|
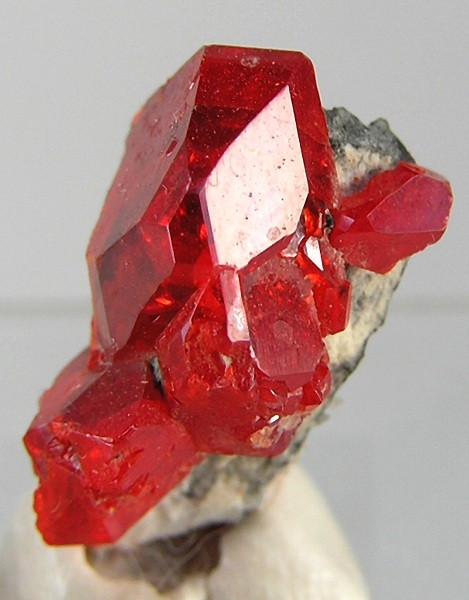
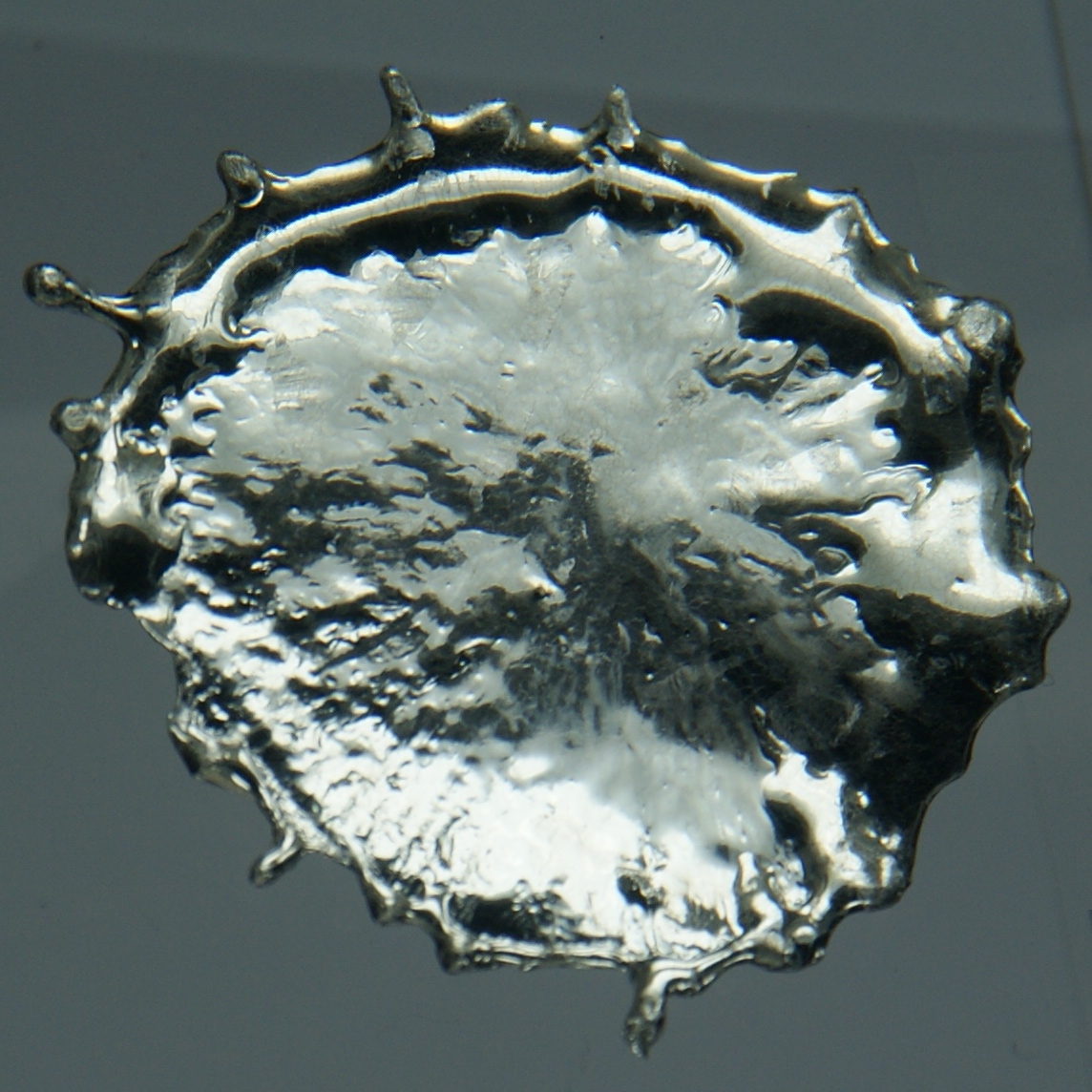
Kesterite
Kësterite is a sulfide mineral with a chemical formula of . In its lattice structure, zinc and iron atoms share the same lattice sites. Kesterite is the Zn-rich variety whereas the Zn-poor form is called ferrokesterite or stannite. Owing to their similarity, kesterite is sometimes called isostannite. The synthetic form of kesterite is abbreviated as CZTS (from copper zinc tin sulfide). The name kesterite is sometimes extended to include this synthetic material and also CZTSe, which contains selenium instead of sulfur. Occurrence Kesterite was first described in 1958 in regard to an occurrence in the Kester deposit (and the associated locality) in Ynnakh Mountain, Yana River, Yana basin, Yakutia, Russia, where it was discovered. It is usually found in quartz-sulfide Vein (geology), hydrothermal veins associated with tin ore deposits. Associated minerals include arsenopyrite, stannoidite, chalcopyrite, chalcocite, sphalerite and tennantite. Stannite and kesterite occur together in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CZTS
Copper zinc tin sulfide (CZTS) is a quaternary semiconducting compound which has received increasing interest since the late 2000s for applications in Thin-film solar cell, thin film solar cells. The class of related materials includes other I2-II-IV-VI4 such as copper zinc tin selenide (CZTSe) and the sulfur-selenium alloy CZTSSe. CZTS offers favorable optical and electronic properties similar to CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide), making it well suited for use as a thin-film solar cell absorber layer, but unlike Copper indium gallium selenide, CIGS (or other thin films such as CdTe), CZTS is composed of only abundant and non-toxic elements. Concerns with the price and availability of indium in CIGS and tellurium in CdTe, as well as toxicity of cadmium have been a large motivator to search for alternative thin film solar cell materials. The power conversion efficiency of CZTS is still considerably lower than CIGS and CdTe, with laboratory cell records of 11.0 % for CZTS and 12.6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CZTSe
Copper zinc tin sulfide (CZTS) is a quaternary semiconducting compound which has received increasing interest since the late 2000s for applications in thin film solar cells. The class of related materials includes other I2-II-IV-VI4 such as copper zinc tin selenide (CZTSe) and the sulfur-selenium alloy CZTSSe. CZTS offers favorable optical and electronic properties similar to CIGS (copper indium gallium selenide), making it well suited for use as a thin-film solar cell absorber layer, but unlike CIGS (or other thin films such as CdTe), CZTS is composed of only abundant and non-toxic elements. Concerns with the price and availability of indium in CIGS and tellurium in CdTe, as well as toxicity of cadmium have been a large motivator to search for alternative thin film solar cell materials. The power conversion efficiency of CZTS is still considerably lower than CIGS and CdTe, with laboratory cell records of 11.0 % for CZTS and 12.6 % for CZTSSe . Crystal structure CZTS is a I2-II-IV ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ynnakh Mountain
Ynnakh Mountain, also known as Arga Ynnakh Khaya (russian: Арга Ыннах Хая), Gora Ulakhan Ynnakh (russian: Гора Улахан Ыннах) and as Mother Mountain (russian: Мать-Гора), is a mountain in Verkhoyansky District, Yakutia, Russian Federation. The mountain has been classified as a natural monument of Russia with number 1420068. It is an important mountain in Yakut culture, where the word "Ynnakh" comes from sah, Ыыннаах, meaning scary, creepy. Geography Ynnakh Mountain is a granite massif located north of the Yana Plateau between the Yana River and the Adycha, a right hand tributary of the Yana. The mountain rises at the western limit of the Chersky Range, near the eastern foothills of the Verkhoyansk Range , a few miles to the southeast of Ese-Khayya. The height of the summit is according to the Operational Navigation Chart. According to other sources it is high. The mineral kesterite is found in the mountain. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfide Mineral
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide (S22−) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, the arsenides, the antimonides, the bismuthinides, the sulfarsenides and the sulfosalts.http://www.minerals.net/mineral/sort-met.hod/group/sulfgrp.htm Minerals.net Dana Classification, SulfidesKlein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, Jr., 1986, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', Wiley, 20th ed., pp 269-293 Sulfide minerals are inorganic compounds. Minerals Common or important examples include: * Acanthite *Chalcocite *Bornite * Galena * Sphalerite *Chalcopyrite *Pyrrhotite *Millerite *Pentlandite *Covellite *Cinnabar *Realgar *Orpiment *Stibnite *Pyrite *Marcasite *Molybdenite Sulfarsenides: *Cobaltite *Arsenopyrite *Gersdorffite Sulfosalts: *Pyrargyrite *Proustite *Tetrahedrite *Tennantite *Enargite *Bournonite * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfide Minerals
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide (S22−) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, the arsenides, the antimonides, the bismuthinides, the sulfarsenides and the sulfosalts.http://www.minerals.net/mineral/sort-met.hod/group/sulfgrp.htm Minerals.net Dana Classification, SulfidesKlein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, Jr., 1986, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', Wiley, 20th ed., pp 269-293 Sulfide minerals are inorganic compounds. Minerals Common or important examples include: * Acanthite *Chalcocite *Bornite *Galena *Sphalerite *Chalcopyrite *Pyrrhotite *Millerite *Pentlandite *Covellite *Cinnabar *Realgar *Orpiment *Stibnite *Pyrite *Marcasite *Molybdenite Sulfarsenides: *Cobaltite *Arsenopyrite *Gersdorffite Sulfosalts: *Pyrargyrite *Proustite *Tetrahedrite *Tennantite *Enargite *Bournonite *Jame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfide Mineral
The sulfide minerals are a class of minerals containing sulfide (S2−) or disulfide (S22−) as the major anion. Some sulfide minerals are economically important as metal ores. The sulfide class also includes the selenides, the tellurides, the arsenides, the antimonides, the bismuthinides, the sulfarsenides and the sulfosalts.http://www.minerals.net/mineral/sort-met.hod/group/sulfgrp.htm Minerals.net Dana Classification, SulfidesKlein, Cornelis and Cornelius S. Hurlbut, Jr., 1986, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', Wiley, 20th ed., pp 269-293 Sulfide minerals are inorganic compounds. Minerals Common or important examples include: * Acanthite *Chalcocite *Bornite * Galena * Sphalerite *Chalcopyrite *Pyrrhotite *Millerite *Pentlandite *Covellite *Cinnabar *Realgar *Orpiment *Stibnite *Pyrite *Marcasite *Molybdenite Sulfarsenides: *Cobaltite *Arsenopyrite *Gersdorffite Sulfosalts: *Pyrargyrite *Proustite *Tetrahedrite *Tennantite *Enargite *Bournonite * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tin Minerals
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal. Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, the so-called "tin cry" can be heard as a result of twinning in tin crystals; this trait is shared by indium, cadmium, zinc, and mercury in the solid state. Pure tin after solidifying presents a mirror-like appearance similar to most metals. In most tin alloys (such as pewter) the metal solidifies with a dull gray color. Tin is a post-transition metal in group 14 of the periodic table of elements. It is obtained chiefly from the mineral cassiterite, which contains stannic oxide, . Tin shows a chemical similarity to both of its neighbors in group 14, germanium and lead, and has two main oxidation states, +2 and the slightly more stable +4. Tin is the 49th most abundant element on Earth and has, with 10 stable isotopes, the largest nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron(II) Minerals
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron Age. In t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Minerals
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form (native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, c. 350 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcocite
Chalcocite (), copper(I) sulfide (Cu2S), is an important copper ore mineral. It is opaque and dark gray to black, with a metallic luster. It has a hardness of 2.5–3 on the Mohs scale. It is a sulfide with a monoclinic crystal system. The term ''chalcocite'' comes from the alteration of the obsolete name ''chalcosine'', from the Greek ''khalkos'', meaning "copper". It is also known as redruthite, vitreous copper, or copper-glance. Occurrence Chalcocite is sometimes found as a primary vein mineral in hydrothermal veins. However, most chalcocite occurs in the supergene enriched environment below the oxidation zone of copper deposits as a result of the leaching of copper from the oxidized minerals. It is also often found in sedimentary rocks. It has been mined for centuries and is one of the most profitable copper ores. The reasons for this is its high copper content (66.7% atomic ratio and nearly 80% by weight) and the ease at which copper can be separated from sulfur. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogenous mixture of two different kinds of atoms in solid state and have a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word "solution" is used to describe the intimate mixing of components at the atomic level and distinguishes these homogeneous materials from physical mixtures of components. Two terms are mainly associated with solid solutions - ''solvents'' and ''solutes,'' depending on the relative abundance of the atomic species. In general if two compounds are isostructural then a solid solution will exist between the end members (also known as parents). For example sodium chloride and potassium chloride have the same cubic crystal structure so it is possible to make a pure compound with any ratio of sodium to potassium (Na1-xKx)Cl by dissolving that ratio of NaCl and KCl in water and then evaporating the solution. A member of this family is sold under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |