|
Infragravity Wave
Infragravity waves are surface gravity waves with frequencies lower than the wind waves – consisting of both wind sea and swell – thus corresponding with the part of the wave spectrum lower than the frequencies directly generated by forcing through the wind. Infragravity waves are ocean surface gravity waves generated by ocean waves of shorter periods. The amplitude of infragravity waves is most relevant in shallow water, in particular along coastlines hit by high amplitude and long period wind waves and ocean swells. Wind waves and ocean swells are shorter, with typical dominant periods of 1 to 25 s. In contrast, the dominant period of infragravity waves is typically 80 to 300 s, which is close to the typical periods of tsunamis, with which they share similar propagation properties including very fast celerities in deep water. This distinguishes infragravity waves from normal oceanic gravity waves, which are created by wind acting on the surface of the sea, and are slowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Gravity Wave
In fluid dynamics, gravity waves are waves generated in a fluid medium or at the interface between two media when the force of gravity or buoyancy tries to restore equilibrium. An example of such an interface is that between the atmosphere and the ocean, which gives rise to wind waves. A gravity wave results when fluid is displaced from a position of equilibrium. The restoration of the fluid to equilibrium will produce a movement of the fluid back and forth, called a ''wave orbit''. Gravity waves on an air–sea interface of the ocean are called surface gravity waves (a type of surface wave), while gravity waves that are the body of the water (such as between parts of different densities) are called ''internal waves''. Wind-generated waves on the water surface are examples of gravity waves, as are tsunamis and ocean tides. The period of wind-generated gravity waves on the free surface of the Earth's ponds, lakes, seas and oceans are predominantly between 0.3 and 30 sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rossby Wave
Rossby waves, also known as planetary waves, are a type of inertial wave naturally occurring in rotating fluids. They were first identified by Sweden-born American meteorologist Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby. They are observed in the atmospheres and oceans of planets owing to the rotation of the planet. Atmospheric Rossby waves on Earth are giant meanders in high-altitude winds that have a major influence on weather. These waves are associated with pressure systems and the jet stream (especially around the polar vortices). Oceanic Rossby waves move along the thermocline: the boundary between the warm upper layer and the cold deeper part of the ocean. Rossby wave types Atmospheric waves Atmospheric Rossby waves result from the conservation of potential vorticity and are influenced by the Coriolis force and pressure gradient. The rotation causes fluids to turn to the right as they move in the northern hemisphere and to the left in the southern hemisphere. For example, a fluid that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
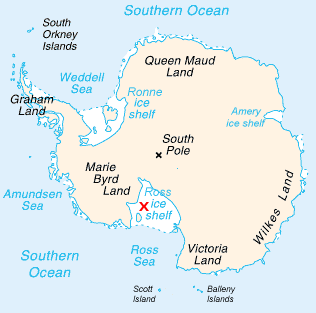
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common conception includes the U.S. states of Oregon, Washington (state), Washington, and Idaho, and the Canadian province of British Columbia. Some broader conceptions reach north into Alaska and Yukon, south into northern California, and east into western Montana. Other conceptions may be limited to the coastal areas west of the Cascade Mountains, Cascade and Coast Mountains, Coast mountains. The variety of definitions can be attributed to partially overlapping commonalities of the region's history, culture, geography, society, ecosystems, and other factors. The Northwest Coast is the coastal region of the Pacific Northwest, and the Northwest Plateau (also commonly known as "British Columbia Interi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sneaker Wave
A sneaker wave, also known as a sleeper wave, or in Australia as a king wave, is a disproportionately large coastal wave that can sometimes appear in a wave train without warning. Terminology The term "sneaker wave" is popular rather than scientific, derived from the observation that such a wave can "sneak up" on an unwary beachgoer. There is no scientific coverage of the phenomenon as a distinct sort of wave with respect to height or predictability as there is on other extreme wave events such as tsunamis or rogue waves, and little or no scientific evidence has been gathered to identify, describe, or define sneaker waves. Although the term "rogue wave" — meaning an unusually tall or steep wave in mid-ocean — is sometimes used as a synonym for "sneaker wave," one American oceanographer distinguishes "rogue waves" as occurring on the ocean and "sneaker waves" as occurring at the shore, while the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration loosely defines rogue waves as offsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group Speed
The group velocity of a wave is the velocity with which the overall envelope shape of the wave's amplitudes—known as the ''modulation'' or ''envelope'' of the wave—propagates through space. For example, if a stone is thrown into the middle of a very still pond, a circular pattern of waves with a quiescent center appears in the water, also known as a capillary wave. The expanding ring of waves is the wave group, within which one can discern individual waves that travel faster than the group as a whole. The amplitudes of the individual waves grow as they emerge from the trailing edge of the group and diminish as they approach the leading edge of the group. Definition and interpretation Definition The group velocity is defined by the equation: :v_ \ \equiv\ \frac\, where is the wave's angular frequency (usually expressed in radians per second), and is the angular wavenumber (usually expressed in radians per meter). The phase velocity is: . The function , which g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stokes Drift
For a pure wave motion in fluid dynamics, the Stokes drift velocity is the average velocity when following a specific fluid parcel as it travels with the fluid flow. For instance, a particle floating at the free surface of water waves, experiences a net Stokes drift velocity in the direction of wave propagation. More generally, the Stokes drift velocity is the difference between the average Lagrangian flow velocity of a fluid parcel, and the average Eulerian flow velocity of the fluid at a fixed position. This nonlinear phenomenon is named after George Gabriel Stokes, who derived expressions for this drift in his 1847 study of water waves. The Stokes drift is the difference in end positions, after a predefined amount of time (usually one wave period), as derived from a description in the Lagrangian and Eulerian coordinates. The end position in the Lagrangian description is obtained by following a specific fluid parcel during the time interval. The corresponding end position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monochrome
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, monochromatic light refers to electromagnetic radiation that contains a narrow band of wavelengths, which is a distinct concept. Application Of an image, the term monochrome is usually taken to mean the same as black and white or, more likely, grayscale, but may also be used to refer to other combinations containing only tones of a single color, such as green-and-white or green-and-red. It may also refer to sepia displaying tones from light tan to dark brown or cyanotype ("blueprint") images, and early photographic methods such as daguerreotypes, ambrotypes, and tintypes, each of which may be used to produce a monochromatic image. In computing, monochrome has two meanings: *it may mean having only one color which is either on or off (also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subharmonic
In music, the undertone series or subharmonic series is a sequence of notes that results from inverting the intervals of the overtone series. While overtones naturally occur with the physical production of music on instruments, undertones must be produced in unusual ways. While the overtone series is based upon arithmetic multiplication of frequencies, resulting in a harmonic series, the undertone series is based on arithmetic division. Nattiez shows the undertone series on E, as Riemann (''Handbuch der Harmonielehre'', 10th ed., 1929, p. 4) and D'Indy (''Cours de composition musicale'', vol. I, 1912, p. 100) had done. Terminology The hybrid term ''subharmonic'' is used in music in a few different ways. In its pure sense, the term ''subharmonic'' refers strictly to any member of the subharmonic series (, , , , etc.). When the subharmonic series is used to refer to frequency relationships, it is written with f representing some highest known reference frequency (, , , , etc. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beacon - Geograph
A beacon is an intentionally conspicuous device designed to attract attention to a specific location. A common example is the lighthouse, which draws attention to a fixed point that can be used to navigate around obstacles or into port. More modern examples include a variety of radio beacons that can be read on radio direction finders in all weather, and radar transponders that appear on radar displays. Beacons can also be combined with semaphoric or other indicators to provide important information, such as the status of an airport, by the colour and rotational pattern of its airport beacon, or of pending weather as indicated on a weather beacon mounted at the top of a tall building or similar site. When used in such fashion, beacons can be considered a form of optical telegraphy. For navigation Beacons help guide navigators to their destinations. Types of navigational beacons include radar reflectors, radio beacons, sonic and visual signals. Visual beacons range from smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.gif)


