|
Intertemporal Consumption
Economic theories of intertemporal consumption seek to explain people's preferences in relation to consumption and saving over the course of their lives. The earliest work on the subject was by Irving Fisher and Roy Harrod, who described 'hump saving', hypothesizing that savings would be highest in the middle years of a person's life as they saved for retirement. In the 1950s, more well-defined models were built on discounted utility theory and approached the question of inter-temporal consumption as a lifetime income optimization problem. Solving this problem mathematically, assuming that individuals are rational and have access to complete markets, Modigliani & Brumberg (1954), Albert Ando, and Milton Friedman (1957) developed what became known as the life-cycle model. See for details. The life-cycle model of consumption suggests that consumption is based on average lifetime income instead of income at any given age. First, young people borrow to consume more than their incom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preferences
In psychology, economics and philosophy, preference is a technical term usually used in relation to choosing between alternatives. For example, someone prefers A over B if they would rather choose A than B. Preferences are central to decision theory because of this relation to behavior. Some methods such as Ordinal Priority Approach use preference relation for decision-making. As connative states, they are closely related to desires. The difference between the two is that desires are directed at one object while preferences concern a comparison between two alternatives, of which one is preferred to the other. In insolvency, the term is used to determine which outstanding obligation the insolvent party has to settle first. Psychology In psychology, preferences refer to an individual's attitude towards a set of objects, typically reflected in an explicit decision-making process (Lichtenstein & Slovic, 2006). The term is also used to mean evaluative judgment in the sense of liking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
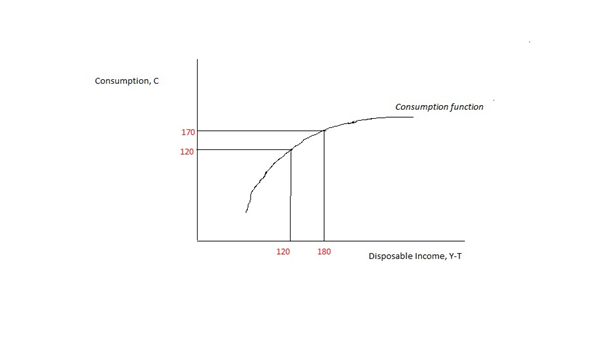
Behavioural Life Cycle
Behavior (American English) or behaviour (British English) is the range of actions and mannerisms made by individuals, organisms, systems or artificial entities in some environment. These systems can include other systems or organisms as well as the inanimate physical environment. It is the computed response of the system or organism to various stimuli or inputs, whether internal or external, conscious or subconscious, overt or covert, and voluntary or involuntary. Taking a behavior informatics perspective, a behavior consists of actor, operation, interactions, and their properties. This can be represented as a behavior vector. Models Biology Although disagreement exists as to how to precisely define behavior in a biological context, one common interpretation based on a meta-analysis of scientific literature states that "behavior is the internally coordinated responses (actions or inactions) of whole living organisms (individuals or groups) to internal and/or external stim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wealth Elasticity Of Demand
{{Original research, date=January 2013 The wealth elasticity of demand, in microeconomics and macroeconomics, is the proportional change in the consumption of a good (economics), good relative to a change in consumers' Wealth (economics), wealth (as distinct from changes in personal income#Meaning in economics and use in economic theory, income). Measuring and accounting for the variability in this Elasticity (economics), elasticity is a continuing problem in behavioral finance and consumer theory. Definition The wealth Elasticity (economics), elasticity of consumption quantity for some good will determine the size of the expenditure shift due to ''unexpected'' changes in net personal wealth, ''ceteris paribus'' (i.e. the size of the so-called "wealth effect" for a given good). It is calculated as ''the ratio of the percent change in consumption to the percent change in wealth that caused it.'' This is analogous to the definition of the income effect from the income elasticity of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Discounting
In economics, time preference (or time discounting, delay discounting, temporal discounting, long-term orientation) is the current relative valuation placed on receiving a good or some cash at an earlier date compared with receiving it at a later date. Time preferences are captured mathematically in the discount function. The higher the time preference, the higher the discount placed on returns receivable or costs payable in the future. One of the factors that may determine an individual's time preference is how long that individual has lived. An older individual may have a lower time preference (relative to what they had earlier in life) due to a higher income and to the fact that they have had more time to acquire durable commodities (such as a college education or a house). Example A practical example: Jim and Bob go out for a drink but Jim has no money so Bob lends Jim $10. The next day Jim visits Bob and says, "Bob, you can have $10 now, or I will give you $15 when I get p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permanent Income Hypothesis
The permanent income hypothesis (PIH) is a model in the field of economics to explain the formation of consumption patterns. It suggests consumption patterns are formed from future expectations and consumption smoothing. The theory was developed by Milton Friedman and published in his ''A Theory of Consumption Function'', published in 1957 and subsequently formalized by Robert Hall in a rational expectations model. Originally applied to consumption and income, the process of future expectations is thought to influence other phenomena. In its simplest form, the hypothesis states changes in permanent income (human capital, property, assets), rather than changes in temporary income (unexpected income), are what drive changes in consumption. The formation of consumption patterns opposite to predictions was an outstanding problem faced by the Keynesian orthodoxy. Friedman's predictions of consumption smoothing, where people spread out transitory changes in income over time, departe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertemporal Choice
Intertemporal choice is the process by which people make decisions about what and how much to do at various points in time, when choices at one time influence the possibilities available at other points in time. These choices are influenced by the relative value people assign to two or more payoffs at different points in time. Most choices require decision-makers to trade off costs and benefits at different points in time. These decisions may be about saving, work effort, education, nutrition, exercise, health care and so forth. Greater preference for immediate smaller rewards has been associated with many negative outcomes ranging from lower salary to drug addiction. Since early in the twentieth century, economists have analyzed intertemporal decisions using the discounted utility model, which assumes that people evaluate the pleasures and pains resulting from a decision in much the same way that financial markets evaluate losses and gains, exponentially 'discounting' the value of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissaving
Dissaving is negative saving. If spending is greater than disposable income, dissaving is taking place. This spending is financed by already accumulated savings, such as money in a savings account, or it can be borrowed. Household dissaving therefore corresponds to an absolute decrease in their financial investments. Usually dissavings start after retirement, when an individual starts deducting money from the amount that he has been saving during his life time. There are also other reasons for dissavings; like big purchases, huge events, and emergencies. On the macro level, also governments could reach a certain situation where they start dissaving from their accumulated funds. Why people save Savings is when an income contributor keeps a certain amount of the income on a side (saving account) and start having an accumulative amount of money based on their savings. People usually save money for certain reasons such as: 1- Emergencies are those unexpected emerging events that might ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superannuation
A pension (, from Latin ''pensiō'', "payment") is a fund into which a sum of money is added during an employee's employment years and from which payments are drawn to support the person's retirement from work in the form of periodic payments. A pension may be a "defined benefit plan", where a fixed sum is paid regularly to a person, or a "defined contribution plan", under which a fixed sum is invested that then becomes available at retirement age. Pensions should not be confused with severance pay; the former is usually paid in regular amounts for life after retirement, while the latter is typically paid as a fixed amount after involuntary termination of employment before retirement. The terms "retirement plan" and "superannuation" tend to refer to a pension granted upon retirement of the individual. Retirement plans may be set up by employers, insurance companies, the government, or other institutions such as employer associations or trade unions. Called ''retirement plans'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Propensity To Consume
In economics, the marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is a metric that quantifies induced consumption, the concept that the increase in personal consumer spending (consumption) occurs with an increase in disposable income (income after taxes and transfers). The proportion of disposable income which individuals spend on consumption is known as propensity to consume. MPC is the proportion of additional income that an individual consumes. For example, if a household earns one extra dollar of disposable income, and the marginal propensity to consume is 0.65, then of that dollar, the household will spend 65 cents and save 35 cents. Obviously, the household cannot spend ''more'' than the extra dollar (without borrowing or using savings). If the extra money accessed by the individual gives more economic confidence, then the MPC of the individual may well exceed 1, as they may borrow or utilise savings. The MPC is higher in the case of poorer people than in rich. According to John Mayna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current Asset
In accounting, a current asset is any asset which can reasonably be expected to be sold, consumed, or exhausted through the normal operations of a business within the current fiscal year or operating cycle or financial year (whichever period is longer). Typical current assets include cash, cash equivalents, short-term investments which in the ordinary activity are mainly related to non-strategic companies in the process of being sold (usually as a result of private negotiations), accounts receivable, stock inventory, supplies, and the portion of prepaid liabilities (sometimes referred to as prepaid expenses) which will be paid within a year. In simple words, assets which are held for a short period are known as current assets. Such assets are expected to be realised in cash or consumed during the normal operating cycle of the business. On a balance sheet, assets will typically be classified into current assets and long-term assets. The current ratio is calculated by dividing to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mental Accounting
Mental accounting (or psychological accounting) attempts to describe the process whereby people code, categorize and evaluate economic outcomes. The concept was first named by Richard Thaler. Mental accounting deals with the budgeting and categorization of expenditures. People budget money into mental accounts for expenses (e.g., saving for a home) or expense categories (e.g., gas money, clothing, utilities). Mental accounts are believed to act as a self-control strategy. People are presumed to make mental accounts as a way to manage and keep track of their spending and resources. People also are assumed to make mental accounts to facilitate savings for larger purposes (e.g., a home or college tuition). Like many other cognitive processes, it can prompt biases and systematic departures from rational, value-maximizing behavior, and its implications are quite robust. Understanding the flaws and inefficiencies of mental accounting is essential to making good decisions and reducing hum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)