|
Inferior Pulvinar Nucleus
Inferior pulvinar nucleus (''nucleus pulvinaris inferior'') is one of four traditionally anatomically distinguished nuclei of the pulvinar of the thalamus. The other three nuclei of the pulvinar are called lateral, anterior and medial pulvinar nuclei. Connections Afferent * Inferior pulvinar nucleus, together with its lateral and medial nuclei, receives afferent input from superior colliculus. Efferent * Inferior pulvinar nucleus, together with its lateral nucleus, both have projections to the early visual cortical areas. Functions * Inferior pulvinar nucleus, together with its lateral and medial nuclei, is thought to be important for the initiation and compensation of saccadic movements of the eyes. Those nuclei also participate in the visual attention regulation.Chalupa, L. (1991). Visual function of the pulvinar. The Neural Basis of Visual Function. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, pp. 140-159. Clinical significance Lesions of the inferior pulvinar nucl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midline Nuclear Group
The midline nuclear group (or midline thalamic nuclei) is a region of the thalamus consisting of the following nuclei: * paraventricular nucleus of thalamus (''nucleus paraventricularis thalami'') - not to be confused with paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus * paratenial nucleus The paratenial nucleus, or parataenial nucleus ( la, nucleus parataenialis), is a component of the midline nuclear group in the thalamus. It is sometimes subdivided into the nucleus parataenialis interstitialis and nucleus parataenialis parvocellu ... (''nucleus parataenialis'') * nucleus reuniens * rhomboid nucleus (''nucleus commissuralis rhomboidalis'') * subfascicular nucleus (''nucleus subfascicularis'') The midline nuclei are often called "nonspecific" in that they project widely to the cortex and elsewhere. This has led to the assumption that they may be involved in general functions such as alerting. However, anatomical connections might suggest more specific functions, with the paraventr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroanatomy
Neuroanatomy is the study of the structure and organization of the nervous system. In contrast to animals with radial symmetry, whose nervous system consists of a distributed network of cells, animals with bilateral symmetry have segregated, defined nervous systems. Their neuroanatomy is therefore better understood. In vertebrates, the nervous system is segregated into the internal structure of the brain and spinal cord (together called the central nervous system, or CNS) and the routes of the nerves that connect to the rest of the body (known as the peripheral nervous system, or PNS). The delineation of distinct structures and regions of the nervous system has been critical in investigating how it works. For example, much of what neuroscientists have learned comes from observing how damage or "lesions" to specific brain areas affects behavior or other neural functions. For information about the composition of non-human animal nervous systems, see nervous system. For information ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neglect Syndromes
Hemispatial neglect is a neuropsychological condition in which, after damage to one hemisphere of the brain (e.g. after a stroke), a deficit in attention and awareness towards the side of space opposite brain damage (contralesional space) is observed. It is defined by the inability of a person to process and perceive stimuli towards the contralesional side of the body or environment. Hemispatial neglect is very commonly contralateral to the damaged hemisphere, but instances of ipsilesional neglect (on the same side as the lesion) have been reported. Presentation Hemispatial neglect results most commonly from strokes and brain unilateral injury to the right cerebral hemisphere, with rates in the critical stage of up to 80% causing visual neglect of the left-hand side of space. Neglect is often produced by massive strokes in the middle cerebral artery region and is variegated, so that most sufferers do not exhibit all of the syndrome's traits. Right-sided spatial neglect is rare be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attention
Attention is the behavioral and cognitive process of selectively concentrating on a discrete aspect of information, whether considered subjective or objective, while ignoring other perceivable information. William James (1890) wrote that "Attention is the taking possession by the mind, in clear and vivid form, of one out of what seem several simultaneously possible objects or trains of thought. Focalization, concentration, of consciousness are of its essence." Attention has also been described as the allocation of limited cognitive processing resources. Attention is manifested by an attentional bottleneck, in terms of the amount of data the brain can process each second; for example, in human vision, only less than 1% of the visual input data (at around one megabyte per second) can enter the bottleneck, leading to inattentional blindness. Attention remains a crucial area of investigation within education, psychology, neuroscience, cognitive neuroscience, and neuropsychology. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccade
A saccade ( , French for ''jerk'') is a quick, simultaneous movement of both eyes between two or more phases of fixation in the same direction.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990. In contrast, in smooth pursuit movements, the eyes move smoothly instead of in jumps. The phenomenon can be associated with a shift in frequency of an emitted signal or a movement of a body part or device. Controlled cortically by the frontal eye fields (FEF), or subcortically by the superior colliculus, saccades serve as a mechanism for fixation, rapid eye movement, and the fast phase of optokinetic nystagmus. The word appears to have been coined in the 1880s by French ophthalmologist Émile Javal, who used a mirror on one side of a page to observe eye movement in silent reading, and found that it involves a succession of discontinuous individual movements. Function Humans and many animals do not look at a scene in f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus and then reaches the visual cortex. The area of the visual cortex that receives the sensory input from the lateral geniculate nucleus is the primary visual cortex, also known as visual area 1 ( V1), Brodmann area 17, or the striate cortex. The extrastriate areas consist of visual areas 2, 3, 4, and 5 (also known as V2, V3, V4, and V5, or Brodmann area 18 and all Brodmann area 19). Both hemispheres of the brain include a visual cortex; the visual cortex in the left hemisphere receives signals from the right visual field, and the visual cortex in the right hemisphere receives signals from the left visual field. Introduction The primary visual cortex (V1) is located in and around the calcarine fissure in the occipital lobe. Each hemisphere's V1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
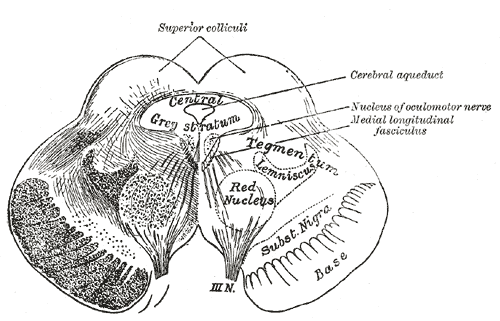
Superior Colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum, or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectal'' is commonly used for both structures. In mammals, the superior colliculus forms a major component of the midbrain. It is a paired structure and together with the paired inferior colliculi forms the corpora quadrigemina. The superior colliculus is a layered structure, with a pattern that is similar to all mammals. The layers can be grouped into the superficial layers ( stratum opticum and above) and the deeper remaining layers. Neurons in the superficial layers receive direct input from the retina and respond almost exclusively to visual stimuli. Many neurons in the deeper layers also respond to other modalities, and some respond to stimuli in multiple modalities. The deeper layers also contain a population of motor-related neurons, capable of activat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medial Pulvinar Nucleus
Medial pulvinar nucleus (''nucleus pulvinaris medialis'') is one of four traditionally anatomically distinguished nuclei of the pulvinar of the thalamus. The other three nuclei of the pulvinar are called lateral, inferior and anterior pulvinar nuclei. Connections Afferent * Medial pulvinar nucleus, together with its lateral and inferior nuclei, receives afferent input from superior colliculus. * Medial pulvinar nucleus also receives many afferent inputs from different cortical areas, including cingulate, posterior parietal, premotor and prefrontal cortical areas. This is the pattern of input connections typical for association relay nuclei of the thalamus. Efferent * Medial pulvinar nucleus sends its widespread projections to the different areas of association cortex, including cingulate, posterior parietal, premotor and prefrontal cortical areas. This is the pattern of output connections typical for association relay nuclei of the thalamus. Functions * Medial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Pulvinar Nucleus
Anterior pulvinar nucleus (''nucleus pulvinaris anterior'') is one of four traditionally anatomically distinguished nuclei of the pulvinar of the thalamus. The other three nuclei of the pulvinar are called lateral, inferior and medial pulvinar nuclei The pulvinar nuclei or nuclei of the pulvinar (nuclei pulvinares) are the nuclei ( cell bodies of neurons) located in the thalamus (a part of the vertebrate brain). As a group they make up the collection called the pulvinar of the thalamus (pulvin .... Connections Functions References {{neuroanatomy-stub Pulvinar nuclei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Pulvinar Nucleus
Lateral pulvinar nucleus (''nucleus pulvinaris lateralis'') is one of four traditionally anatomically distinguished nuclei of the pulvinar of the thalamus. The other three nuclei of the pulvinar are called anterior, inferior and medial pulvinar nuclei. Connections Afferent * Lateral pulvinar nucleus, together with its inferior and medial nuclei, receives afferent input from superior colliculus. * The dorsal part of the lateral pulvinar nucleus also receives afferent input from posterior parietal cortex and the dorsal stream cortical areas. Efferent * Lateral pulvinar nucleus, together with its inferior nucleus, both have projections to the early visual cortical areas. * The dorsal part of the lateral pulvinar nucleus also sends its efferent output connections to the posterior parietal cortex and the dorsal stream cortical areas. Functions * Lateral pulvinar nucleus, together with its inferior and medial nuclei, is thought to be important for the initiati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalamus
The thalamus (from Greek θάλαμος, "chamber") is a large mass of gray matter located in the dorsal part of the diencephalon (a division of the forebrain). Nerve fibers project out of the thalamus to the cerebral cortex in all directions, allowing hub-like exchanges of information. It has several functions, such as the relaying of sensory signals, including motor signals to the cerebral cortex and the regulation of consciousness, sleep, and alertness. Anatomically, it is a paramedian symmetrical structure of two halves (left and right), within the vertebrate brain, situated between the cerebral cortex and the midbrain. It forms during embryonic development as the main product of the diencephalon, as first recognized by the Swiss embryologist and anatomist Wilhelm His Sr. in 1893. Anatomy The thalamus is a paired structure of gray matter located in the forebrain which is superior to the midbrain, near the center of the brain, with nerve fibers projecting out to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleus (neuroanatomy)
In neuroanatomy, a nucleus (plural form: nuclei) is a cluster of neurons in the central nervous system, located deep within the cerebral hemispheres and brainstem. The neurons in one nucleus usually have roughly similar connections and functions. Nuclei are connected to other nuclei by tracts, the bundles (fascicles) of axons (nerve fibers) extending from the cell bodies. A nucleus is one of the two most common forms of nerve cell organization, the other being layered structures such as the cerebral cortex or cerebellar cortex. In anatomical sections, a nucleus shows up as a region of gray matter, often bordered by white matter. The vertebrate brain contains hundreds of distinguishable nuclei, varying widely in shape and size. A nucleus may itself have a complex internal structure, with multiple types of neurons arranged in clumps (subnuclei) or layers. The term "nucleus" is in some cases used rather loosely, to mean simply an identifiably distinct group of neurons, even if they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |