|
International Comity
In law, comity is "a practice among different political entities (as countries, states, or courts of different jurisdictions)" involving the "mutual recognition of legislative, executive, and judicial acts." Etymology Comity derives from the Latin ''comitas'', courtesy, from ''cemis'', friendly, courteous. International law The doctrine of international comity has been described variously "as a choice-of-law principle, a synonym for private international law, a rule of public international law, a moral obligation, expediency, courtesy, reciprocity, utility, or diplomacy. Authorities disagree as to whether comity is a rule of natural law, custom, treaty, or domestic law. Indeed, there is not even agreement that comity is a rule of law at all." Because the doctrine touches on many different principles, it is regarded as "one of the more confusing doctrines evoked in cases touching upon the interests of foreign states." The doctrine of international comity was created by a group of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court
A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law. In both common law and civil law legal systems, courts are the central means for dispute resolution, and it is generally understood that all people have an ability to bring their claims before a court. Similarly, the rights of those accused of a crime include the right to present a defense before a court. The system of courts that interprets and applies the law is collectively known as the judiciary. The place where a court sits is known as a venue. The room where court proceedings occur is known as a courtroom, and the building as a courthouse; court facilities range from simple and very small facilities in rural communities to large complex facilities in urban communities. The practical authority given to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulrich Huber
Ulrik Huber (13 March 1636 in Dokkum – 8 November 1694 in Franeker), also known as Ulrich Huber or Ulricus Huber, was a professor of law at the University of Franeker and a political philosopher. Huber studied in Franeker, Utrecht and Heidelberg. He started in 1657 – at a very young age – as professor of Eloquence and History at the University of Franeker and as of 1665 he became professor of law. From 1679 to 1682 he was a judge at the Court of Appeal of Friesland and thereafter returned his position as professor of law until his death in 1694. His major work, , was published initially in 1672 and continued to be revised until 1694. Huber considered captivity in war, criminal conviction, voluntary renunciation of liberty, and birth from a female slave legal grounds for slavery. Apart from this work, he was internationally well-known for his studies on Roman law. In the Netherlands he is also well known for his work (1686, 1768) (The Jurisprudence of My Time). In this work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
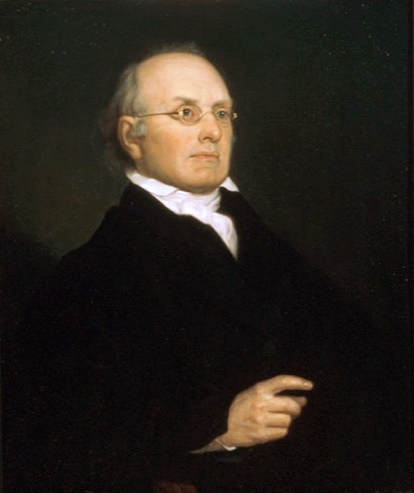
Joseph Story
Joseph Story (September 18, 1779 – September 10, 1845) was an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States, serving from 1812 to 1845. He is most remembered for his opinions in ''Martin v. Hunter's Lessee'' and ''United States v. The Amistad'', and especially for his ''Commentaries on the Constitution of the United States'', first published in 1833. Dominating the field in the 19th century, this work is a cornerstone of early American jurisprudence. It is the second comprehensive treatise on the provisions of the U.S. Constitution and remains a critical source of historical information about the forming of the American republic and the early struggles to define its law. Story opposed Jacksonian democracy, saying it was "oppression" of property rights by republican governments when popular majorities began in the 1830s to restrict and erode the property rights of the minority of rich men. R. Kent Newmyer presents Story as a "Statesman of the Old Republic" who tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Livermore (legal Writer)
Samuel Livermore (c. 1786–1833) was an American lawyer and legal writer, known for his works on agency law and conflict of laws. Livermore graduated from Phillips Exeter Academy in 1800 and from Harvard in 1804. He subsequently studied law and was admitted to the bar. He moved to New Orleans, where he lived until his death. Livermore authored two treatises on the law, ''A Treatise on the Law of Principal and Agent, and of Sales by Auction'' (Boston, 1811; republished in 2 vols., Baltimore, 1818), and ''Dissertations on the Questions which arise from the Contrariety of the Positive Laws of Different States and Nations'' (New Orleans, 1828), the latter work on conflict of laws. Livermore's works continue to be cited in court decisions, most recently by the U.S. Supreme Court in ''Domino's Pizza, Inc. v. McDonald ''Domino's Pizza, Inc. v. McDonald'', 546 U.S. 470 (2006), is a decision by the Supreme Court of the United States involving claims for racial discrimination against ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery In The United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From 1526, during early colonial days, it was practiced in what became Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until abolition. In the decades after the end of Reconstruction, many of slavery's economic and social functions were continued through segregation, sharecropping, and convict leasing. By the time of the American Revolution (1775–1783), the status of enslaved people had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. During and immediately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perform some form of work while also having their location or residence dictated by the enslaver. Many historical cases of enslavement occurred as a result of breaking the law, becoming indebted, or suffering a military defeat; other forms of slavery were instituted along demographic lines such as race. Slaves may be kept in bondage for life or for a fixed period of time, after which they would be granted freedom. Although slavery is usually involuntary and involves coercion, there are also cases where people voluntarily enter into slavery to pay a debt or earn money due to poverty. In the course of human history, slavery was a typical feature of civilization, and was legal in most societies, but it is now outlawed in most countries of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of King's Bench (England)
The Court of King's Bench, formally known as The Court of the King Before the King Himself, was a court of common law in the English legal system. Created in the late 12th to early 13th century from the '' curia regis'', the King's Bench initially followed the monarch on his travels. The King's Bench finally joined the Court of Common Pleas and Exchequer of Pleas in Westminster Hall in 1318, making its last travels in 1421. The King's Bench was merged into the High Court of Justice by the Supreme Court of Judicature Act 1873, after which point the King's Bench was a division within the High Court. The King's Bench was staffed by one Chief Justice (now the Lord Chief Justice of England and Wales) and usually three Puisne Justices. In the 15th and 16th centuries, the King's Bench's jurisdiction and caseload was significantly challenged by the rise of the Court of Chancery and equitable doctrines as one of the two principal common law courts along with the Common Pleas. To recov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somerset V Stewart
''Somerset v Stewart'' (177298 ER 499(also known as ''Somersett's case'', ''v. XX Sommersett v Steuart and the Mansfield Judgment)'' is a judgment of the English Court of King's Bench in 1772, relating to the right of an enslaved person on English soil not to be forcibly removed from the country and sent to Jamaica for sale. Lord Mansfield decided that: Slavery had never been authorized by statute within England and Wales, and Lord Mansfield found it also to be unsupported within England by the common law, although he made no comment on the position in the overseas territories of the British Empire. The case was closely followed throughout the Empire, particularly in the Thirteen American Colonies. Scholars have disagreed over precisely what legal precedent the case set. Facts James Somerset, an enslaved African, was purchased by Charles Stewart (or Steuart), a customs officer when he was in Boston, Province of Massachusetts Bay, a British crown colony in North America. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Policy
Public policy is an institutionalized proposal or a decided set of elements like laws, regulations, guidelines, and actions to solve or address relevant and real-world problems, guided by a conception and often implemented by programs. Public policy can be considered to be the sum of government direct and indirect activities and has been conceptualized in a variety of ways. They are created and/or enacted on behalf of the public typically by a government. Sometimes they are made by nonprofit organisations or are made in co-production with communities or citizens, which can include potential experts, scientists, engineers and stakeholders or scientific data, or sometimes use some of their results. They are typically made by policy-makers affiliated with (in democratic polities) currently elected politicians. Therefore, the "policy process is a complex political process in which there are many actors: elected politicians, political party leaders, pressure groups, civil servants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Murray, 1st Earl Of Mansfield
William Murray, 1st Earl of Mansfield, PC, SL (2 March 170520 March 1793) was a British barrister, politician and judge noted for his reform of English law. Born to Scottish nobility, he was educated in Perth, Scotland, before moving to London at the age of 13 to take up a place at Westminster School. He was accepted into Christ Church, Oxford, in May 1723, and graduated four years later. Returning to London from Oxford, he was called to the Bar by Lincoln's Inn on 23 November 1730, and quickly gained a reputation as an excellent barrister. He became involved in politics in 1742, beginning with his election as a Member of Parliament for Boroughbridge, now in North Yorkshire, and appointment as Solicitor General. In the absence of a strong Attorney General, he became the main spokesman for the government in the House of Commons, and was noted for his "great powers of eloquence" and described as "beyond comparison the best speaker" in the House of Commons. With the promotion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Law
English law is the common law legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly criminal law and civil law, each branch having its own courts and procedures. Principal elements of English law Although the common law has, historically, been the foundation and prime source of English law, the most authoritative law is statutory legislation, which comprises Acts of Parliament, regulations and by-laws. In the absence of any statutory law, the common law with its principle of '' stare decisis'' forms the residual source of law, based on judicial decisions, custom, and usage. Common law is made by sitting judges who apply both statutory law and established principles which are derived from the reasoning from earlier decisions. Equity is the other historic source of judge-made law. Common law can be amended or repealed by Parliament. Not being a civil law system, it has no comprehensive codification. However, most of its criminal law has been codified from its common la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Will
Free will is the capacity of agents to choose between different possible courses of action unimpeded. Free will is closely linked to the concepts of moral responsibility, praise, culpability, sin, and other judgements which apply only to actions that are freely chosen. It is also connected with the concepts of advice, persuasion, deliberation, and prohibition. Traditionally, only actions that are freely willed are seen as deserving credit or blame. Whether free will exists, what it is and the implications of whether it exists or not are some of the longest running debates of philosophy and religion. Some conceive of free will as the right to act outside of external influences or wishes. Some conceive free will to be the capacity to make choices undetermined by past events. Determinism suggests that only one course of events is possible, which is inconsistent with a libertarian model of free will. Ancient Greek philosophy identified this issue, which remains a major focus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |