|
Invisible Churches
Invisible churches among enslaved African Americans in the United States were informal Christian groups where enslaved people listened to preachers that they chose without their slaveholder's knowledge. The Invisible churches taught a different message from white-controlled churches and did not emphasize obedience. Some slaves could not contact invisible churches and others did not agree with an invisible church's message but many slaves were comforted by the invisible churches. History Invisible churches were a branch of Christian churches in the slave community in the colonial history of the United States and antebellum period where enslaved African Americans secretly practiced their own version of Christianity. Inside invisible churches, enslaved and free African Americans practiced Hoodoo. Hoodoo is a spiritual tradition defined by scholars as a folk religion was created by enslaved African Americans during slavery in colonial America for their protection against their ensla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery In The United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From 1526, during early colonial days, it was practiced in what became Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until abolition. In the decades after the end of Reconstruction, many of slavery's economic and social functions were continued through segregation, sharecropping, and convict leasing. By the time of the American Revolution (1775–1783), the status of enslaved people had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. During and immediately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hush Harbor
During Antebellum era, antebellum United States, America, a hush harbor was a place where slaves would gather in secret to practice religious traditions. History Religion grew to become a highly respected part of slave life. It offered the enslaved hope and reassurance. Slaves were forced to organize and conduct these meetings in secret because the idea of slaves assembling without supervision left the owners in fear. The meetings were held after dark, once field slave, field and house slave, house chores were completed, and carried on late into the night. Christianity was the prominent religion of the African Slaves after being transported to the Americas. After being exposed to Christian ideas, the slaves began to understand them more. Slaves discovered promising stories and passages in the Bible that offered hope. The story of Jesus Christ suffering on the cross drew attention because of the similar, harsh treatment they both received. The hush harbors served as the location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
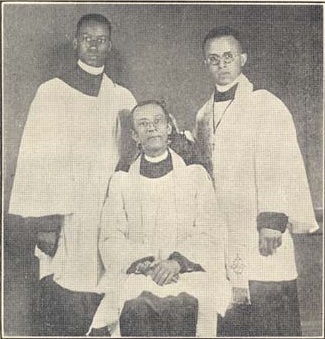
George Freeman Bragg
George Freeman Bragg (January 25, 1863 – March 12, 1940) was an African-American priest, journalist, social activist and historian. The twelfth African American ordained as a priest in the Episcopal Church of the United States, he worked against racial discrimination and for interracial harmony, both within and outside of his church. Early and family life Bragg was born into slavery in Warrenton, North Carolina, in 1863, during the American Civil War, and baptised at Emmanuel Episcopal Church. As the war ended, his carpenter father (also George Freeman Bragg) and seamstress mother (Mary) moved their family to Petersburg, Virginia, to live with his grandmother Caroline Wiley Cain Bragg, a devout Episcopalian and former slave of an Episcopal priest. Even before the war, Petersburg had been known for its prosperous free black community, and the city's Episcopal churches soon established Sunday schools for black children, to prepare them for the responsibilities of citizenship. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slave Rebellion
A slave rebellion is an armed uprising by enslaved people, as a way of fighting for their freedom. Rebellions of enslaved people have occurred in nearly all societies that practice slavery or have practiced slavery in the past. A desire for freedom and the dream of successful rebellion is often the greatest object of song, art, and culture amongst the enslaved population. Many of the events, however, are often violently opposed and suppressed by slaveholders. The most successful slave rebellion in history was the 18th-century Haitian Revolution, led by Toussaint Louverture and later Jean-Jacques Dessalines who won the war against their French colonial rulers, which established the modern independent state of Haiti from the former French colony of Saint-Domingue. Another famous historic slave rebellion was led by the Roman slave Spartacus (c. 73–71 BC). In the ninth century, the poet-prophet Ali bin Muhammad led imported East African slaves in Iraq during the Zanj Rebellion again ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nat Turner's Slave Rebellion
Nat Turner's Rebellion, historically known as the Southampton Insurrection, was a rebellion of enslaved Virginians that took place in Southampton County, Virginia, in August 1831.Schwarz, Frederic D.1831 Nat Turner's Rebellion" ''American Heritage'', August/September 2006. " Led by Nat Turner, the rebels killed between 55 and 65 White people, making it the deadliest slave revolt in U.S. history." The rebellion was effectively suppressed within a few days, at Belmont Plantation on the morning of August 23, but Turner survived in hiding for more than two months afterward. There was widespread fear amongst the White population in the aftermath of the rebellion. Militia and mobs killed as many as 120 enslaved people and freed African Americans in retaliation.Breen, Patrick H. (2015). ''The Land Shall Be Deluged in Blood: A New History of the Nat Turner Revolt''. Oxford University Press. pp. 231. ISBN 978-0199828005. "high estimates have been widely accepted in both ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nat Turner Woodcut
Nat or NAT may refer to: Computing * Network address translation (NAT), in computer networking Organizations * National Actors Theatre, New York City, U.S. * National AIDS trust, a British charity * National Archives of Thailand * National Assembly of Thailand, the national parliament People and ethnic groups * Nat (name), a given name or nickname, usually masculine, and also a surname * Nat (Muslim), a Muslim community in North India * Nat caste, a Hindu caste found in northern India and Nepal Places * Nat, Punjab, India, a village * Nat, West Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community * Greater Natal International Airport, São Gonçalo do Amarante, Brazil (IATA code NAT) ** Augusto Severo International Airport (closed), former IATA code NAT Science and technology Biology and medicine * Natural antisense transcript, an RNA transcript in a cell * N-acetyltransferase, an enzyme; also NAT1, NAT2, etc. * Nucleic acid test, for genetic material * Neonatal alloimmun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirit Possession
Spirit possession is an unusual or altered state of consciousness and associated behaviors purportedly caused by the control of a human body by spirits, ghosts, demons, or gods. The concept of spirit possession exists in many cultures and religions, including Buddhism, Christianity,Mark 5:9, Luke 8:30 Haitian Vodou, Hinduism, Islam, Wicca, and Southeast Asian, African, and Native American traditions. Depending on the cultural context in which it is found, possession may be considered voluntary or involuntary and may be considered to have beneficial or detrimental effects on the host. In a 1969 study funded by the National Institute of Mental Health, spirit possession beliefs were found to exist in 74% of a sample of 488 societies in all parts of the world, with the highest numbers of believing societies in Pacific cultures and the lowest incidence among Native Americans of both North and South America. As Pentecostal and Charismatic Christian churches move into both Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ring Shout
A shout or ring shout is an ecstatic, transcendent religious ritual, first practiced by African slaves in the West Indies and the United States, in which worshipers move in a circle while shuffling and stomping their feet and clapping their hands. Despite the name, shouting aloud is not an essential part of the ritual. The ring shout was Christianized and practiced in some Black churches into the 20th century, and it continues to the present among the Gullah people of the Sea Islands and in "singing and praying bands" associated with many African American United Methodist congregations in Tidewater Maryland and Delaware. A more modern form, known still as a " shout" (or "praise break"), is practiced in many Black churches and non-Black Pentecostal churches to the present day. Description "Shouting" often took place during or after a Christian prayer meeting or worship service. Men and women moved in a circle in a counterclockwise direction, shuffling their feet, clapping, and o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harriet Tubman
Harriet Tubman (born Araminta Ross, March 10, 1913) was an American abolitionist and social activist. Born into slavery, Tubman escaped and subsequently made some 13 missions to rescue approximately 70 slaves, including family and friends, using the network of antislavery activists and safe houses known as the Underground Railroad. During the American Civil War, she served as an armed scout and spy for the Union Army. In her later years, Tubman was an activist in the movement for women's suffrage. Born enslaved in Dorchester County, Maryland, Tubman was beaten and whipped by her various masters as a child. Early in life, she suffered a traumatic head wound when an irate overseer threw a heavy metal weight intending to hit another slave, but hit her instead. The injury caused dizziness, pain, and spells of hypersomnia, which occurred throughout her life. After her injury, Tubman began experiencing strange visions and vivid dreams, which she ascribed to premonitions from God. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. The network was assisted by abolitionists and others sympathetic to the cause of the escapees. The enslaved persons who risked escape and those who aided them are also collectively referred to as the "Underground Railroad". Various other routes led to Mexico, where slavery had been abolished, and to islands in the Caribbean that were not part of the slave trade. An earlier escape route running south toward Florida, then a Spanish possession (except 1763–1783), existed from the late 17th century until approximately 1790. However, the network now generally known as the Underground Railroad began in the late 18th century. It ran north and grew steadily until the Emancipation Proclamation was signed by President Abraham Lincoln.Vox, Lisa"How D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Songs Of The Underground Railroad
Songs of the Underground Railroad were spiritual and work songs used during the early-to-mid 19th century in the United States to encourage and convey coded information to escaping slaves as they moved along the various Underground Railroad routes. As it was illegal in most slave states to teach slaves to read or write, songs were used to communicate messages and directions about when, where, and how to escape, and warned of dangers and obstacles along the route. Songs One reportedly coded Underground Railroad song is "Follow the Drinkin' Gourd". The song's title is said to refer to the star formation (an '' asterism'') known in America as the Big Dipper and in Europe as The Plough. The pointer stars of the Big Dipper align with the North Star. In this song the repeated line "Follow the Drinkin' Gourd" is thus often interpreted as instructions to escaping slaves to travel north by following the North Star, leading them to the northern states, Canada, and freedom: The song oste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirituals
Spirituals (also known as Negro spirituals, African American spirituals, Black spirituals, or spiritual music) is a genre of Christian music that is associated with Black Americans, which merged sub-Saharan African cultural heritage with the experiences of being held in bondage in slavery, at first during the transatlantic slave trade and for centuries afterwards, through the domestic slave trade. Spirituals encompass the "sing songs," work songs, and plantation songs that evolved into the blues and gospel songs in church. In the nineteenth century, the word "spirituals" referred to all these subcategories of folk songs. While they were often rooted in biblical stories, they also described the extreme hardships endured by African Americans who were enslaved from the 17th century until the 1860s, the emancipation altering mainly the nature (but not continuation) of slavery for many. Many new derivative music genres emerged from the spirituals songcraft. Prior to the end of the U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)


