|
Inhibitor Cystine Knot
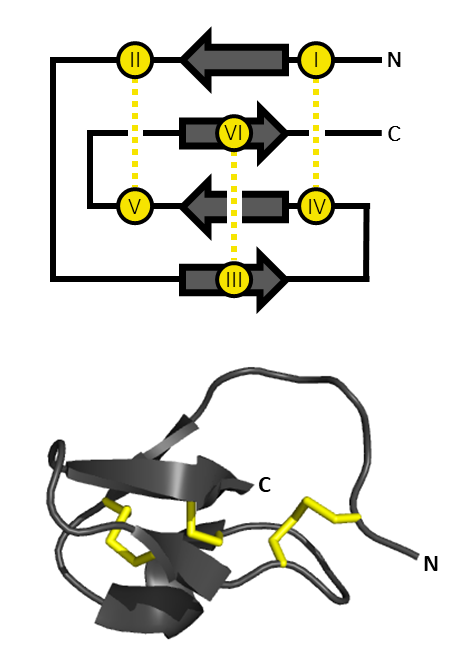
An inhibitor cystine knot (aka ICK or Knottin) is a protein structural motif containing three disulfide bridges. Knottins are one of three folds in the cystine knot motif; the other closely related knots are the Growth Factor Cystine Knot (GFCK) and the Cyclic Cystine Knot (CCK; cyclotide). Types include a) cyclic mobius, b) cyclic bracelet, c) acyclic inhibitor knottins. Cystine knot motifs are found frequently in nature in a plethora of plants, animals, and fungi and serve diverse functions from appetite suppression to anti-fungal activity. Along with the sections of polypeptide between them, two disulfides form a loop through which the third disulfide bond (linking the 3rd and 6th cysteine in the sequence) passes, forming a knot. The motif is common in invertebrate toxins such as those from arachnids and molluscs. The motif is also found in some inhibitor proteins found in plants, but the plant and animal motifs are thought to be a product of convergent evolution. The ICK moti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knottin Structure
An inhibitor cystine knot (aka ICK or Knottin) is a protein structural motif containing three disulfide bridges. Knottins are one of three folds in the cystine knot motif; the other closely related knots are the Growth Factor Cystine Knot (GFCK) and the Cyclic Cystine Knot (CCK; cyclotide). Types include a) cyclic mobius, b) cyclic bracelet, c) acyclic inhibitor knottins. Cystine knot motifs are found frequently in nature in a plethora of plants, animals, and fungi and serve diverse functions from appetite suppression to anti-fungal activity. Along with the sections of polypeptide between them, two disulfides form a loop through which the third disulfide bond (linking the 3rd and 6th cysteine in the sequence) passes, forming a knot. The motif is common in invertebrate toxins such as those from arachnids and molluscs. The motif is also found in some inhibitor proteins found in plants, but the plant and animal motifs are thought to be a product of convergent evolution. The ICK moti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammotoxin
Grammotoxin is a toxin in the venom of the tarantula '' Grammostola spatulata''. It is a protein toxin that inhibits P-, Q- and N-type voltage-gated calcium channels (Ca 2+ channels) in neurons. Grammotoxin is also known as omega-grammotoxin SIA. Chemistry Grammotoxin is a 36 amino acid protein toxin, with the sequence Asp-Cys-Val-Arg-Phe-Trp-Gly-Lys-Cys-Ser-Gln-Thr-Ser-Asp-Cys-Cys-Pro-His-Leu-Ala-Cys-Lys-Ser-Lys-Trp-Pro-Arg-Asn-Ile-Cys-Val-Trp-Asp-Gly-Ser-Val (DCVRFWGKCSQTSDCCPHLACKSKWPRNICVWDGSV), and disulfide bridges between Cys2-Cys16, Cys9-Cys21 and Cys15-Cys30. It forms an inhibitor cystine knot motif, common in spider toxins. Its chemical formula is: C177H268N52O50S6 Grammotoxin can be purified from ''Grammostola spatulata'' venom by reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography. Mode of action The toxin binding site on the channels has high affinity for the toxins when they are closed and low affinity when channels are activated. As a result, the toxin p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stromatoxin
Stromatoxin is a spider toxin that blocks certain delayed-rectifier and A-type voltage-gated potassium channels. Etymology Stromatoxin was first identified in the venom of the African tarantula ''Stromatopelma calceatum'' (the featherleg baboon spider), from which it derives its name. The technical abbreviation for the toxin is ScTx1. Chemistry Stromatoxin is a peptide consisting of 34 amino acids that belongs to the structural family of ‘inhibitor cystine knot’ spider peptides. The toxin was identified using a systematical screening of the effects of toxins of several species of tarantulas on Kv2-channels of ''Xenopus laevis'' (the African clawed frog) . Bioassay guided fractionation and chromatography identified stromatoxin as the functional component. The full sequence of the venom was obtained in a single run of Edman sequencing and confirmed by mass spectrometry. The sequence of this toxin is ‘dctrmfgacr rdsdccphlg ckptskycaw dgti’, for an explanation of these symbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robustoxin
Delta atracotoxin (δ-ACTX-Ar1, robustoxin, or robustotoxin) is a low-molecular-weight neurotoxin, neurotoxic polypeptide found in the venom of the Sydney funnel-web spider (''Atrax robustus''). Delta atracotoxin produces potentially fatal neurotoxicity, neurotoxic symptoms in primates, by slowing the inactivation of sodium ion channels in autonomic and motor neurons. In the spiders' intended insect prey, the toxin exerts this same activity upon potassium ion channel, potassium and calcium channel, calcium ion channels. The structure of atracotoxin comprises a core beta region with a inhibitor cystine knot, cystine knot Short linear motif, motif, a feature seen in other neurotoxic polypeptides. History Since 1927, records are kept of envenomations of humans by the Sydney funnel-web spider, and 14 deaths have been reported in medical literature between 1927 and 1981, when the antivenom became available. In all cases in which the sex of the spider was determined, death occurred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psalmotoxin
Psalmotoxin (PcTx1) is a spider toxin from the venom of the Trinidad tarantula ''Psalmopoeus cambridgei''. It selectively blocks Acid Sensing Ion Channel 1-a (ASIC1a), which is a proton-gated sodium channel. Sources Psalmotoxin is a toxin produced in the venom glands of the South American tarantula ''Psalmopoeus cambridgei''. Chemistry The psalmotoxin structure can be classified as an inhibitor cystine knot (ICK) protein. Many ion channel effectors from snail, spider, and scorpion venoms share a similar ICK structure, although they possess very different pharmalogical profiles. Among ICK toxins, psalmotoxin is the only peptide known to act on homomeric ASIC1 channels. Psalmotoxin is a 40-amino acid peptide, possessing 6 cysteines linked by three disulfide bridges. The three-dimensional structure consists of a compact disulfide-bonded core from which three loops and the N and C termini emerge. The main element of the structure is a three-stranded antiparallel β-sheet. Targe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrixotoxin
Phrixotoxins are peptide toxins derived from the venom of the Chilean copper tarantula ''Phrixotrichus auratus'', also named ''Paraphysa scrofa''. Phrixotoxin-1 and -2 block A-type voltage-gated potassium channels; phrixotoxin-3 blocks voltage-gated sodium channels. Similar toxins are found in other species, for instance the Chilean rose tarantula. Sources Phrixotoxins are purified from the venom of the spider ''Phrixotrichus auratus'' , but they can also be produced by chemical peptide synthesis . Structure There are three different phrixotoxins: *Phrixotoxin-1 (PaTx1) – which is composed of 29 amino acids *Phrixotoxin-2 (PaTx2) – which is composed of 31 amino acids *Phrixotoxin-3 (PaurTx3 or Beta-theraphotoxin-Ps1a) – which is composed of 34 amino acids PaTx1 is 83.3% identical to PATx2, differing only by two acidic residues. Phrixotoxin-1 and -2 are similar to heteropodatoxin, which also has a blocking activity on Kv4.2 channels . Phrixotoxin-1, -2 and -3 contain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TLTx
Theraphosa leblondi toxin (TLTx) is a toxin occurring in three different forms (subtypes) that are purified and sequenced from the venom of the giant tarantula ''Theraphosa blondi''. This toxin selectively inhibits Kv4.2 voltage-gated potassium channels by acting as a gating modifier. Sources The toxin is a component of the venom of the Goliath bird-eating spider '' Theraphosa leblondi''. Chemistry TLTx is part of the family of Kv4-specific tarantula toxins, which are short peptides with a disulfide-bonded core domain. Other members of this family are heteropodatoxins and phrixotoxins. Three homologous peptides (TLTx1, 2 and 3) have been isolated from the venom of the tarantula. They consist of 35 amino acids, with a mass of <5 kDa. They form a total of 3 disulfide bonds between the side chains of cysteine, of which the positions in the sequence are identical in all subtypes of the toxin. The homology with other tarantula toxins suggests that TLTx also forms and |
Maurocalcine
Maurocalcine (MCa) is a protein, 33 Amino acid residues in length, isolated from the venom of the scorpion '' Maurus palmatus'', which belongs to the family Chactidae, first characterized in 2000. The toxin is present in such small amounts that it could not be isolated to analyze it, so a chemical synthesis of this toxin was performed by the solid-phase technique so it could be fully characterized. It shares 82% sequence identity with imperatoxin A (IpTx A), a scorpion toxin from the venom of ''Pandinus imperator''. IpTx A acts by modifying the activity of the type 1 ryanodine receptor of skeletal muscle. RyR controls the intracellular Ca2+ permeability of various cell types and is central in the process of excitation–contraction of muscle tissues. The synthesized toxin, sMCa is active on RyR1 and it binds onto a site different from that of ryanodine itself. Structural components MCa folds folds into the inhibitor cystine knot An inhibitor cystine knot (aka ICK o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huwentoxin
Huwentoxins (HWTX) are a group of neurotoxic peptides found in the venom of the Chinese bird spider '' Haplopelma schmidti''. The species was formerly known as ''Haplopelma huwenum'', ''Ornithoctonus huwena'' and ''Selenocosmia huwena''. While structural similarity can be found among several of these toxins, HWTX as a group possess high functional diversity. Sources Huwentoxins are neurotoxic peptides produced by the Chinese bird spider, ''Haplopelma schmidti''. Overview The venom of ''H. schmidti'' contains a large variety of neurotoxins, which function to paralyze the spider's prey. So far, 14 of the isolated primarily neurotoxic peptide components have been characterized and investigated. In the following, two subfamilies of the HWTX are described: those targeting voltage-gated calcium channels, and those targeting voltage-gated sodium channels. Toxins targeting voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCC) Huwentoxin-I HWTX-I is the most abundant toxic component in the venom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heteroscodratoxin-1
Heteroscodratoxin-1 (also known as κ-theraphototoxin-Hm1a, κ-TRTX-Hm1a, δ-theraphotoxin-Hm1a, δ-TRTX-Hm1a, Hm1a or HmTx1) is a neurotoxin produced by the venom glands of '' Heteroscodra maculata'' (Togo starburst tarantula) that shifts the activation threshold of voltage-gated potassium channels and the inactivation of Nav1.1 sodium channels to more positive potentials. Sources Heteroscodratoxin-1 can be obtained from venom glands of '' Heteroscodra maculata'' (Togo starburst tarantula or Togo starburst baboon spider). Chemistry Heteroscodratoxin-1 is a basic protein (isoelectric point of 7.7) composed of 35 amino acids with a carboxylated C-terminus. Its sequence shows strong similarity with other tarantula toxins such as scodratoxin, hanatoxin and SGTx1. Structurally the protein belongs to the huwentoxin-1 family of inhibitory spider peptides based on its knottin backbone that consists of three crossing disulfide bridges (Cys1-Cys4/Cys2-Cys5/Cys3-Cys6). Hm1a has the foll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanatoxin
Hanatoxin is a toxin found in the venom of the '' Grammostola spatulata'' tarantula. The toxin is mostly known for inhibiting the activation of voltage-gated potassium channels, most specifically Kv4.2 and Kv2.1, by raising its activation threshold. Sources Hanatoxin is a spider toxin from the venom of ''Grammostola spatulata''. Chemistry Hanatoxin is the common name for two 4.1 kDa protein toxins, HaTx1 and HaTx2, which are similar in structure. HaTx is a peptide consisting of the following 35 amino-acids: Glu-Cys-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Phe-Gly-Gly-Cys-Lys-Thr-Thr-***-Asp-Cys-Cys-Lys-His-Leu-Gly-Cys-Lys-Phe-Arg-Asp-Lys-Tyr-Cys-Ala-Trp-Asp-Phe-Thr-Phe-Ser where *** is Ser for HaTx1 and Ala for HaTx2. First discovered in 1995, the difference in amino-acids and structure compared to other toxins known at that time has made hanatoxin the founding member of a family of spider toxins which inhibit voltage-gated potassium channels by modifying the voltage-sensor. Its amino-acid sequenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |