|
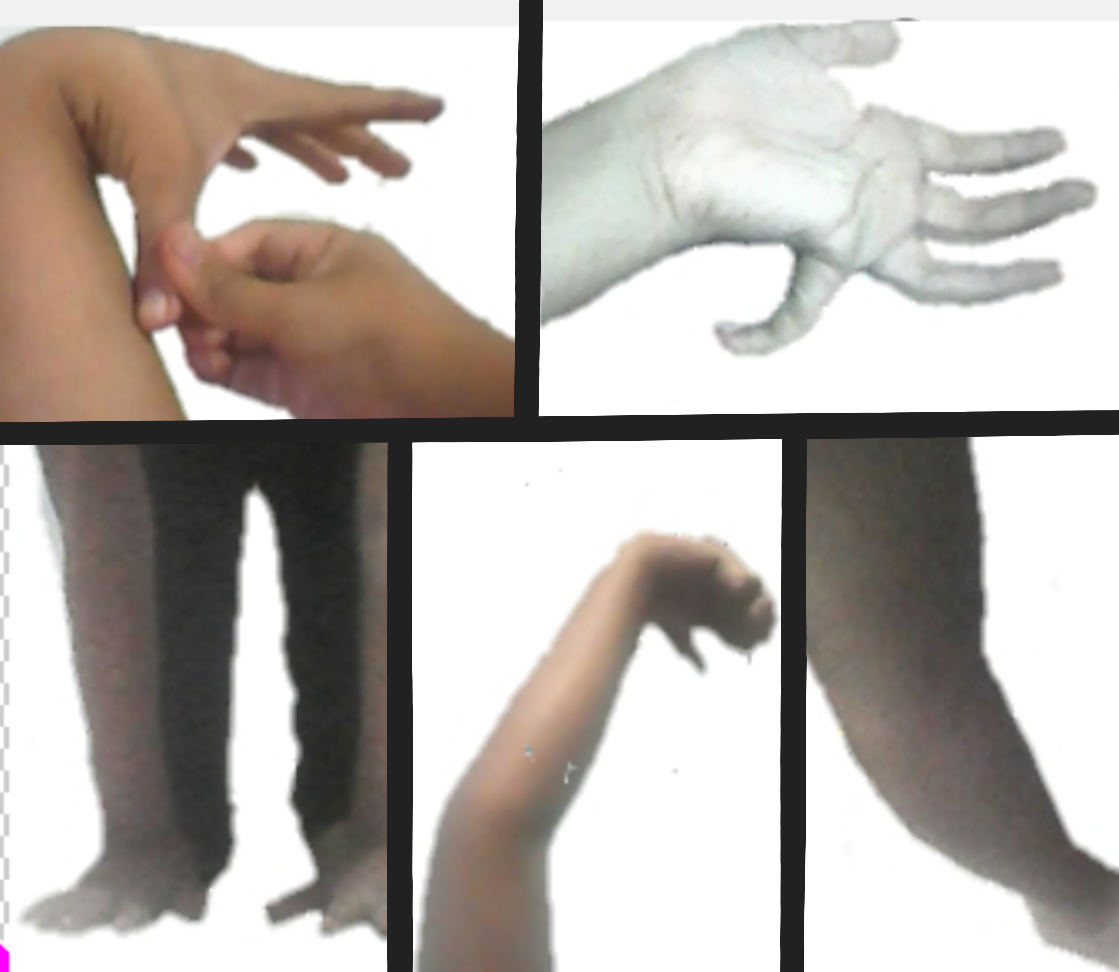
Joint Hypermobility Syndrome
Hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD), related to earlier diagnoses such as hypermobility syndrome (HMS), and joint hypermobility syndrome (JHS) is a heritable connective tissue disorder that affects joints and ligaments. Different forms and sub-types have been distinguished, but it does not include asymptomatic joint hypermobility, sometimes known as double-jointedness. Symptoms can include the inability to walk properly or for long distances, and pain in affected areas. Some people with HSD have hypersensitive nerves and a weaker immune system. It can also cause severe fatigue and some cases cause depressive episodes. It is somewhat similar to other genetic connective tissue disorders such as Ehlers–Danlos syndromes. There is a strong association between HSD and neurodevelopmental disorders such as ADHD (Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) and ASD (autism spectrum disorder). Classification Hypermobility spectrum disorders are diagnosed when individuals have symptoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Hypermobility
Hypermobility, also known as double-jointedness, describes joints that stretch farther than normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists, bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the head or perform other contortionist "tricks". It can affect one or more joints throughout the body. Hypermobile joints are common and occur in about 10 to 25% of the population, but in a minority of people, pain and other symptoms are present. This may be a sign of what is known as joint hypermobility syndrome (JMS) or, more recently, hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD). Hypermobile joints are a feature of genetic connective tissue disorders such as hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD) or Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS). Until new diagnostic criteria were introduced, hypermobility syndrome was sometimes considered identical to hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (hEDS), formerly called EDS Type 3. As no genetic test can distinguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypermobility (joints)
Hypermobility, also known as double-jointedness, describes joints that stretch farther than normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists, bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the head or perform other contortionist "tricks". It can affect one or more joints throughout the body. Hypermobile joints are common and occur in about 10 to 25% of the population, but in a minority of people, pain and other symptoms are present. This may be a sign of what is known as joint hypermobility syndrome (JMS) or, more recently, hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD). Hypermobile joints are a feature of genetic connective tissue disorders such as hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD) or Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS). Until new diagnostic criteria were introduced, hypermobility syndrome was sometimes considered identical to hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (hEDS), formerly called EDS Type 3. As no genetic test can distinguish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracetamol
Paracetamol, also known as acetaminophen, is a medication used to treat fever and mild to moderate pain. Common brand names include Tylenol and Panadol. At a standard dose, paracetamol only slightly decreases body temperature; it is inferior to ibuprofen in that respect, and the benefits of its use for fever are unclear. Paracetamol may relieve pain in acute mild migraine but only slightly in episodic tension headache. However, the aspirin/paracetamol/caffeine combination helps with both conditions where the pain is mild and is recommended as a first-line treatment for them. Paracetamol is effective for post- surgical pain, but it is inferior to ibuprofen. The paracetamol/ibuprofen combination provides further increase in potency and is superior to either drug alone. The pain relief paracetamol provides in osteoarthritis is small and clinically insignificant. The evidence in its favor for the use in low back pain, cancer pain, and neuropathic pain is insufficient. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient education, physical intervention, rehabilitation, disease prevention, and health promotion. Physical therapists are known as physiotherapists in many countries. In addition to clinical practice, other aspects of physical therapist practice include research, education, consultation, and health administration. Physical therapy is provided as a primary care treatment or alongside, or in conjunction with, other medical services. In some jurisdictions, such as the United Kingdom, physical therapists have the authority to prescribe medication. Overview Physical therapy addresses the illnesses or injuries that limit a person's abilities to move and perform functional activities in their daily lives. PTs use an individual's history and phys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is divi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthostatic Tachycardia
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a condition characterized by an abnormally large increase in heart rate upon standing. Symptoms may include lightheadedness, brain fog, blurred vision, weakness, fatigue, headaches, heart palpitations, exercise intolerance, nausea, diminished concentration, tremulousness (shaking), syncope (fainting), coldness or pain in the extremities, chest pain and shortness of breath. Other conditions associated with POTS include Ehlers–Danlos syndrome, mast cell activation syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, insomnia, chronic headaches, chronic fatigue syndrome, and fibromyalgia. POTS symptoms may be treated with lifestyle changes such as increasing fluid and salt intake, wearing compression stockings, gentler and slow postural changes, avoiding prolonged bedrest, medication and physical therapy. The causes of POTS are varied. POTS may develop after a viral infection, surgery, trauma or pregnancy. It has been shown to eme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classification Of Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
Classification is a process related to categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated and understood. Classification is the grouping of related facts into classes. It may also refer to: Business, organizations, and economics * Classification of customers, for marketing (as in Master data management) or for profitability (e.g. by Activity-based costing) * Classified information, as in legal or government documentation * Job classification, as in job analysis * Standard Industrial Classification, economic activities Mathematics * Attribute-value system, a basic knowledge representation framework * Classification theorems in mathematics * Mathematical classification, grouping mathematical objects based on a property that all those objects share * Statistical classification, identifying to which of a set of categories a new observation belongs, on the basis of a training set of data Media * Classification (literature), a figure of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos Syndrome
Hypermobility, also known as double-jointedness, describes joints that stretch farther than normal. For example, some hypermobile people can bend their thumbs backwards to their wrists, bend their knee joints backwards, put their leg behind the head or perform other contortionist "tricks". It can affect one or more joints throughout the body. Hypermobile joints are common and occur in about 10 to 25% of the population, but in a minority of people, pain and other symptoms are present. This may be a sign of what is known as joint hypermobility syndrome (JMS) or, more recently, hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD). Hypermobile joints are a feature of genetic connective tissue disorders such as hypermobility spectrum disorder (HSD) or Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS). Until new diagnostic criteria were introduced, hypermobility syndrome was sometimes considered identical to hypermobile Ehlers–Danlos syndrome (hEDS), formerly called EDS Type 3. As no genetic test can distinguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zebra (medicine)
Zebra is the American medical slang for arriving at a surprising, often exotic, medical diagnosis when a more commonplace explanation is more likely. It is shorthand for the aphorism coined in the late 1940s by Theodore Woodward, professor at the University of Maryland School of Medicine, who instructed his medical interns: "When you hear hoofbeats behind you, don't expect to see a zebra." (Since zebras are much rarer than horses in the United States, the sound of hoofbeats would almost certainly be from a horse.) By 1960, the aphorism was widely known in medical circles. Medical novices are predisposed to make rare diagnoses because of (a) the availability heuristic ("events more easily remembered are judged more probable") and (b) the phenomenon first enunciated in ''Rhetorica ad Herennium'' (circa 85 BC), "the striking and the novel stay longer in the mind." Thus, the aphorism is an important caution against these biases when teaching medical students to weigh medical evidence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypermobility Beighton Score .
{{disambiguation ...
Hypermobility may refer to: * Hypermobility (joints), joints that stretch farther than normal ** Hypermobility spectrum disorder, a heritable connective tissue disorder * Hypermobility (travel), frequent travelers It should not be confused with flexibility Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force. The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is. Calculations The stiffness, k, of a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Spasm
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ such as the bladder. A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a muscle cramp which is accompanied by a sudden burst of pain. A muscle cramp is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes. It is typically caused by ion imbalance or muscle overload. There are other causes of involuntary muscle contractions, and some of these may cause a health problem. Description and causes Various kinds of involuntary muscle activity may be referred to as a "spasm". A spasm may be a muscle contraction caused by abnormal nerve stimulation or by abnormal activity of the muscle itself. A spasm may lead to muscle strains or tears in tendons and ligaments if the force of the spasm exceeds the tensile strength of the underlying connective tissue. This can occur with a particularly strong spasm or with weakened connective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exhaustion
Fatigue describes a state of tiredness that does not resolve with rest or sleep. In general usage, fatigue is synonymous with extreme tiredness or exhaustion that normally follows prolonged physical or mental activity. When it does not resolve after rest or sleep, or occurs independently of physical or mental exertion, it may be a symptom of a medical condition that may become severe or progressive. Fatigue can be a feature of a mental disorder such as depression; may be associated with conditions of chronic pain such as fibromyalgia; it may also feature in conditions of chronic low-level inflammation, and be a disease-related symptom in many other conditions. Fatigue often has no known cause, and is recognised as being very complex in nature. Fatigability describes a susceptibility to fatigue. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive abil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |