|
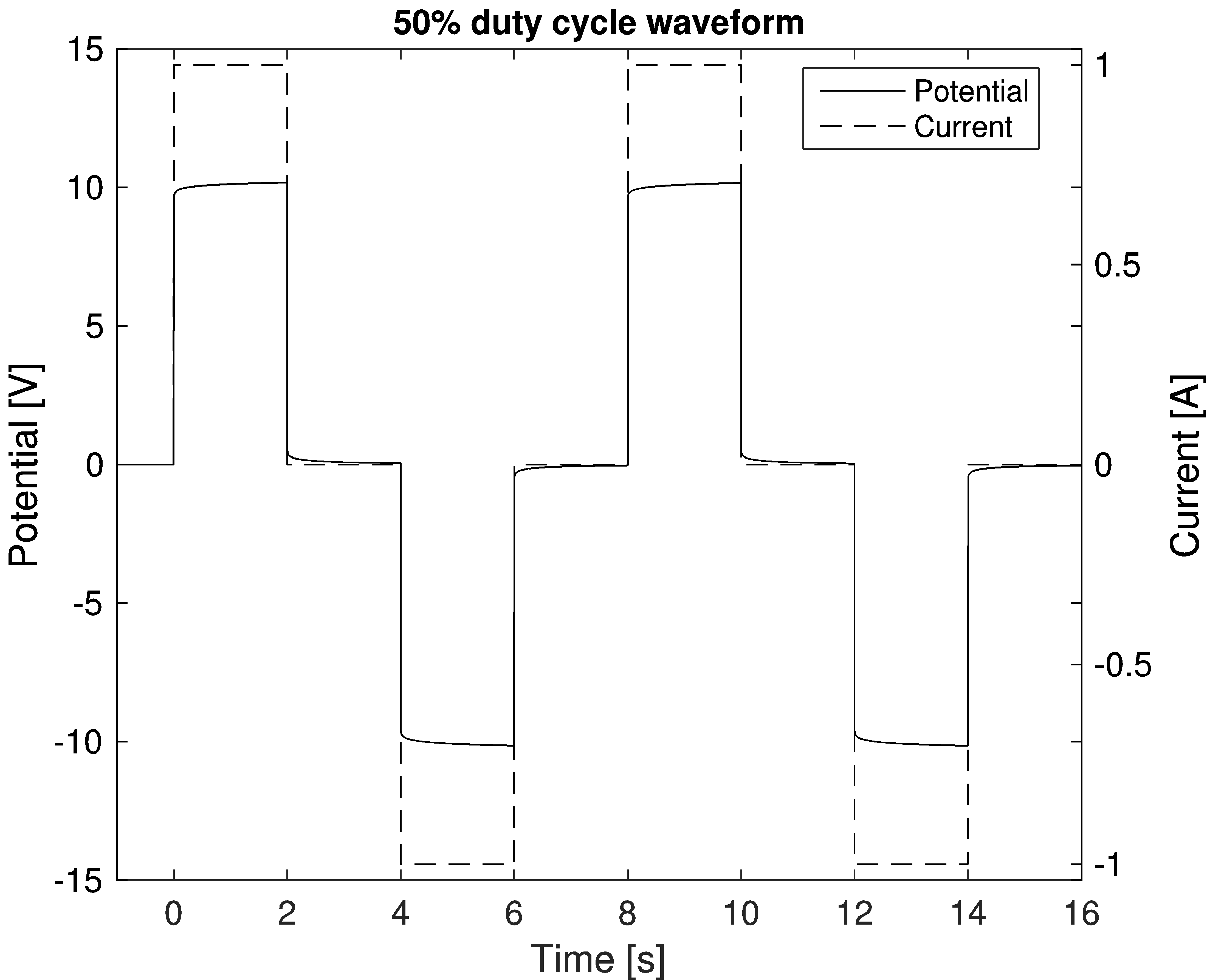
Induced Polarization
Induced polarization (IP) is a geophysical imaging technique used to identify the electrical chargeability of subsurface materials, such as ore. The polarization effect was originally discovered by Conrad Schlumberger when measuring the resistivity of rock. The survey method is similar to electrical resistivity tomography (ERT), in that an electric current is transmitted into the subsurface through two electrodes, and voltage is monitored through two other electrodes. Induced polarization is a geophysical method used extensively in mineral exploration and mining operations. Resistivity and IP methods are often applied on the ground surface using multiple four-electrode sites. In an IP survey (and when making resistivity measurements), capacitive properties of the subsurface materials are determined as well. As a result, IP surveys provide additional information about the spatial variation in lithology and grain-surface chemistry. The IP survey can be made in time-domain an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geophysical Imaging
Geophysical imaging (also known as geophysical tomography) is a minimally destructive geophysical technique that investigates the subsurface of a terrestrial planet. Geophysical imaging is a noninvasive imaging technique with a high parametrical and spatio-temporal resolution. It can be used to model a surface or object understudy in 2D or 3D as well as monitor changes. There are many applications of geophysical imaging some of which include imaging the lithosphere and imaging glaciers. Many different techniques exist to perform geophysical imaging including seismic methods, electrical resistivity tomography, ground-penetrating radar, etc. Types of geophysical imaging: *Electrical resistivity tomography *Ground-penetrating radar *Induced polarization * Seismic tomography and Reflection seismology *Magnetotellurics Applications Imaging the Lithosphere Some geophysical imaging techniques for the Earth's lithosphere and upper mantle include teleseismic tomography, surface-wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cole–Cole Equation
The Cole–Cole equation is a relaxation model that is often used to describe dielectric relaxation in polymers. It is given by the equation : \varepsilon^*(\omega) = \varepsilon_\infty + \frac where \varepsilon^* is the complex dielectric constant, \varepsilon_s and \varepsilon_\infty are the "static" and "infinite frequency" dielectric constants, \omega is the angular frequency and \tau is a dielectric relaxation time constant. The exponent parameter \alpha, which takes a value between 0 and 1, allows the description of different spectral shapes. When \alpha=0, the Cole-Cole model reduces to the Debye model. When \alpha>0, the relaxation is ''stretched''. That is, it extends over a wider range on a logarithmic \omega scale than Debye relaxation. The separation of the complex dielectric constant \varepsilon(\omega) was reported in the original paper by Kenneth Stewart Cole and Robert Hugh Cole as follows: \varepsilon' = \varepsilon_\infty+ (\varepsilon_s-\varepsilon_\inft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Society Of Exploration Geophysicists
The Society of Exploration Geophysicists (SEG) is a learned society dedicated to promoting the science and education of exploration geophysics in particular and geophysics in general. The Society fosters the expert and ethical practice of geophysics in the exploration and development of natural resources, in characterizing the near-surface, and in mitigating earth hazards. SEG has more than 14,000 members working in more than 114 countries. SEG was founded in 1930 in Houston, Texas but its business office has been headquartered in Tulsa, Oklahoma since the mid-1940s. While most SEG members are involved in exploration for petroleum, SEG members also are involved in application of geophysics methods to mineral exploration as well as environmental and engineering problems, archaeology, and other scientific endeavors. SEG publishes ''The Leading Edge'' (''TLE''), a monthly professional magazine, ''Geophysics'', a peer-reviewed archival publication, and ''Interpretation'', a peer-revi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geophysics (journal)
''Geophysics'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of research, exploration, and education in applied geophysics. It was established in 1936 and is published by the Society of Exploration Geophysicists. The current editor-in-chief is Jeffrey Shragge (Colorado School of Mines). According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2018 impact factor of 2.793. See also * List of scientific journals in earth and atmospheric sciences This list presents notable scientific journals in earth and atmospheric sciences and its various subfields. Multi-disciplinary Atmospheric science Geochemistry * ''Chemical Geology'' * '' Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta'' * '' Geostan ... References External links * {{Official website, http://library.seg.org/journal/gpysa7 Geophysics journals English-language journals Academic journals established in 1936 Academic journals published by learned and professional societies Bimonthly jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
John Wiley & Sons, Inc
John Wiley & Sons, Inc., commonly known as Wiley (), is an American multinational publishing company that focuses on academic publishing and instructional materials. The company was founded in 1807 and produces books, journals, and encyclopedias, in print and electronically, as well as online products and services, training materials, and educational materials for undergraduate, graduate, and continuing education students. History The company was established in 1807 when Charles Wiley opened a print shop in Manhattan. The company was the publisher of 19th century American literary figures like James Fenimore Cooper, Washington Irving, Herman Melville, and Edgar Allan Poe, as well as of legal, religious, and other non-fiction titles. The firm took its current name in 1865. Wiley later shifted its focus to scientific, technical, and engineering subject areas, abandoning its literary interests. Wiley's son John (born in Flatbush, New York, October 4, 1808; died in East O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geophysical Imaging
Geophysical imaging (also known as geophysical tomography) is a minimally destructive geophysical technique that investigates the subsurface of a terrestrial planet. Geophysical imaging is a noninvasive imaging technique with a high parametrical and spatio-temporal resolution. It can be used to model a surface or object understudy in 2D or 3D as well as monitor changes. There are many applications of geophysical imaging some of which include imaging the lithosphere and imaging glaciers. Many different techniques exist to perform geophysical imaging including seismic methods, electrical resistivity tomography, ground-penetrating radar, etc. Types of geophysical imaging: *Electrical resistivity tomography *Ground-penetrating radar *Induced polarization * Seismic tomography and Reflection seismology *Magnetotellurics Applications Imaging the Lithosphere Some geophysical imaging techniques for the Earth's lithosphere and upper mantle include teleseismic tomography, surface-wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electrical Resistivity Measurement Of Concrete
Concrete electrical resistivity can be obtained by applying a current into the concrete and measuring the response voltage. There are different methods for measuring concrete resistivity. Laboratory methods Two electrodes Concrete electrical resistance can be measured by applying a current using two electrodes attached to the ends of a uniform cross-section specimen. Electrical resistivity is obtained from the equation: :\rho = R \frac, \,\! :''R'' is the electrical resistance of the specimen, the ratio of voltage to current (measured in ohms, Ω) :''\ell'' is the length of the piece of material (measured in metres, m) :''A'' is the cross-sectional area of the specimen (measured in square metres, m2). This method suffers from the disadvantage that contact resistance can significantly add to the measured resistance causing inaccuracy. Conductive gels are used to improve the contact of the electrodes with the sample. Four electrodes The problem of contact resistance can be ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
AC Impedance Spectroscopy
Dielectric spectroscopy (which falls in a subcategory of the impedance spectroscopy) measures the dielectric properties of a medium as a function of frequency.Kremer F., Schonhals A., Luck W. Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy. – Springer-Verlag, 2002. It is based on the interaction of an external field with the electric dipole moment of the sample, often expressed by permittivity. It is also an experimental method of characterizing electrochemical systems. This technique measures the impedance of a system over a range of frequencies, and therefore the frequency response of the system, including the energy storage and dissipation properties, is revealed. Often, data obtained by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) is expressed graphically in a Bode plot or a Nyquist plot. Impedance is the opposition to the flow of alternating current (AC) in a complex system. A passive complex electrical system comprises both energy dissipater (resistor) and energy storage (capacitor) e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Apparent Resistivity (or ostensible authority) relates to the doctrines of the law of agency
*Apparent, apparently
{{disambiguation ...
Apparent may refer to: *Apparent magnitude, a measure of brightness of a celestial body as seen by an observer on Earth *Apparent places, the actual coordinates of stars as seen from Earth *Heir apparent, a person who is first in line of succession *Apparent death, an antipredator behavior known as playing dead *Apparent wind, a wind experienced by a moving object *Eire Apparent, a band from Northern Ireland *Apparent authority In law, apparent authority (also called "ostensible authority") relates to the doctrines of the law of agency. It is relevant particularly in corporate law and constitutional law. Apparent authority refers to a situation where a reasonable third pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alternating Current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in which electric power is delivered to businesses and residences, and it is the form of electrical energy that consumers typically use when they plug kitchen appliances, televisions, Fan (machine), fans and electric lamps into a wall socket. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', respectively, as when they modify ''Electric current, current'' or ''voltage''. The usual waveform of alternating current in most electric power circuits is a sine wave, whose positive half-period corresponds with positive direction of the current and vice versa (the full period is called a ''wave cycle, cycle''). "Alternating current" most commonly refers to power distribution, but a wide range of other appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Frequency-domain
In mathematics, physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency (and possibly phase), rather than time, as in time series. While a time-domain graph shows how a signal changes over time, a frequency-domain graph shows how the signal is distributed within different frequency bands over a range of frequencies. A complex valued frequency-domain representation consists of both the magnitude and the phase of a set of sinusoids (or other basis waveforms) at the frequency components of the signal. Although it is common to refer to the magnitude portion (the real valued frequency-domain) as the frequency response of a signal, the phase portion is required to uniquely define the signal. A given function or signal can be converted between the time and frequency domains with a pair of mathematical operators called transforms. An example is the Fourier transfor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |