|
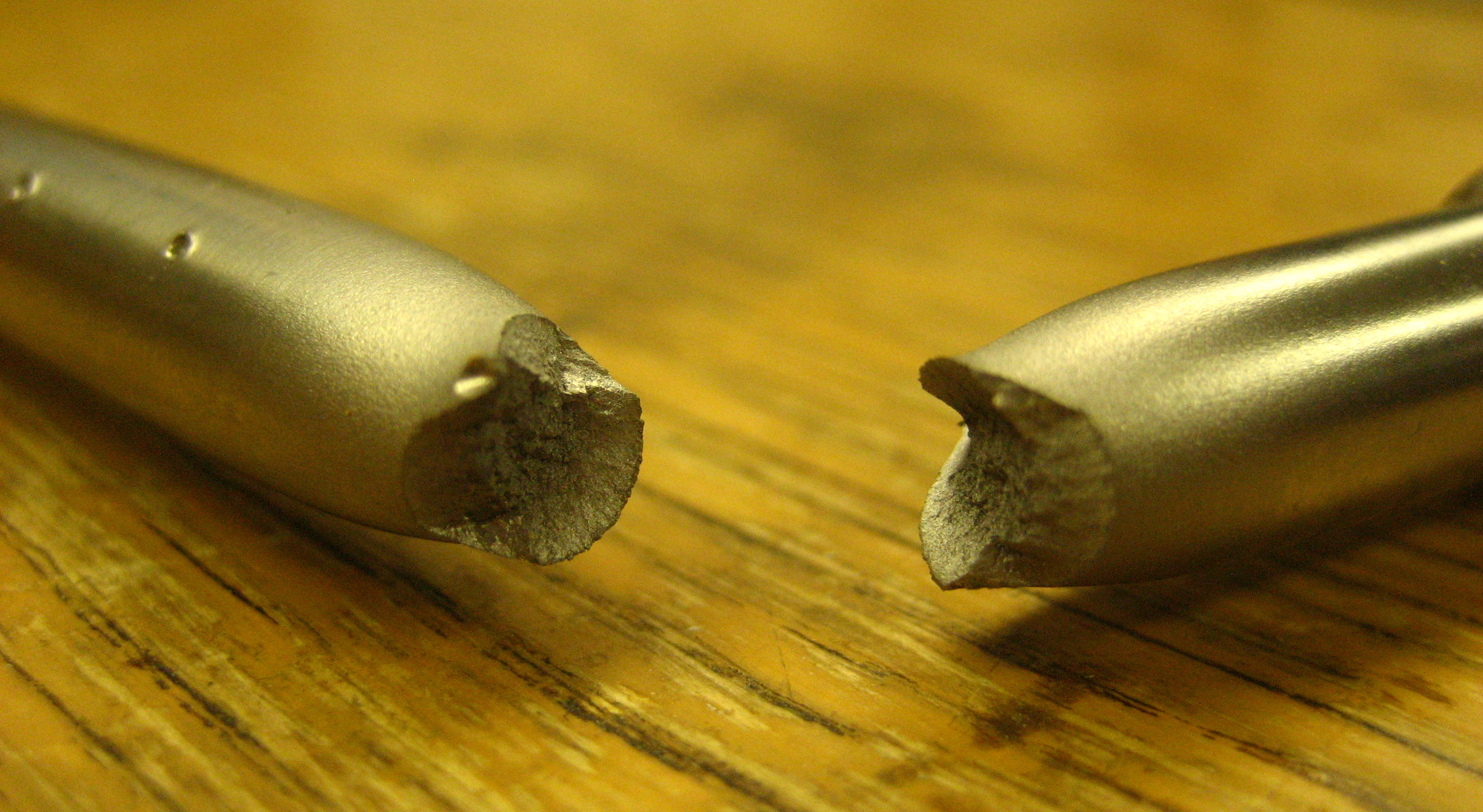
Intergranular Fracture
Intergranular fracture, intergranular cracking or intergranular embrittlement occurs when a crack propagates along the grain boundaries of a material, usually when these grain boundaries are weakened.Norman E. Dowling, Mechanical Behavior of Materials, Fourth Edition, Pearson Education Limited. The more commonly seen transgranular fracture, occurs when the crack grows through the material grains. As an analogy, in a wall of bricks, intergranular fracture would correspond to a fracture that takes place in the mortar that keeps the bricks together. Intergranular cracking is likely to occur if there is a hostile environmental influence and is favored by larger grain sizes and higher stresses. Intergranular cracking is possible over a wide range of temperatures. While transgranular cracking is favored by strain localization (which in turn is encouraged by smaller grain sizes), intergranular fracture is promoted by strain homogenization resulting from coarse grains. Embrittlement, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture
Fracture is the separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band or dislocation. Brittle fractures occur with no apparent deformation before fracture. Ductile fractures occur after visible deformation. Fracture strength, or breaking strength, is the stress when a specimen fails or fractures. The detailed understanding of how a fracture occurs and develops in materials is the object of fracture mechanics. Strength Fracture strength, also known as breaking strength, is the stress at which a specimen fails via fracture. This is usually determined for a given specimen by a tensile test, which charts the stress–strain c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fracture Mechanics
Fracture mechanics is the field of mechanics concerned with the study of the propagation of cracks in materials. It uses methods of analytical solid mechanics to calculate the driving force on a crack and those of experimental solid mechanics to characterize the material's resistance to fracture. Theoretically, the stress ahead of a sharp crack tip becomes infinite and cannot be used to describe the state around a crack. Fracture mechanics is used to characterise the loads on a crack, typically using a single parameter to describe the complete loading state at the crack tip. A number of different parameters have been developed. When the plastic zone at the tip of the crack is small relative to the crack length the stress state at the crack tip is the result of elastic forces within the material and is termed linear elastic fracture mechanics (LEFM) and can be characterised using the stress intensity factor K. Although the load on a crack can be arbitrary, in 1957 G. Irwin foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallite
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains. Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites. Structure The orientation of crystallites can be random with no preferred direction, called random Texture (chemistry), texture, or directed, possibly due to growth and processing conditions. While the structure of a (single crystal, single) crystal is highly ordered and its crystal lattice, lattice is continuous and unbroken, Amorphous solid, amorphous materials, such as glass and many polymers, are non-crystalline and do not display any structures, as their constituents are not arranged in an ordered manner. Polycrystalline structures and paracrystalline phases are in-between these two extremes. Polycrystalline materials, or polycrystals, are solids that are composed of many crystallites of varying size and orientation. Most materials are po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intergranular Corrosion
In materials science, intergranular corrosion (IGC), also known as intergranular attack (IGA), is a form of corrosion where the boundaries of crystallites of the material are more susceptible to corrosion than their insides. (''Cf.'' transgranular corrosion.) Description This situation can happen in otherwise corrosion-resistant alloys, when the grain boundaries are depleted, known as ', of the corrosion-inhibiting elements such as chromium by some mechanism. In nickel alloys and austenitic stainless steels, where chromium is added for corrosion resistance, the mechanism involved is precipitation of chromium carbide at the grain boundaries, resulting in the formation of chromium-depleted zones adjacent to the grain boundaries (this process is called sensitization). Around 12% chromium is minimally required to ensure passivation, a mechanism by which an ultra thin invisible film, known as passive film, forms on the surface of stainless steels. This passive film protects the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgranular Fracture
A transgranular fracture is a fracture that follows the edges of lattices in a granular material, ignoring the grains in the individual lattices. This results in a fairly smooth looking fracture with fewer sharp edges than one that follows the changing grains. This can be visualized as several wooden jigsaw puzzle pieces with the grains showing, but with each piece having grains running in a different direction. A transgranular fracture follows the grains in the wood, not the edges of the puzzle pieces. This is opposed to an intergranular fracture Intergranular fracture, intergranular cracking or intergranular embrittlement occurs when a crack propagates along the grain boundaries of a material, usually when these grain boundaries are weakened.Norman E. Dowling, Mechanical Behavior of Materi .... References Granularity of materials Fracture mechanics {{materials-sci-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Embrittlement
Hydrogen embrittlement (HE), also known as hydrogen-assisted cracking or hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC), is a reduction in the ductility of a metal due to absorbed hydrogen. Hydrogen atoms are small and can permeate solid metals. Once absorbed, hydrogen lowers the stress required for cracks in the metal to initiate and propagate, resulting in embrittlement. Hydrogen embrittlement occurs most notably in steels, as well as in iron, nickel, titanium, cobalt, and their alloys. Copper, aluminium, and stainless steels are less susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement. The essential facts about the nature of hydrogen embrittlement have been known since the 19th century. Hydrogen embrittlement is maximised at around room temperature in steels, and most metals are relatively immune to hydrogen embrittlement at temperatures above 150 °C. Hydrogen embrittlement requires the presence of both atomic ("diffusible") hydrogen and a mechanical stress to induce crack growth, although that str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (material)
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure. Fatigue has traditionally been associated with the failure of metal components which led to the term metal fatigue. In the nineteenth century, the sudden failing of metal railway axles was thought to be caused by the metal ''crystallising'' because of the brittle appearance of the fracture surface, but this has since been disproved. Most materials, such as composites, plastics and ceramics, seem to experience some sort of fatigue-related failure. To aid in predicting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grain Boundaries
In materials science, a grain boundary is the interface between two grains, or crystallites, in a polycrystalline material. Grain boundaries are two-dimensional crystallographic defect, defects in the crystal structure, and tend to decrease the electrical conductivity, electrical and thermal conductivity of the material. Most grain boundaries are preferred sites for the onset of corrosion and for the precipitation (chemistry), precipitation of new Phase (matter), phases from the solid. They are also important to many of the mechanisms of Creep (deformation), creep. On the other hand, grain boundaries disrupt the motion of dislocations through a material, so reducing crystallite size is a common way to improve mechanical strength, as described by the Hall–Petch relationship. High and low angle boundaries It is convenient to categorize grain boundaries according to the extent of misorientation between the two grains. ''Low-angle grain boundaries'' (''LAGB'') or ''subgrain boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, such as phase transformations, from occurring. It does this by reducing the window of time during which these undesired reactions are both thermodynamically favorable, and kinetically accessible; for instance, quenching can reduce the crystal grain size of both metallic and plastic materials, increasing their hardness. In metallurgy, quenching is most commonly used to harden steel by inducing a martensite transformation, where the steel must be rapidly cooled through its eutectoid point, the temperature at which austenite becomes unstable. In steel alloyed with metals such as nickel and manganese, the eutectoid temperature becomes much lower, but the kinetic barriers to phase transformation remain the same. This allows quenching to start at a lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grain Boundary
In materials science, a grain boundary is the interface between two grains, or crystallites, in a polycrystalline material. Grain boundaries are two-dimensional defects in the crystal structure, and tend to decrease the electrical and thermal conductivity of the material. Most grain boundaries are preferred sites for the onset of corrosion and for the precipitation of new phases from the solid. They are also important to many of the mechanisms of creep. On the other hand, grain boundaries disrupt the motion of dislocations through a material, so reducing crystallite size is a common way to improve mechanical strength, as described by the Hall–Petch relationship. High and low angle boundaries It is convenient to categorize grain boundaries according to the extent of misorientation between the two grains. ''Low-angle grain boundaries'' (''LAGB'') or ''subgrain boundaries'' are those with a misorientation less than about 15 degrees. Generally speaking they are composed of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
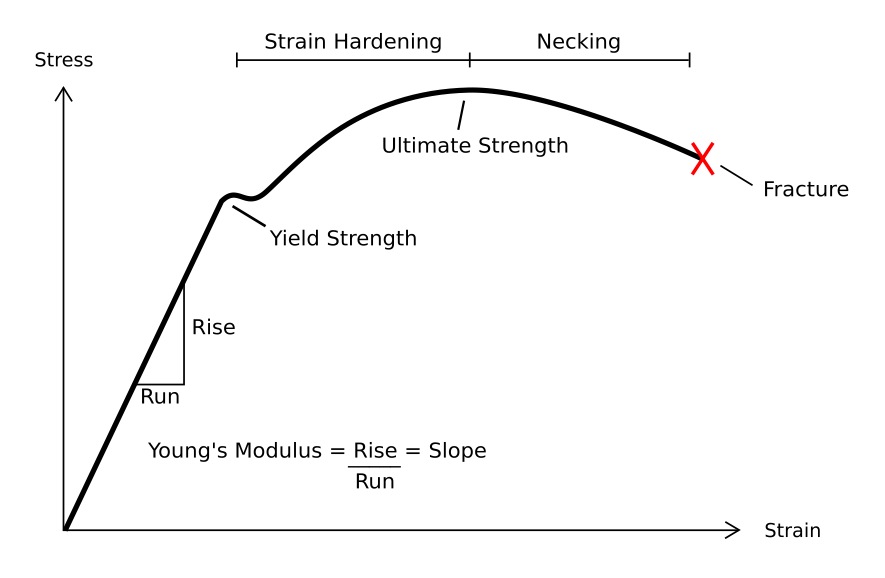
Plastic Deformation
In engineering, deformation refers to the change in size or shape of an object. ''Displacements'' are the ''absolute'' change in position of a point on the object. Deflection is the relative change in external displacements on an object. Strain is the ''relative'' internal change in shape of an infinitesimally small cube of material and can be expressed as a non-dimensional change in length or angle of distortion of the cube. Strains are related to the forces acting on the cube, which are known as stress, by a stress-strain curve. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is elastic. The linear relationship for a material is known as Young's modulus. Above the yield point, some degree of permanent distortion remains after unloading and is termed plastic deformation. The determination of the stress and strain throughout a solid object is given by the field of strength of materials and for a structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stress Corrosion Cracking
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment. It can lead to unexpected and sudden failure of normally ductile metal alloys subjected to a tensile stress, especially at elevated temperature. SCC is highly chemically specific in that certain alloys are likely to undergo SCC only when exposed to a small number of chemical environments. The chemical environment that causes SCC for a given alloy is often one which is only mildly corrosive to the metal. Hence, metal parts with severe SCC can appear bright and shiny, while being filled with microscopic cracks. This factor makes it common for SCC to go undetected prior to failure. SCC often progresses rapidly, and is more common among alloys than pure metals. The specific environment is of crucial importance, and only very small concentrations of certain highly active chemicals are needed to produce catastrophic cracking, often leading to devastating and unexpected failure.ASM Internation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |