|
Interclavicular Ligament
The interclavicular ligament is a flattened band, which varies considerably in form and size in different individuals, it passes in a curved direction from the upper part of the sternal end of one clavicle to that of the other, and is also attached to the upper margin of the sternum. It is in relation, in front, with the integument and Sternocleidomastoidei; behind, with the Sternothyreoidei The sternothyroid muscle, or sternothyroideus, is an Infrahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscle in the neck. It acts to depress the hyoid bone. It is below the sternohyoid muscle. It is shorter and wider than the sternohyoid. Structure The sternothyr .... References External links * Ligaments of the upper limb {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternoclavicular Articulation
The sternoclavicular joint or sternoclavicular articulation is a synovial saddle joint between the manubrium of the sternum, and the clavicle, as well as the first rib. The joint possesses a joint capsule, and an articular disk, and is reinforced by multiple ligaments. Structure The joint is structurally classed as a synovial plane joint and functionally classed as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It is composed of two portions separated by an articular disc of fibrocartilage. The joint is formed by the sternal end of the clavicle, the clavicular notch (the superior and lateral part of the sternum), and (the superior surface of) the cartilage of the first rib (visible from the outside as the suprasternal notch). The articular surface of the clavicle is larger than that of the sternum, and is invested with a layer of cartilage, which is considerably thicker than that of the sternum. The joint receives arterial supply via branches of the internal thoracic artery, and of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
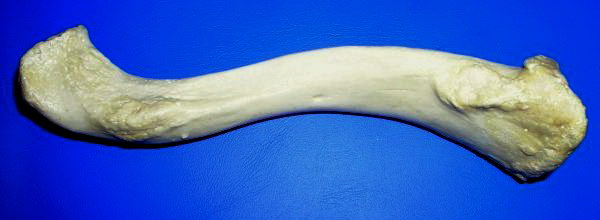
Clavicle
The clavicle, or collarbone, is a slender, S-shaped long bone approximately 6 inches (15 cm) long that serves as a strut between the shoulder blade and the sternum (breastbone). There are two clavicles, one on the left and one on the right. The clavicle is the only long bone in the body that lies horizontally. Together with the shoulder blade, it makes up the shoulder girdle. It is a palpable bone and, in people who have less fat in this region, the location of the bone is clearly visible. It receives its name from the Latin ''clavicula'' ("little key"), because the bone rotates along its axis like a key when the shoulder is abducted. The clavicle is the most commonly fractured bone. It can easily be fractured by impacts to the shoulder from the force of falling on outstretched arms or by a direct hit. Structure The collarbone is a thin doubly curved long bone that connects the arm to the trunk of the body. Located directly above the first rib, it acts as a strut to k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Sternum
The sternum or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels from injury. Shaped roughly like a necktie, it is one of the largest and longest flat bones of the body. Its three regions are the manubrium, the body, and the xiphoid process. The word "sternum" originates from the Ancient Greek στέρνον (stérnon), meaning "chest". Structure The sternum is a narrow, flat bone, forming the middle portion of the front of the chest. The top of the sternum supports the clavicles (collarbones) and its edges join with the costal cartilages of the first two pairs of ribs. The inner surface of the sternum is also the attachment of the sternopericardial ligaments. Its top is also connected to the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternum consists of three main parts, listed from the top: * Manubrium * Body (gladiolus) * X ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternocleidomastoidei
The sternocleidomastoid muscle is one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscles. The primary actions of the muscle are rotation of the head to the opposite side and Anatomical terms of motion#Flexion and extension, flexion of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid is innervated by the accessory nerve. Etymology and location It is given the name ''sternocleidomastoid'' because it originates at the manubrium of the Human sternum, sternum (''sterno-'') and the clavicle (''cleido-'') and has an Insertion (anatomy), insertion at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the human skull, skull. Structure The sternocleidomastoid muscle originates from two locations: the manubrium of the Human sternum, sternum and the clavicle. It travels obliquely across the side of the neck and inserts at the mastoid process of the temporal bone of the human skull, skull by a thin aponeurosis. The sternocleidomastoid is thick and narrow at its centre, and broader and thinner at either end. The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternothyreoidei
The sternothyroid muscle, or sternothyroideus, is an Infrahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscle in the neck. It acts to depress the hyoid bone. It is below the sternohyoid muscle. It is shorter and wider than the sternohyoid. Structure The sternothyroid arises from the posterior surface of the Sternum, manubrium of the sternum, below the origin of the sternohyoid. It also arises from the edge of the cartilage of the first rib. It is inserted into the oblique line on the lamina of the thyroid cartilage. It is in close contact with its fellow at the lower part of the neck, but diverges somewhat as it ascends. It is occasionally traversed by a transverse or oblique tendinous inscription. Innervation The sternothyroid muscle is innervated by the ansa cervicalis. Variations Doubling; absence; accessory slips to the thyrohyoid, inferior pharyngeal constrictor, or to the carotid sheath. Function The sternothyroid muscle depresses the hyoid bone, along with the other infrahyoid muscle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |