|
Isoguanine
Isoguanine or 2-hydroxyadenine is a purine base that is an isomer of guanine. It is a product of oxidative damage to DNA and has been shown to cause mutation. It is also used in combination with isocytosine in studies of unnatural nucleic acid analogues of the normal base pairs in DNA.Christopher Roberts, Rajanikanth Bandaru, Christopher Switzer: „Theoretical and Experimental Study of Isoguanine and Isocytosine: Base Pairing in an Expanded Genetic System", ''J. Am. Chem. Soc.'', 1997, ''119'' (20), pp. 4640–4649 (). It is used as a nucleobase Nucleobases, also known as ''nitrogenous bases'' or often simply ''bases'', are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic b ... of hachimoji nucleic acids. In hachimoji DNA, it pairs with 1-methylcytosine, while in hachimoji RNA, it pairs with isocytosine. References Purines Nucleobases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleic Acid Analogues
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research. Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases. An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix). Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries. Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
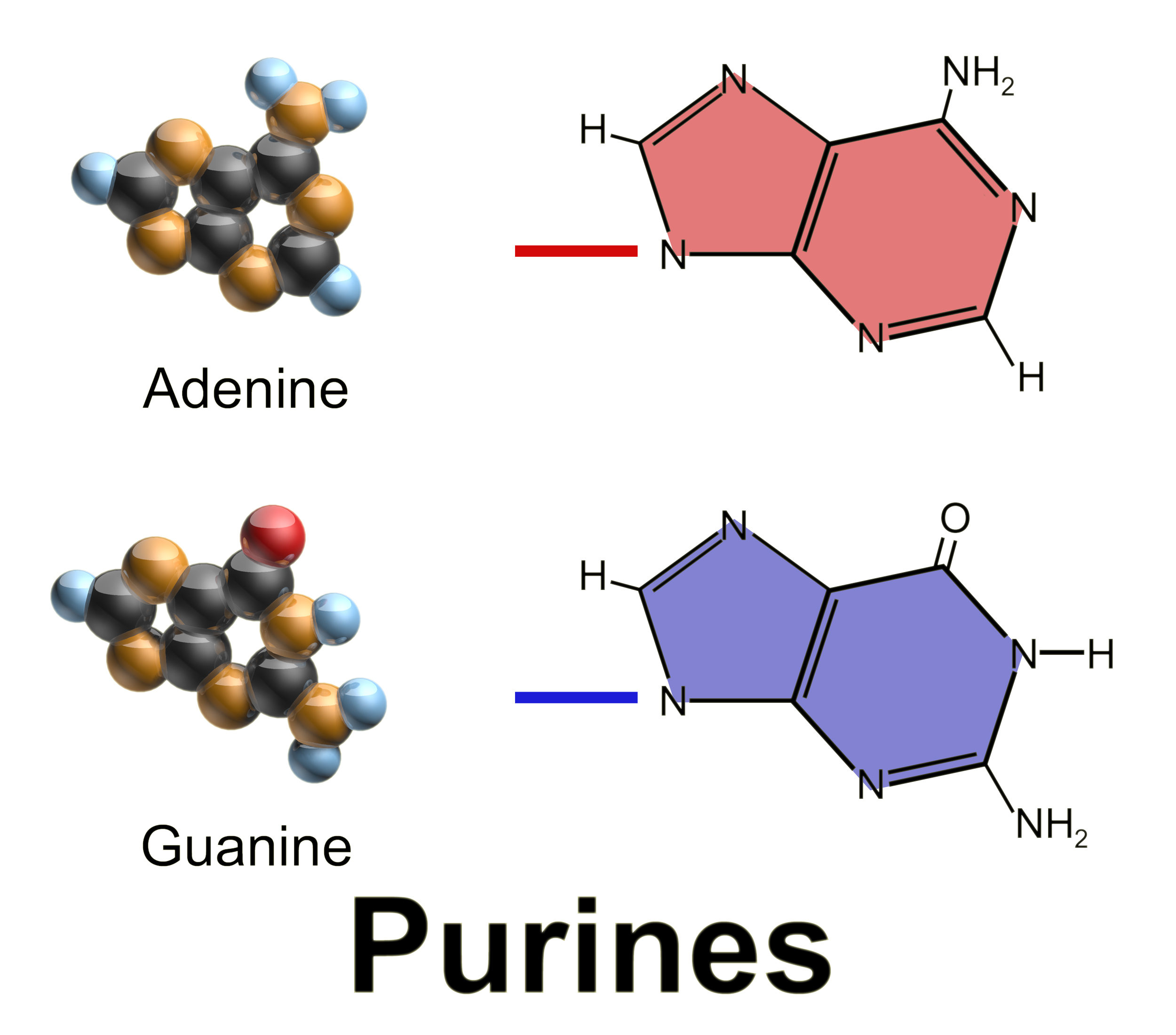
Purine
Purine is a heterocyclic compound, heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings (pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature. Dietary sources Purines are found in high concentration in meat and meat products, especially internal organs such as liver and kidney. In general, plant-based diets are low in purines. High-purine plants and algae include some legumes (lentils and Black-eyed pea, black eye peas) and Spirulina (dietary supplement), spirulina. Examples of high-purine sources include: sweetbreads, Anchovies as food, anchovies, Sardines as food, sardines, liver, beef kidneys, Brain as food, brains, meat extracts (e.g., Oxo (food), Oxo, Bovril), herring, mackerel, scallops, game meats, yeast (beer, yeast extract, nutritional yeast) and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isocytosine
Isocytosine or 2-aminouracil is a pyrimidine base that is an isomer of cytosine. It is used in combination with isoguanine in studies of unnatural nucleic acid analogues of the normal base pairs in DNA. In particular, it is used as a nucleobase of hachimoji RNA. It can be synthesized from guanidine and malic acid. It is also used in physical chemical studies involving metal complex binding, hydrogen bonding, and tautomerism Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydr ... and proton transfer effects in nucleobases. References {{reflist Pyrimidones Nucleobases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleobase
Nucleobases, also known as ''nitrogenous bases'' or often simply ''bases'', are nitrogen-containing biological compounds that form nucleosides, which, in turn, are components of nucleotides, with all of these monomers constituting the basic building blocks of nucleic acids. The ability of nucleobases to form base pairs and to stack one upon another leads directly to long-chain helical structures such as ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Five nucleobases—adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T), and uracil (U)—are called ''primary'' or ''canonical''. They function as the fundamental units of the genetic code, with the bases A, G, C, and T being found in DNA while A, G, C, and U are found in RNA. Thymine and uracil are distinguished by merely the presence or absence of a methyl group on the fifth carbon (C5) of these heterocyclic six-membered rings. In addition, some viruses have aminoadenine (Z) instead of adenine. It differs in having an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1-methylcytosine
1-Methylcytosine is a methylated form of the DNA base cytosine. In 1-methylcytosine, a methyl group is attached to the 1st atom in the 6-atom ring. This methyl group distinguishes 1-methylcytosine from cytosine. History Miriam Rossi worked on the refinement of 1-methylcytosine. 1-Methylcytosine is used as a nucleobase of hachimoji DNA, in which it pairs with isoguanine Isoguanine or 2-hydroxyadenine is a purine base that is an isomer of guanine. It is a product of oxidative damage to DNA and has been shown to cause mutation. It is also used in combination with isocytosine in studies of unnatural nucleic acid a .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Methylcytosine1 Nucleobases Pyrimidones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purines
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings ( pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature. Dietary sources Purines are found in high concentration in meat and meat products, especially internal organs such as liver and kidney. In general, plant-based diets are low in purines. High-purine plants and algae include some legumes (lentils and black eye peas) and spirulina. Examples of high-purine sources include: sweetbreads, anchovies, sardines, liver, beef kidneys, brains, meat extracts (e.g., Oxo, Bovril), herring, mackerel, scallops, game meats, yeast (beer, yeast extract, nutritional yeast) and gravy. A moderate amount of purine is also contained in red meat, beef, pork, poultry, fish and seafood, asparagus, cauliflower, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isomer
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers. Isomers do not necessarily share similar chemical or physical properties. Two main forms of isomerism are structural or constitutional isomerism, in which ''bonds'' between the atoms differ; and stereoisomerism or spatial isomerism, in which the bonds are the same but the ''relative positions'' of the atoms differ. Isomeric relationships form a hierarchy. Two chemicals might be the same constitutional isomer, but upon deeper analysis be stereoisomers of each other. Two molecules that are the same stereoisomer as each other might be in different conformational forms or be different isotopologues. The depth of analysis depends on the field of study or the chemical and physical properties of interest. The English word "isomer" () is a back-for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanine
Guanine () ( symbol G or Gua) is one of the four main nucleobases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA, the others being adenine, cytosine, and thymine (uracil in RNA). In DNA, guanine is paired with cytosine. The guanine nucleoside is called guanosine. With the formula C5H5N5O, guanine is a derivative of purine, consisting of a fused pyrimidine-imidazole ring system with conjugated double bonds. This unsaturated arrangement means the bicyclic molecule is planar. Properties Guanine, along with adenine and cytosine, is present in both DNA and RNA, whereas thymine is usually seen only in DNA, and uracil only in RNA. Guanine has two tautomeric forms, the major keto form (see figures) and rare enol form. It binds to cytosine through three hydrogen bonds. In cytosine, the amino group acts as the hydrogen bond donor and the C-2 carbonyl and the N-3 amine as the hydrogen-bond acceptors. Guanine has the C-6 carbonyl group that acts as the hydrogen bond acceptor, while a group at N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Base Pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The Complementarity (molecular biology), complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hachimoji DNA
Hachimoji DNA (from Japanese ''hachimoji'', "eight letters") is a synthetic nucleic acid analog that uses four synthetic nucleotides in addition to the four present in the natural nucleic acids, DNA and RNA. This leads to four allowed base pairs: two unnatural base pairs formed by the synthetic nucleobases in addition to the two normal pairs. Hachimoji bases have been demonstrated in both DNA and RNA analogs, using deoxyribose and ribose respectively as the backbone sugar. Benefits of such a nucleic acid system may include an enhanced ability to store data, as well as insights into what may be possible in the search for extraterrestrial life. The hachimoji DNA system produced one type of catalytic RNA (ribozyme or aptamer) ''in vitro''. Description Natural DNA is a molecule carrying the genetic instructions used in the growth, development, functioning, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are nucleic acids; alon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |