|
Knee-joint
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the human body. The knee is a modified hinge joint, which permits flexion and extension as well as slight internal and external rotation. The knee is vulnerable to injury and to the development of osteoarthritis. It is often termed a ''compound joint'' having tibiofemoral and patellofemoral components. (The fibular collateral ligament is often considered with tibiofemoral components.) Structure The knee is a modified hinge joint, a type of synovial joint, which is composed of three functional compartments: the patellofemoral articulation, consisting of the patella, or "kneecap", and the patellar groove on the front of the femur through which it slides; and the medial and lateral tibiofemoral articulations linking the femur, or thigh bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Musculoskeletal System
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system provides form, support, stability, and movement to the body. It is made up of the bones of the skeleton, muscles, cartilage, tendons, ligaments, joints, and other connective tissue that supports and binds tissues and organs together. The musculoskeletal system's primary functions include supporting the body, allowing motion, and protecting vital organs. The skeletal portion of the system serves as the main storage system for calcium and phosphorus and contains critical components of the hematopoietic system. This system describes how bones are connected to other bones and muscle fibers via connective tissue such as tendons and ligaments. The bones provide stability to the body. Muscles keep bones in place and also play a role in the movement ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray246
Grey (more common in British English) or gray (more common in American English) is an intermediate color between black and white. It is a neutral or achromatic color, meaning literally that it is "without color", because it can be composed of black and white. It is the color of a cloud-covered sky, of ash and of lead. The first recorded use of ''grey'' as a color name in the English language was in 700 CE.Maerz and Paul ''A Dictionary of Color'' New York:1930 McGraw-Hill Page 196 ''Grey'' is the dominant spelling in European and Commonwealth English, while ''gray'' has been the preferred spelling in American English; both spellings are valid in both varieties of English. In Europe and North America, surveys show that grey is the color most commonly associated with neutrality, conformity, boredom, uncertainty, old age, indifference, and modesty. Only one percent of respondents chose it as their favorite color. Etymology ''Grey'' comes from the Middle English or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Condyle Of Femur
The medial condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of femur, the other being the lateral condyle. The medial condyle is larger than the lateral (outer) condyle due to more weight bearing caused by the centre of mass being medial to the knee. On the posterior surface of the condyle the linea aspera The linea aspera ( la, rough line) is a ridge of roughened surface on the posterior surface of the shaft of the femur. It is the site of attachments of muscles and the intermuscular septum. Its margins diverge above and below. The linea asper ... (a ridge with two lips: medial and lateral; running down the posterior shaft of the femur) turns into the medial and lateral supracondylar ridges, respectively. The outermost protrusion on the medial surface of the medial condyle is referred to as the "medial epicondyle" and can be palpated by running fingers medially from the patella with the knee in flexion. It is important to take into consideration the differen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Condyle Of Femur
The lateral condyle is one of the two projections on the lower extremity of the femur. The other one is the medial condyle. The lateral condyle is the more prominent and is broader both in its front-to-back and transverse diameters. Clinical significance The most common injury to the lateral femoral condyle is an osteochondral fracture combined with a patellar dislocation. The osteochondral fracture occurs on the weight-bearing portion of the lateral condyle. Typically, the condyle will fracture (and the patella may dislocate) as a result of severe impaction from activities such as downhill skiing and parachuting. Open reduction and internal fixation Internal fixation is an operation in orthopedics that involves the surgical implementation of implants for the purpose of repairing a bone, a concept that dates to the mid-nineteenth century and was made applicable for routine treatment in the m ... surgery is typically used to repair an osteochondral fracture. For a Type B1 parti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
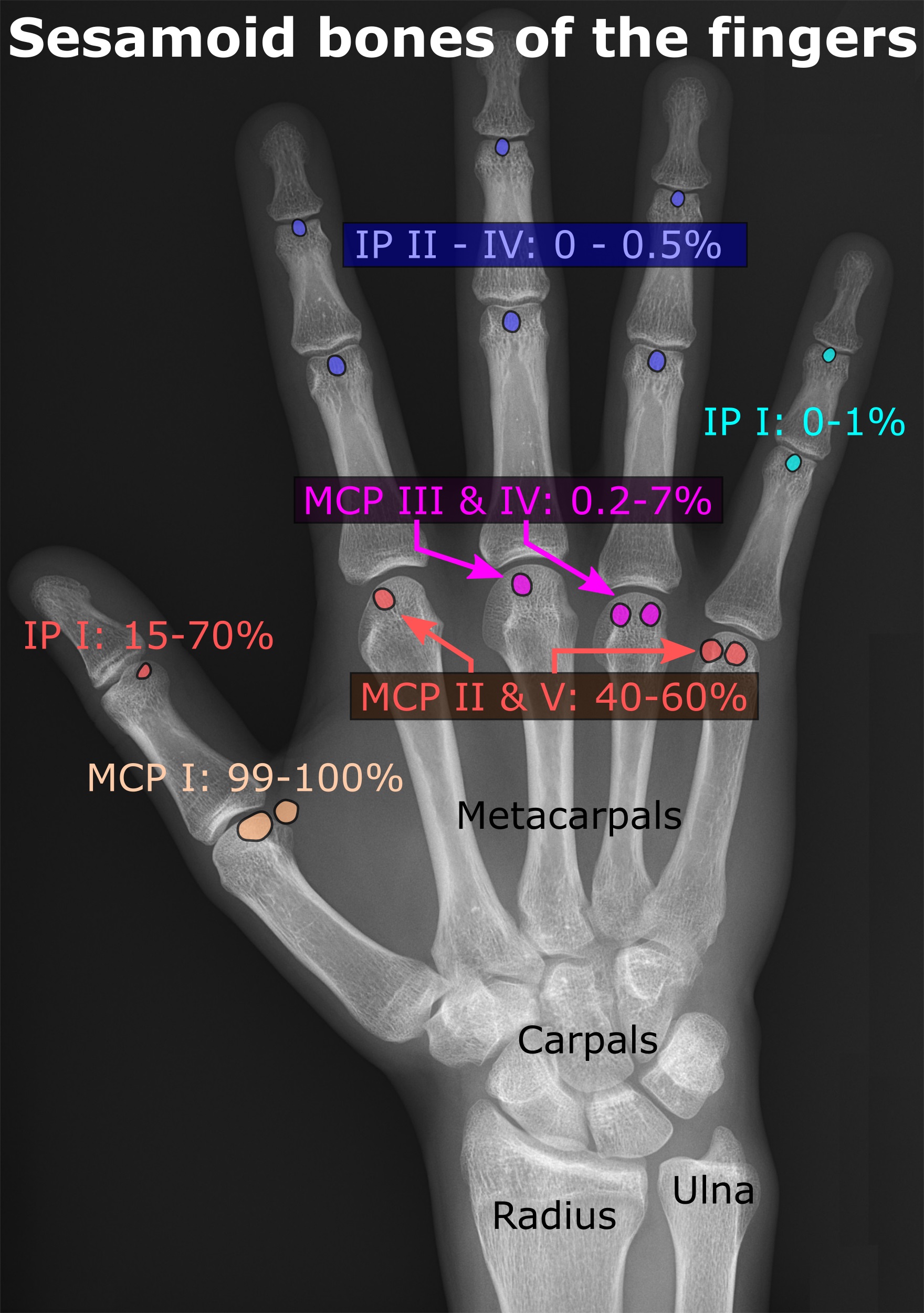
Sesamoid Bone
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for ' sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be present as a normal variant. The patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body. Sesamoids act like pulleys, providing a smooth surface for tendons to slide over, increasing the tendon's ability to transmit muscular forces. Structure Sesamoid bones can be found on joints throughout the body, including: * In the knee—the patella (within the quadriceps tendon). This is the largest sesamoid bone. * In the hand—two sesamoid bones are commonly found in the distal portions of the first metacarpal bone (within the tendons of adductor pollicis and flexor pollicis brevis). There is also commonly a sesamoid bone in distal portions of the second metacarpal bone. * In the wrist—The pisiform of the wrist is a sesamoid bone (within the tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone
A bone is a Stiffness, rigid Organ (biology), organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red blood cell, red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable animal locomotion, mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple Function (biology), functions. Bone tissue (osseous tissue), which is also called bone in the mass noun, uncountable sense of that word, is hard tissue, a type of specialized connective tissue. It has a honeycomb-like matrix (biology), matrix internally, which helps to give the bone rigidity. Bone tissue is made up of different types of bone cells. Osteoblasts and osteocytes are involved in the formation and mineralization (biology), mineralization of bone; osteoclasts are involved in the bone resorption, resor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossification
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue ( mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor. In fracture healing, endochondral osteogenesis is the most commonly occurring process, for example in fractures of long bones treated by plaster of Paris, whereas fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation with metal plates, screws, pins, rods and nails may heal by intramembranous osteogenesis. Heterotopic ossification is a process resulting in the formation of bone tissue that is often atypical, at an extraskeletal location. Calcification is often confused with ossification. Calcification is sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterolateral Corner
Posterolateral corner injuries (PLC injuries) of the knee are injuries to a complex area formed by the interaction of multiple structures. Injuries to the posterolateral corner can be debilitating to the person and require recognition and treatment to avoid long term consequences. Injuries to the PLC often occur in combination with other ligamentous injuries to the knee; most commonly the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and posterior cruciate ligament (PCL). As with any injury, an understanding of the anatomy and functional interactions of the posterolateral corner is important to diagnosing and treating the injury. Signs and symptoms Patients often complain of pain and instability at the joint. With concurrent Nerve injury, nerve injuries, patients may experience numbness, tingling and weakness of the Ankle dorsiflexion, ankle dorsiflexors and great toe extensors, or a footdrop. Complications Follow-up studies by Levy et al. and Stannard at al. both examined failure rates for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Articular Capsule Of The Knee Joint
The articular capsule of the knee joint (commonly referred to as the capsular ligament) is the wide and lax joint capsule of the knee. It is thin in front and at the side, and contains the patella, ligaments, menisci, and bursae of the knee.Platzer (2004), p 206 The capsule consists of an inner synovial membrane, and an outer fibrous membrane separated by fatty deposits anteriorly and posteriorly.Platzer (2004), p 210 Synovial membrane Anteriorly, the reflection of the synovial membrane lies on the femur; located at some distance from the cartilage because of the presence of the suprapatellar bursa. Above, the reflection appears lifted from the bone by underlying periosteal connective tissue. In a standing posture, the suprapatellar bursa is seemingly redundant. It is however also referred to as the ''suprapatellar synovial recess'' as it gradually unfolds as the knee is flexed; to open up completely when the knee is flexed 130 degrees.''Thieme Atlas of Anatomy'', pp 40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synovial Membrane
The synovial membrane (also known as the synovial stratum, synovium or stratum synoviale) is a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints and tendon sheath. It makes direct contact with the fibrous membrane on the outside surface and with the synovial fluid lubricant on the inside surface. In contact with the synovial fluid at the tissue surface are many rounded macrophage-like synovial cells (type A) and also type B cells, which are also known as fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). Type A cells maintain the synovial fluid by removing wear-and-tear debris. As for the FLS, they produce hyaluronan, as well as other extracellular components in the synovial fluid. Structure The synovial membrane is variable but often has two layers: * The outer layer, or subintima, can be of almost any type of connective tissue – fibrous (dense collagenous type), adipose (fatty; e.g. in intra-articular fat pads) or areolar (loose collagenous typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synovial Fluid
Synovial fluid, also called synovia, elp 1/sup> is a viscous, non-Newtonian fluid found in the cavities of synovial joints. With its egg white–like consistency, the principal role of synovial fluid is to reduce friction between the articular cartilage of synovial joints during movement. Synovial fluid is a small component of the transcellular fluid component of extracellular fluid. Structure The inner membrane of synovial joints is called the synovial membrane and secretes synovial fluid into the joint cavity. Synovial fluid is an ultrafiltrate from plasma, and contains proteins derived from the blood plasma and proteins that are produced by cells within the joint tissues. The fluid contains hyaluronan secreted by fibroblast-like cells in the synovial membrane, lubricin (proteoglycan 4; PRG4) secreted by the surface chondrocytes of the articular cartilage and interstitial fluid filtered from the blood plasma. This fluid forms a thin layer (roughly 50 μm) at the surface of c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

