|
Infraspinatus
In human anatomy, the infraspinatus muscle is a thick triangular muscle, which occupies the chief part of the infraspinatous fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'', see infobox. As one of the four muscles of the rotator cuff, the main function of the infraspinatus is to externally rotate the humerus and stabilize the shoulder joint. Structure It attaches medially to the infraspinous fossa of the scapula and laterally to the middle facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The muscle arises by fleshy fibers from the medial two-thirds of the infraspinatous fossa, and by tendinous fibers from the ridges on its surface; it also arises from the infraspinatous fascia which covers it, and separates it from the teres major and teres minor. The fibers converge to a tendon, which glides over the lateral border of the spine of the scapula and passing across the posterior part of the capsule of the shoulder-joint, is inserted into the middle impression on the greater tubercle of the humerus. The trape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are the supraspinatus muscle, the infraspinatus muscle, teres minor muscle, and the subscapularis muscle. Structure Muscles composing rotator cuff The supraspinatus muscle spreads out in a horizontal band to insert on the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The greater tubercle projects as the most lateral structure of the humeral head. Medial to this, in turn, is the lesser tubercle of the humeral head. The subscapularis muscle origin is divided from the remainder of the rotator cuff origins as it is deep to the scapula. The four tendons of these muscles converge to form the rotator cuff tendon. These tendinous insertions along with the articular capsule, the coracohumeral ligament, and the glenohumeral ligament complex, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and their tendons that act to stabilize the human shoulder and allow for its extensive range of motion. Of the seven scapulohumeral muscles, four make up the rotator cuff. The four muscles are the supraspinatus muscle, the infraspinatus muscle, teres minor muscle, and the subscapularis muscle. Structure Muscles composing rotator cuff The supraspinatus muscle spreads out in a horizontal band to insert on the superior facet of the greater tubercle of the humerus. The greater tubercle projects as the most lateral structure of the humeral head. Medial to this, in turn, is the lesser tubercle of the humeral head. The subscapularis muscle origin is divided from the remainder of the rotator cuff origins as it is deep to the scapula. The four tendons of these muscles converge to form the rotator cuff tendon. These tendinous insertions along with the articular capsule, the coracohumeral ligament, and the glenohumeral ligament complex, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraspinatous Fossa
The infraspinous fossa (infraspinatus fossa or infraspinatous fossa) of the scapula is much larger than the supraspinatous fossa; toward its vertebral margin a shallow concavity is seen at its upper part; its center presents a prominent convexity, while near the axillary border is a deep groove which runs from the upper toward the lower part. The medial two-thirds of the fossa give origin to the Infraspinatus; the lateral third is covered by this muscle. Additional images File:Infraspinatus fossa of left scapula- animation.gif, Left scapula. Infraspinatous fossa shown in red. File:Infraspinatus fossa - animation.gif, Animation. Infraspinatous fossa shown in red. File:Infraspinatous fossa of scapula01.png, Still image. File:Gray203.png, Left scapula. Dorsal surface. ("Infra-spinatous" fossa visible at bottom right.) File:Scapula post.jpg, Left scapula. Dorsal surface. Infraspinatous fossa not labeled, but visible at center. File:Infraspinatus muscle back2.png, Infraspin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infraspinous Fossa
The infraspinous fossa (infraspinatus fossa or infraspinatous fossa) of the scapula is much larger than the supraspinatous fossa; toward its vertebral margin a shallow concavity is seen at its upper part; its center presents a prominent convexity, while near the axillary border is a deep groove which runs from the upper toward the lower part. The medial two-thirds of the fossa give origin to the Infraspinatus; the lateral third is covered by this muscle. Additional images File:Infraspinatus fossa of left scapula- animation.gif, Left scapula. Infraspinatous fossa shown in red. File:Infraspinatus fossa - animation.gif, Animation. Infraspinatous fossa shown in red. File:Infraspinatous fossa of scapula01.png, Still image. File:Gray203.png, Left scapula. Dorsal surface. ("Infra-spinatous" fossa visible at bottom right.) File:Scapula post.jpg, Left scapula. Dorsal surface. Infraspinatous fossa not labeled, but visible at center. File:Infraspinatus muscle back2.png, Infraspin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprascapular Nerve
The suprascapular nerve is a nerve that branches from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus. It is responsible for the innervation of two of the muscles that originate from the scapula, namely the supraspinatus muscle, supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles. Structure The suprascapular nerve arises from the upper trunk of the brachial plexus which is formed by the union of the Anterior ramus of spinal nerve, ventral rami of the fifth and sixth cervical nerves. After branching from the upper trunk, the nerve passes across the posterior triangle of the neck parallel to the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle and deep to the trapezius muscle. It then runs along the Scapula#Borders, superior border of the scapula through the suprascapular canal, in which it enters via the suprascapular notch inferior to the superior transverse scapular ligament and enters the supraspinous fossa. It then passes beneath the supraspinatus, and curves around the lateral border of the spine of the scapul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scapula
The scapula (plural scapulae or scapulas), also known as the shoulder blade, is the bone that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) with the clavicle (collar bone). Like their connected bones, the scapulae are paired, with each scapula on either side of the body being roughly a mirror image of the other. The name derives from the Classical Latin word for trowel or small shovel, which it was thought to resemble. In compound terms, the prefix omo- is used for the shoulder blade in medical terminology. This prefix is derived from ὦμος (ōmos), the Ancient Greek word for shoulder, and is cognate with the Latin , which in Latin signifies either the shoulder or the upper arm bone. The scapula forms the back of the shoulder girdle. In humans, it is a flat bone, roughly triangular in shape, placed on a posterolateral aspect of the thoracic cage. Structure The scapula is a thick, flat bone lying on the thoracic wall that provides an attachment for three groups of muscles: intrin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suprascapular
The suprascapular artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk on the neck. Structure At first, it passes downward and laterally across the scalenus anterior and phrenic nerve, being covered by the sternocleidomastoid muscle; it then crosses the subclavian artery and the brachial plexus, running behind and parallel with the clavicle and subclavius muscle and beneath the inferior belly of the omohyoid to the superior border of the scapula. It passes over the superior transverse scapular ligament in most of the cases while below it through the suprascapular notch in some cases. The artery then enters the supraspinous fossa of the scapula. It travels close to the bone, running through the suprascapular canal underneath the supraspinatus muscle, to which it supplies branches. It then descends behind the neck of the scapula, through the great scapular notch and under cover of the inferior transverse ligament of scapula, inferior transverse ligament, to reach the infraspinatous fos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
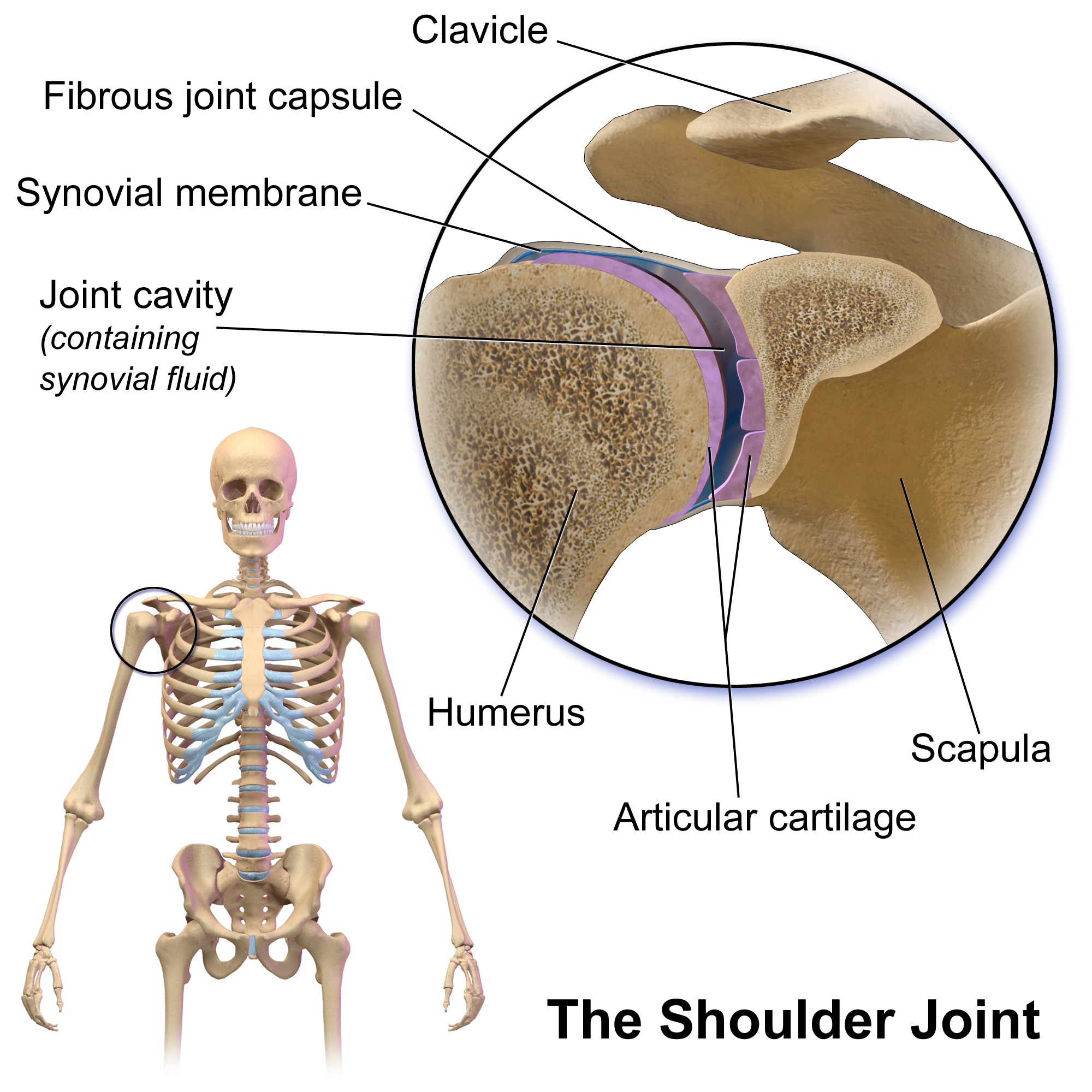
Shoulder-joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The normal glenohumeral space is 4–5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenohumeral Joint
The shoulder joint (or glenohumeral joint from Greek ''glene'', eyeball, + -''oid'', 'form of', + Latin ''humerus'', shoulder) is structurally classified as a synovial ball-and-socket joint and functionally as a diarthrosis and multiaxial joint. It involves an articulation between the glenoid fossa of the scapula (shoulder blade) and the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). Due to the very loose joint capsule that gives a limited interface of the humerus and scapula, it is the most mobile joint of the human body. Structure The shoulder joint is a ball-and-socket joint between the scapula and the humerus. The socket of the glenoid fossa of the scapula is itself quite shallow, but it is made deeper by the addition of the glenoid labrum. The glenoid labrum is a ring of cartilaginous fibre attached to the circumference of the cavity. This ring is continuous with the tendon of the biceps brachii above. Spaces Significant joint spaces are: * The normal glenohumeral space is 4– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
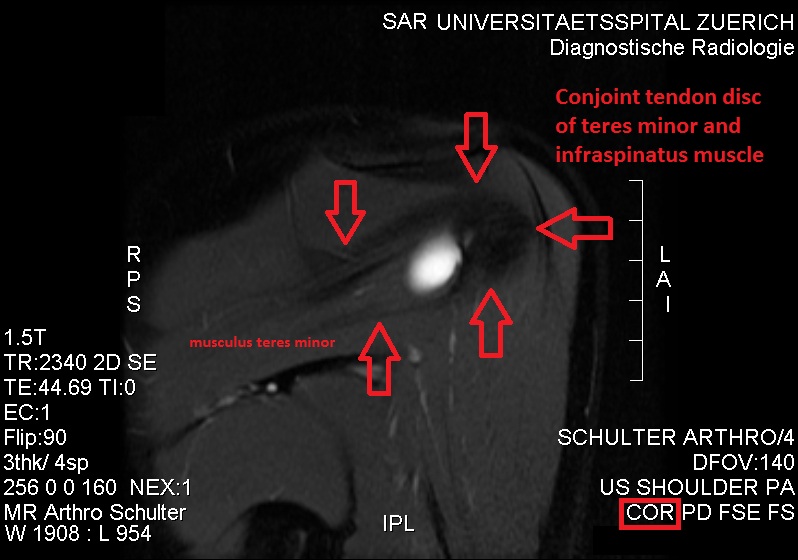
Teres Minor
The teres minor (Latin ''teres'' meaning 'rounded') is a narrow, elongated muscle of the rotator cuff. The muscle originates from the lateral border and adjacent posterior surface of the corresponding right or left scapula and inserts at both the greater tubercle of the humerus and the posterior surface of the joint capsule. The primary function of the teres minor is to modulate the action of the deltoid, preventing the humeral head from sliding upward as the arm is abducted. It also functions to rotate the humerus laterally. The teres minor is innervated by the axillary nerve. Structure It arises from the dorsal surface of the axillary border of the scapula for the upper two-thirds of its extent, and from two aponeurotic laminae, one of which separates it from the infraspinatus muscle, the other from the teres major muscle. Its fibers run obliquely upwards and laterally; the upper ones end in a tendon which is inserted into the lowest of the three impressions on the greater tub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscles Of The Upper Limb
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscle tissue, and are often known as muscle fibers. The muscle tissue of a skeletal muscle is striated – having a striped appearance due to the arrangement of the sarcomeres. Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles under the control of the somatic nervous system. The other types of muscle are cardiac muscle which is also striated and smooth muscle which is non-striated; both of these types of muscle tissue are classified as involuntary, or, under the control of the autonomic nervous system. A skeletal muscle contains multiple fascicles – bundles of muscle fibers. Each individual fiber, and each muscle is surrounded by a type of connective tissue layer of fascia. Muscle fibers are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts in a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coracoid Process
The coracoid process (from Greek κόραξ, raven) is a small hook-like structure on the lateral edge of the superior anterior portion of the scapula (hence: coracoid, or "like a raven's beak"). Pointing laterally forward, it, together with the acromion, serves to stabilize the shoulder joint. It is palpable in the deltopectoral groove between the deltoid and pectoralis major muscles. Structure The coracoid process is a thick curved process attached by a broad base to the upper part of the neck of the scapula; it runs at first upward and medialward; then, becoming smaller, it changes its direction, and projects forward and lateralward. Anatomically it is divided into intervals of: base of coracoid process, angle of coracoid process, shaft and the apex of the coracoid process. The coracoglenoid notch is an indentation localized between the coracoid process and the glenoid. As the coracoid process projects laterally, it house underneath it the subcoracoid space. The ''ascend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |