. He is the recipient of numerous honours, including an honorary doctorate from the National University of Ireland. He was keynote speak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Vision
Color vision, a feature of visual perception, is an ability to perceive differences between light composed of different wavelengths (i.e., different spectral power distributions) independently of light intensity. Color perception is a part of the larger visual system and is mediated by a complex process between neurons that begins with differential stimulation of different types of photoreceptors by light entering the eye. Those photoreceptors then emit outputs that are propagated through many layers of neurons and then ultimately to the brain. Color vision is found in many animals and is mediated by similar underlying mechanisms with common types of biological molecules and a complex history of evolution in different animal taxa. In primates, color vision may have evolved under selective pressure for a variety of visual tasks including the foraging for nutritious young leaves, ripe fruit, and flowers, as well as detecting predator camouflage and emotional states in other pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consilience
In science and history, consilience (also convergence of evidence or concordance of evidence) is the principle that evidence from independent, unrelated sources can "converge" on strong conclusions. That is, when multiple sources of evidence are in agreement, the conclusion can be very strong even when none of the individual sources of evidence is significantly so on its own. Most established scientific knowledge is supported by a convergence of evidence: if not, the evidence is comparatively weak, and there will probably not be a strong scientific consensus. The principle is based on unity of knowledge; measuring the same result by several different methods should lead to the same answer. For example, it should not matter whether one measures distances within the Giza pyramid complex The Giza pyramid complex ( ar, مجمع أهرامات الجيزة), also called the Giza necropolis, is the site on the Giza Plateau in Greater Cairo, Egypt that includes the Great Pyramid of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct And Indirect Realism
In the philosophy of perception and philosophy of mind, the question of direct or naïve realism, as opposed to indirect or representational realism, is the debate over the nature of conscious experience;Lehar, Steve. (2000)The Function of Conscious Experience: An Analogical Paradigm of Perception and Behavior, ''Consciousness and Cognition''.Lehar, Steve. (2000), ''The Function of Conscious Experience''. out of the metaphysical question of whether the world we see around us is the real world itself or merely an internal perceptual copy of that world generated by our conscious experience. Naïve realism is known as ''direct'' realism when developed to counter ''indirect'' or representative realism, also known as epistemological dualism, the philosophical position that our conscious experience is not of the real world itself but of an internal representation, a miniature virtual-reality replica of the world. Indirect realism is broadly equivalent to the materialist view of perce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Problem Of Consciousness
The hard problem of consciousness is the problem of explaining why and how humans have qualia or phenomenal experiences. This is in contrast to the "easy problems" of explaining the physical systems that give us and other animals the ability to discriminate, integrate information, and so forth. These problems are seen as relatively easy because all that is required for their solution is to specify the mechanisms that perform such functions. Philosopher David Chalmers writes that even once we have solved all such problems about the brain and experience, the hard problem will still persist. The existence of a "hard problem" is controversial. It has been accepted by philosophers of mind such as Joseph Levine, Colin McGinn, and Ned Block and cognitive neuroscientists such as Francisco Varela, Giulio Tononi, and Christof Koch. However, its existence is disputed by philosophers of mind such as Daniel Dennett, Massimo Pigliucci, Thomas Metzinger, Patricia Churchland, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |