|
Intrahepatic Duct
Intrahepatic bile ducts compose the outflow system of exocrine bile product from the liver. They can be divided into: * Lobar ducts (right and left hepatic ducts) - stratified columnar epithelium. * Interlobar ducts (between the main hepatic ducts and the interlobular ducts) - pseudostratified columnar epithelium. * Interlobular bile ducts (between the interlobar ducts and the lobules) - simple columnar epithelium. * Intralobular bile ducts (cholangioles or Canals of Hering) - simple cuboidal epithelium, then by hepatocytes * Bile canaliculi - two half-canaliculi formed by the hepatocytes facing the perisinusoidal space The perisinusoidal space (or space of Disse) is a location in the liver between a hepatocyte and a sinusoid. It contains the blood plasma. Microvilli of hepatocytes extend into this space, allowing proteins and other plasma components from the ... References Hepatology {{Digestive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exocrine
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have eccrine and apocrine types. Classification Structure Exocrine glands contain a glandular portion and a duct portion, the structures of which can be used to classify the gland. * The duct portion may be branched (called compound) or unbranched (called simple) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
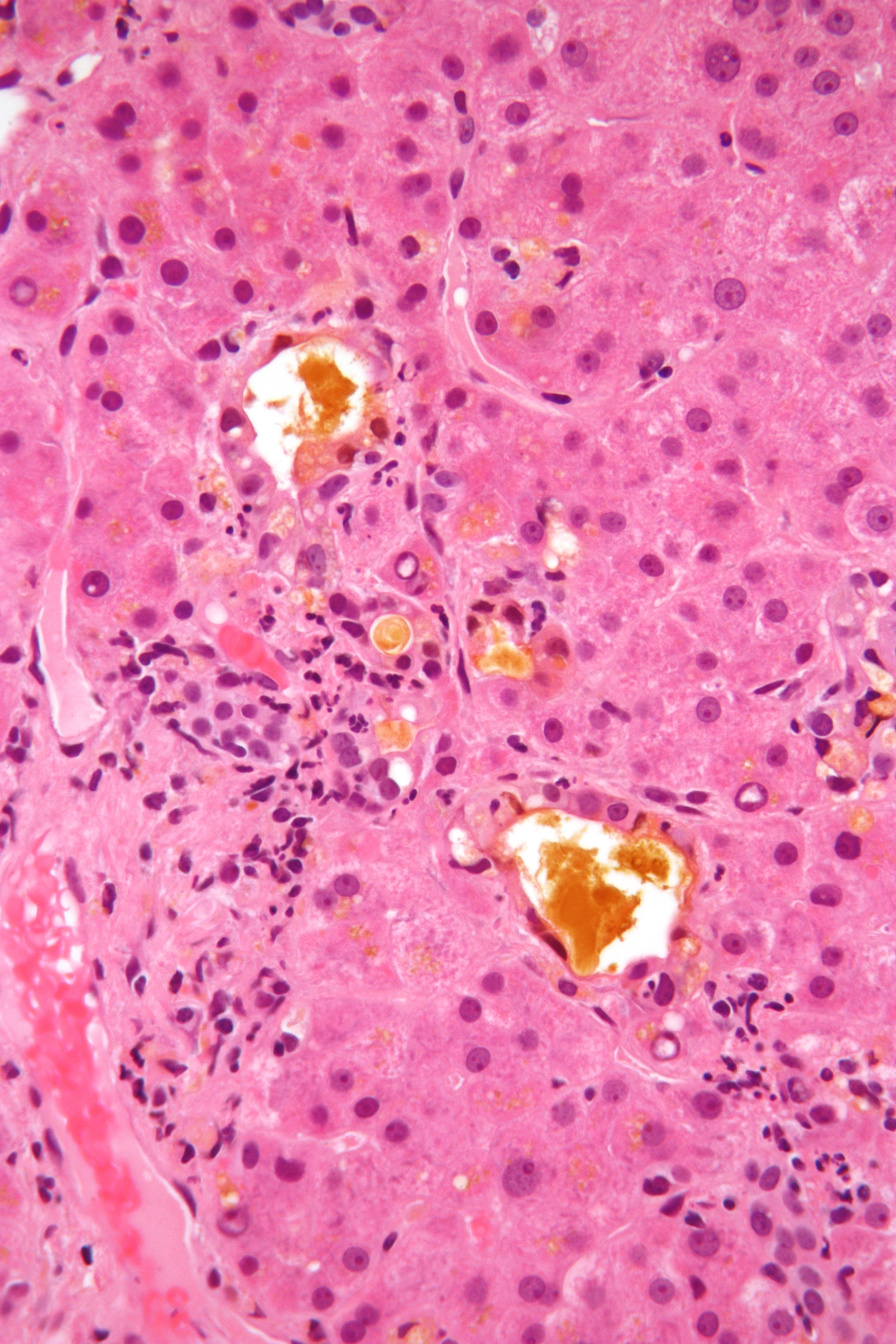
Bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver bile) and stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After eating, this stored bile is discharged into the duodenum. The composition of hepatic bile is (97–98)% water, 0.7% bile salts, 0.2% bilirubin, 0.51% fats (cholesterol, fatty acids, and lecithin), and 200 meq/L inorganic salts. The two main pigments of bile are bilirubin, which is yellow, and its oxidised form biliverdin, which is green. When mixed, they are responsible for the brown color of feces. About 400 to 800 millilitres of bile is produced per day in adult human beings. Function Bile or gall acts to some extent as a surfactant, helping to emulsify the lipids in food. Bile salt anions are hydrophilic on one side and hydrophobic on the other side; consequently, they tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatic Duct
The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. Structure The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It is formed by the convergence of the right hepatic duct (which drains bile from the right functional lobe of the liver) and the left hepatic duct (which drains bile from the left functional lobe of the liver). It then joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct. The duct is usually 6–8 cm long. The common hepatic duct is about 6 mm in diameter in adults, with some variation.Gray's Anatomy, 39th ed, p. 1228 The inner surface is covered in a simple columnar epithelium. Variation Around 1.7% of people have additional accessory hepatic ducts that join onto the common hepatic duct. Rarely, the common hepatic duct joins onto the gallbladder directly, leading to illness. Function The hepatic duct is part of the bil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interlobular Bile Ducts
The interlobular bile ducts (or interlobular ductules) carry bile in the liver between the Canals of Hering and the interlobar bile ducts. They are part of the interlobular portal triad and can be easily localized by looking for the much larger portal vein. The cells of the ducts are described as cuboidal epithelium with increasing amounts of connective tissue Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ... around it. References Hepatology {{digestive-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canals Of Hering
The canals of Hering, or intrahepatic bile ductules, are part of the outflow system of exocrine bile product from the liver. Liver stem cells are located in the canals of Hering. Structure They are found between the bile canaliculi and interlobular bile ducts near the outer edge of a classic liver lobule. Histology Histologically, the cells of the ductule are described as simple cuboidal epithelium, lined partially by cholangiocytes and hepatocytes. They may not be readily visible but can be differentially stained by cytokeratins CK19 and CK7. Clinical relevance The canals of Hering are destroyed early in primary biliary cholangitis and may be primary sites of scarring in methotrexate toxicity. Research has indicated the presence of intraorgan stem cells of the liver that can proliferate in disease states, so-called oval cells. History They are named for Ewald Hering Karl Ewald Konstantin Hering (5 August 1834 – 26 January 1918) was a German physiologist who did mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perisinusoidal Space
The perisinusoidal space (or space of Disse) is a location in the liver between a hepatocyte and a sinusoid. It contains the blood plasma. Microvilli of hepatocytes extend into this space, allowing proteins and other plasma components from the sinusoids to be absorbed by the hepatocytes. Fenestration and discontinuity of the endothelium facilitates this transport. This space may be obliterated in liver disease, leading to decreased uptake by hepatocytes of nutrients and wastes such as bilirubin. The perisinusoidal space also contains hepatic stellate cells (also known as ''Ito cells''), which store fat or fat soluble vitamins including vitamin A). A variety of insults that cause inflammation can result in the cells transforming into myofibroblasts, resulting in collagen production, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. The Space of Disse was named after German anatomist Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasonography Of Dilated Bile Ducts
Ultrasound is sound waves with frequencies higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz (20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz. Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoises use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles. History Acoustics, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |